- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
What is Automated Clearing House Transfer? Full analysis of advantages, disadvantages, operation methods, and common misunderstandings

Image Source: unsplash
You’ve likely noticed that ACH transfers are a cornerstone of the U.S. financial system. Managed by Nacha, the ACH network has driven the shift from paper checks to electronic payments. Many businesses now use ACH transfers for payroll, bill payments, or online shopping. The table below shows the steady growth of ACH transaction volume in the U.S., with over 7 billion transactions processed in 2020:
| Year | Transaction Volume Growth |
|---|---|
| 2012 | Growth initiated |
| 2020 | Over 50% growth |
| 2020 | Over 7 billion transactions |
Understanding the advantages, limitations, and proper operations of ACH transfers will help you manage your finances effectively.
Key Points
- ACH transfers are a low-cost electronic payment method, ideal for payroll and bill payments, with fees typically lower than wire transfers.
- Processing times are usually 1–3 business days, so plan ahead to avoid delays.
- Ensure accurate account information to prevent failed transfers or lost funds.
- Regularly monitor account activity and adopt security measures to prevent unauthorized transactions and data breaches.
- Understand the fee structures of different payment methods to choose the most cost-effective option.
ACH Transfer Definition

Image Source: pexels
Core Functions
You can think of an ACH transfer as an electronic payment method between banks, regulated by Nacha, which enforces strict rules to ensure secure and compliant transactions. The table below outlines key regulatory requirements:
| Rule Name | Key Details |
|---|---|
| WEB Debit Fraud Detection Standards | First-time use requires pre-notification, micro-transaction verification, or third-party validation. |
| Improper and Permissible Reversals | Specifies reversible reasons (e.g., incorrect date) and formats. |
| Warranty Claim Limits | Non-consumer accounts can claim within 1 year of settlement; consumer accounts within 2 years. |
In the U.S. banking system, ACH transfers enable efficient electronic fund movements between accounts. Compared to paper checks, they are faster and more environmentally friendly, eliminating the need for mailed documents or risks of lost checks. The ACH system uses batch processing to handle large transaction volumes, reducing costs for individuals and businesses. You can also set up recurring payments, such as monthly bill deductions. The table below summarizes key features and benefits:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Fees typically lower than wire or credit card payments. |
| Batch Processing | Handles payments in batches, ideal for businesses. |
| Recurring Payments | Facilitates subscriptions or automated bill payments. |
Tip: Most U.S. bank accounts automatically support ACH transfers without additional setup.
Primary Uses
You can use ACH transfers for a variety of financial operations, including:
- Direct Deposits: Receive salaries, government benefits, or tax refunds.
- Bill Payments: Set up automatic deductions for utilities, mortgages, or credit card bills.
- Online Shopping: Use ACH as a payment option on some e-commerce platforms.
- Unemployment and Social Security: Government agencies disburse benefits via ACH.
- Business Payments: Companies pay suppliers or contractors regularly.
- Employee Reimbursements: Businesses transfer expense reimbursements directly to employee accounts.
In the U.S., ACH transfers enable efficient, low-cost fund flows for businesses and individuals, supporting one-time or recurring payments through authorization. You can also transfer funds between bank accounts for easy reconciliation and management.
Note: While ACH transfers are prevalent in the U.S., similar services in mainland China or Hong Kong may have different names and processes. Consult your bank for cross-border transfers.
Advantages of ACH Transfers
Low Cost
In the U.S., ACH transfers stand out for their cost efficiency compared to wire transfers. The table below compares fees for common transfer methods:
| Transfer Type | Fee Range |
|---|---|
| ACH Transfer | Typically under $5 |
| Wire Transfer | Average ~$30 |
For businesses, ACH transfer fees are even lower. The table below shows average per-transaction costs:
| Source | Average Fee |
|---|---|
| GoCardless | $0.29 |
| Tipalti | $0.29 |
| Plaid | $0.26–$0.50 |
For bulk payroll or supplier payments, ACH transfers significantly reduce costs, making them ideal for businesses and institutions.
Ease of Use
When handling large payment volumes, ACH transfers save time and effort. The ACH network allows you to group multiple authorized transactions into a single batch for processing, automating individual transaction handling. This streamlines operations and minimizes manual errors. You can also set up recurring deductions, eliminating the need for monthly manual payments. For businesses, batch processing boosts efficiency and reduces errors.
Tip: The ACH system processes transactions on a fixed schedule, often ensuring same-day fund transfers, enhancing liquidity.
Security
ACH transfers offer robust security. Nacha, as the governing body, enforces strict protocols to ensure compliance. Security measures include:
- KYC Practices: Verifying recipient identities to prevent unauthorized payments.
- Data Encryption: Securing sensitive data during transmission and storage.
- Transaction Monitoring: Real-time detection of suspicious activities.
- Regular Security Audits: Identifying potential vulnerabilities for businesses.
- Fraud Response Plans: Protocols for addressing anomalies quickly.
Nacha’s risk management frameworks and certifications enhance system security. By following bank and system security prompts, you can mitigate most risks in daily operations.
Disadvantages of ACH Transfers
Processing Time
A common drawback of ACH transfers is their slower processing time compared to wire transfers. They typically take 1–3 business days. The table below compares processing times:
| Transfer Type | Processing Time |
|---|---|
| ACH Transfer | 1–3 business days after request |
| Wire Transfer | Same-day, often within hours |
The ACH network operates only on business days (Monday–Friday), excluding federal holidays. Transactions initiated on Fridays, weekends, or holidays are processed the next business day, potentially delaying funds. Extended holidays can further prolong processing.
Tip: For urgent fund needs, opt for faster methods like wire transfers.
Risk Factors
When using ACH transfers, you face several risks, including:
- Unauthorized Debits: Fraudsters may access your bank details via phishing or breaches, initiating unauthorized withdrawals.
- Payroll/Supplier Redirection: Criminals may impersonate employees or vendors, redirecting payments to fraudulent accounts.
- Fake Credits: Fraudsters exploit false data to claim tax refunds or benefits, then quickly transfer funds.
- Check Cashing Scams: Some exploit ACH delays to withdraw funds before transactions clear, causing losses.
Protect your account details, be cautious of suspicious emails or texts, and avoid falling prey to fraud in the U.S. market.
Dispute Resolution
ACH transfer disputes may arise from:
- Unauthorized Transactions: Deductions made without your consent.
- Duplicate Transactions: Payments processed multiple times in error.
- Incorrect Amounts: Deducted amounts not matching expectations.
- Insufficient Funds: Failed deductions due to low account balances.
- Failed Stop Payments: Deductions proceeding despite stop requests.
- Fraudulent Activity: Account breaches or insider misconduct.
To resolve disputes:
- Notify your bank immediately upon spotting an issue.
- The bank collects details and investigates.
- The bank determines if funds are refunded and informs you of the outcome.
You have 60 days from the transaction date to file a dispute. Banks typically process returns within 1–5 days of receiving your written statement, with full resolution taking over 10 days. Keep records for smoother communication.
ACH Transfer Process
Image Source: unsplash
Account Setup
Before initiating an ACH transfer, prepare your account with these steps:
- Choose a service provider. Compare fees, processing times, and account management options. Understand how to withdraw funds from customer accounts.
- Create an account following the provider’s guidelines, completing identity verification.
- Investigate payment details. Third-party processors often assign unique account and routing numbers, distinct from standard bank accounts.
- Notify customers of your ACH transfer account setup. You can initiate transactions by entering customer details or letting them provide the information.
Tip: In the U.S., ACH transfers are commonly used for payroll and bill payments. In mainland China or Hong Kong, similar services may differ; consult your bank.
Information Entry
When initiating an ACH transfer, accurately provide:
- Payment Amount
- Currency Type
- Transfer Date
- Recipient’s Full Name
- Recipient’s Bank Account Number
- Recipient’s ABA Routing Number
- Recipient’s Address (if required)
- Recipient Bank’s Address (if required)
As the payer, you must also provide your full name, bank account number, ABA routing number, and address. Ensure all details match bank records to avoid transfer failures.
Confirmation and Tracking
To track an ACH transfer:
- Obtain the ACH tracking number. Request it from the payer if unavailable.
- Contact your bank’s customer service, found on their website or statements.
- Provide details like the tracking number, transaction date, and amount for the bank to check the status.
If payroll, supplier payments, or remittances are delayed, use these steps to verify. In the U.S., ACH transfers typically complete within 1–3 business days.
Common Misconceptions
Information Errors
Errors in ACH transfer details, such as incorrect account or routing numbers, often cause failures. The table below lists common error types and causes:
| Return Code | Description | Common Cause |
|---|---|---|
| R01 | Insufficient Funds | Account balance too low for transfer |
| R03 | No Account Found | Valid account structure but no match |
| R09 | Insufficient Uncollected Balance | Sufficient balance but uncollected funds |
| R10 | Customer Not Authorized | Customer claims unauthorized or incorrect amount |
Transfers may also fail if accounts aren’t set for specific transactions or if Nacha guidelines aren’t followed. Insufficient funds are a frequent issue.
Tip: Double-check all details before initiating to avoid costly errors.
Ignoring Processing Times
You may overlook ACH transfer processing times, which typically take 1–3 business days due to batch processing. Weekend or holiday submissions delay transfers to the next business day, potentially missing bill or payroll deadlines and affecting credit or operations.
Fee Misunderstandings
You might assume ACH transfers are nearly free, but disputes can lead to deductions from merchant accounts and additional processing fees. Misunderstanding the process or fee structure can create financial strain.
- ACH disputes may lead to fund deductions.
- Merchants face extra fees for dispute handling.
- Misunderstanding fees impacts financial planning.
Tip: Confirm all potential fees with your bank or provider before transferring.
Security Oversights
Neglecting security exposes you to data breaches and financial losses. Weak protections allow hackers to access sensitive information, and non-compliance with Nacha standards may lead to fines. Security lapses harm finances and erode customer trust.
- Data breaches cause financial and reputational damage.
- Non-compliance incurs hefty fines.
- Loss of customer trust is hard to recover.
Always prioritize account and data security, update passwords regularly, and avoid unsecured networks.
Mitigation Strategies
Information Verification
Before initiating an ACH transfer, thoroughly verify account details. Incorrect account or routing numbers can lead to failed transfers or lost funds. The table below outlines best practices:
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Account Verification | Confirm account accuracy before initiating. |
| Identity Verification | Verify payment details via phone for authenticity. |
| Continuous Monitoring | Regularly check ACH files and statements for issues. |
Call suppliers or partners to confirm payment details, avoiding reliance on emails or texts to prevent fraud.
Understanding Processing Cycles
Familiarize yourself with ACH transfer processing cycles. The table below compares processing times:
| ACH Transfer Type | Processing Time |
|---|---|
| Standard ACH | ~4 business days |
| Same-Day ACH | ~1 business day |
| Return Code Processing | Standard ACH ~48 hours, Same-Day ACH <24 hours |
Plan payroll or bill payments with sufficient lead time to avoid delays impacting credit or operations.
Clarifying Fees
Understand fee structures before choosing a payment method. The table below compares typical fees and processing times:
| Payment Method | Typical Fee Structure | Avg. Fee ($1,000 Payment) | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACH Transfer | Fixed ($0.20–$1.50) | $0.75–$3 | 1–3 business days |
| Credit Card | 2.5%–3.5% + $0.10–$0.30 | $25–$35 | Instant |
| Wire Transfer | Fixed ($25–$50) | $25–$50 | Same day |
| Digital Apps | 2.5%–3% (business) | $25–$30 | Instant to 1–3 days |
| Paper Check | $3–$6+ total | $3–$6+ | 5–7 business days |
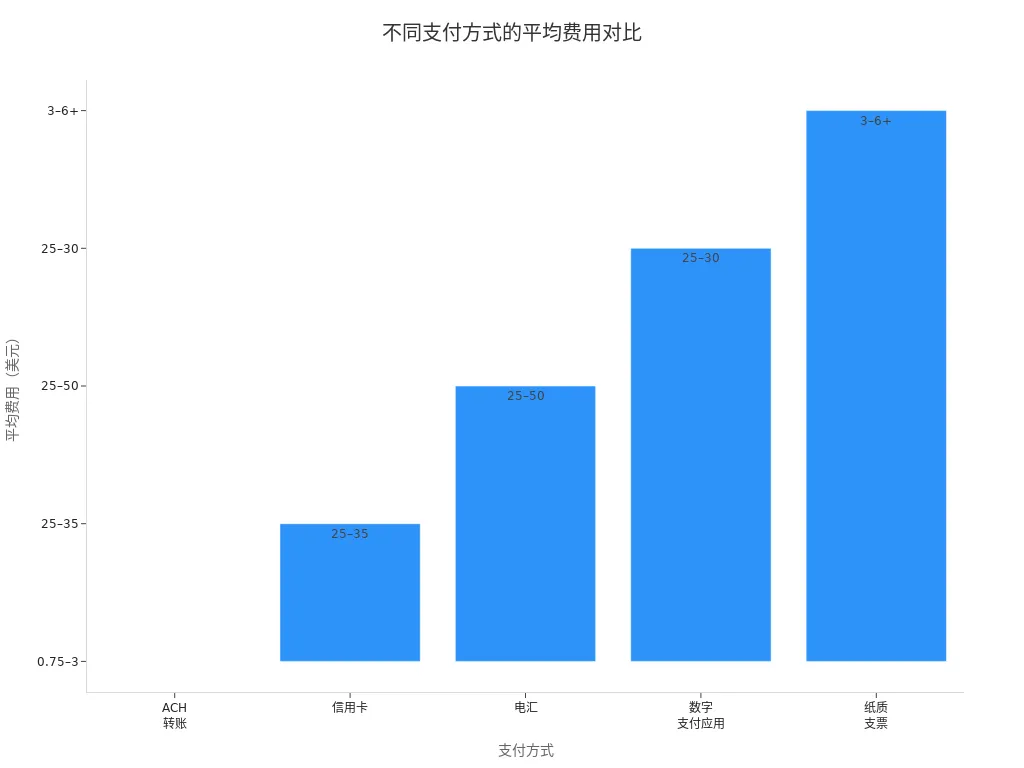
Choose the most suitable method based on needs and budget to minimize costs.
Enhancing Security
Adopt robust security measures for ACH transfers. Use data encryption to ensure only authorized parties access information, as required by Nacha for unsecured networks. Implement multi-factor authentication and authorization processes to reduce fraud risks. Regularly monitor accounts for anomalies to ensure fund safety.
Tip: In mainland China or Hong Kong, prioritize account and data security for similar services to avoid losses.
When choosing ACH transfers, consider these factors:
- Urgency of the transaction
- Cost compared to alternatives
- Need for enhanced security
- U.S.-based destination
- Ease of mobile or online access
By understanding the process and verifying details, you can avoid common pitfalls. Tailor ACH transfers to your needs to enhance financial efficiency.
FAQ
What’s the main difference between ACH and wire transfers?
ACH transfers take 1–3 business days with low fees. Wire transfers settle same-day but have higher fees, ideal for urgent large transfers.
Can I use ACH transfers for international remittances?
ACH transfers are primarily for U.S. bank accounts and cannot be used directly for remittances to mainland China or Hong Kong. Consult your bank for alternatives.
Will funds be lost if I enter incorrect details?
Incorrect details typically result in returned funds. Contact your bank promptly to verify. Funds aren’t lost but may be delayed.
Are there limits on ACH transfer amounts?
Most U.S. banks impose per-transaction and daily ACH limits, varying by bank and account type. Check with your bank for specifics.
How can I track an ACH transfer’s progress?
Track ACH transfers via your bank’s website, app, or customer service. Provide the transaction date and amount for status updates.
By mastering ACH transfers’ pros, cons, and operations, you’re equipped to manage funds efficiently, but high cross-border fees, currency volatility, and offshore account complexities can limit your U.S. market payments or investments, especially for swift payroll or bill deductions. Imagine a platform with 0.5% remittance fees, same-day global transfers, and zero-fee transactions, enabling seamless operations via one account?
BiyaPay is tailored for ACH users, offering instant fiat-to-digital conversions to meet U.S. payment demands nimbly. With real-time exchange rate query, monitor USD trends and transfer at optimal moments to cut costs. Covering most regions with instant arrivals, it powers rapid supplier payments or investment account funding. Crucially, trade U.S. and Hong Kong markets through a single account, leveraging zero-fee transfers for budget-driven fund management.
Whether streamlining payments or dodging data entry errors, BiyaPay fuels your efficiency. Sign up now, visit stocks for U.S. prospects—quick setup unlocks cost-effective, data-driven financial management. Join global users and excel in 2025 markets!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















