- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Think Like a Value Investor: Finding Potential Stocks with Price-to-Earnings (PE) Ratio!

Image Source: unsplash
Do you want to find truly promising stocks like a value investor? The Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) can help you quickly assess whether a stock’s price is reasonable, but you need to be aware of its limitations. Many investors select stocks solely based on PE, which can easily overlook some key risks:
- A high PE may indicate that a stock is overvalued, which could be due to a price increase or a decline in earnings per share.
- During market volatility, PE values can fluctuate significantly, and relying solely on this metric can lead to misjudgments.
- A high PE does not necessarily indicate a company’s growth potential; you also need to combine financial and fundamental analysis.
You should combine information such as the company’s profitability and growth potential to make wiser investment decisions.
Key Points
- The Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) is a tool for assessing the reasonableness of a stock’s price, but it cannot be relied upon alone. Analyzing it in conjunction with company fundamentals and industry characteristics is more important.
- A high PE may indicate market expectations for a company’s future growth, but it could also carry overvaluation risks. Analysis should consider the industry and company growth potential.
- A low PE is not always a good opportunity; it may indicate a lack of growth potential. A comprehensive evaluation of the company’s financial health and market expectations is necessary.
- When selecting stocks, combine multiple financial metrics, such as Earnings Per Share (EPS) and Return on Equity (ROE), to comprehensively assess the company’s investment value.
- Regularly monitor market trends and company performance, dynamically adjust investment strategies, to more effectively identify potential stocks.
PE Basics

Image Source: pexels
Definition and Calculation
You can use the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) to measure whether a company’s stock price is reasonable. The PE ratio is a commonly used valuation tool by investors. It reflects how much the market is willing to pay for each dollar of a company’s earnings. You can calculate the PE ratio in the following two ways:
| Calculation Method | Formula |
|---|---|
| Ratio of stock price to earnings per share | P/E = Stock Price / Earnings Per Share (EPS) |
| Ratio of market capitalization to net income | P/E = Market Capitalization / Net Income |
- P/E = Stock Price / Earnings Per Share (EPS)
- P/E = Market Capitalization / Net Income
For example, if a U.S.-listed company’s stock price is USD 50 and its earnings per share is USD 5, then the PE ratio is 10. This means you need to pay USD 10 to obtain USD 1 of the company’s earnings. By comparing the PE ratios of different companies, you can preliminarily determine which stocks may be undervalued or overvalued.
Role and Limitations
The PE ratio can help you quickly compare the relationship between a stock’s price and the company’s earnings. You can use it to evaluate whether a stock is worth buying. By analyzing the PE ratio, you can determine whether a stock is overvalued, undervalued, or reasonably priced. You can also compare a company’s PE ratio with other companies in the same industry and its historical PE ratio to understand the stock’s valuation status.
Note: The PE ratio is not a cure-all. When using the PE ratio, you need to consider the following points:
- The PE ratio is easily influenced by investor expectations and market sentiment, which may lead to significant fluctuations. A high PE ratio does not necessarily indicate strong company fundamentals; it may simply reflect high market enthusiasm.
- PE ratios vary significantly across different industries. For example, tech companies and retail companies in the U.S. market typically have different PE ratios, and direct comparisons may be misleading.
- Changes in accounting principles can affect reported earnings, thereby impacting the reliability of the PE ratio. You need to pay attention to the comparability of financial statements.
- Historical PE ratios are based on past earnings and may not accurately reflect future performance. A company’s profitability can be affected by various factors, and one year’s earnings cannot fully reflect future potential.
- Macroeconomic factors also affect the PE ratio. High inflation typically leads to lower PE ratios, while low inflation may result in higher PE ratios.
When analyzing the PE ratio, you should combine company fundamentals, industry characteristics, and market conditions to avoid making decisions based solely on numbers. This approach allows for a more scientific evaluation of a stock’s investment value.
Interpreting High and Low PE
Meaning of Low PE
When analyzing stocks, you often encounter companies with low Price-to-Earnings (PE) ratios. A low PE is not always a good thing. It may indicate that the company is undervalued by the market, or it may suggest a lack of growth potential. You can understand the different meanings of a low PE more clearly through the table below:
| Perspective | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Meaning of a low P/E ratio | It may indicate that the company is undervalued or lacks growth potential. |
| Investment Opportunity | A low P/E ratio may provide investors with an opportunity to buy the company at an attractive price. |
You also need to note that companies with low PE ratios sometimes have low market expectations for growth, but this may also make it easier for the company to exceed earnings forecasts.
- A low PE may indicate lower market expectations for the company’s growth.
- A low PE may also suggest that the company is undervalued, presenting an investment opportunity.
- Within a five-year period, low PE stocks have a 75% probability of outperforming the market average, with annual excess returns ranging from 7% to 15%.
Risks of High PE
High PE stocks may appear expensive, but you cannot judge the risk solely based on PE. You need to combine industry and company growth potential for analysis.
- High PE stocks may carry various risks, including high company debt, poor cash flow, or significant earnings volatility.
- The PE ratio is a retrospective indicator and cannot accurately predict future value.
- Management and accounting policies may also affect the calculation of the PE ratio.
- When the overall market performs well, high PE stocks are more popular, but the risks also increase.
Some industries, such as information technology and consumer discretionary, typically have higher PE ratios. The high PE in these industries reflects strong investor expectations for future earnings growth. You can refer to the chart below to understand the relationship between high PE ratios and growth potential in different industries:
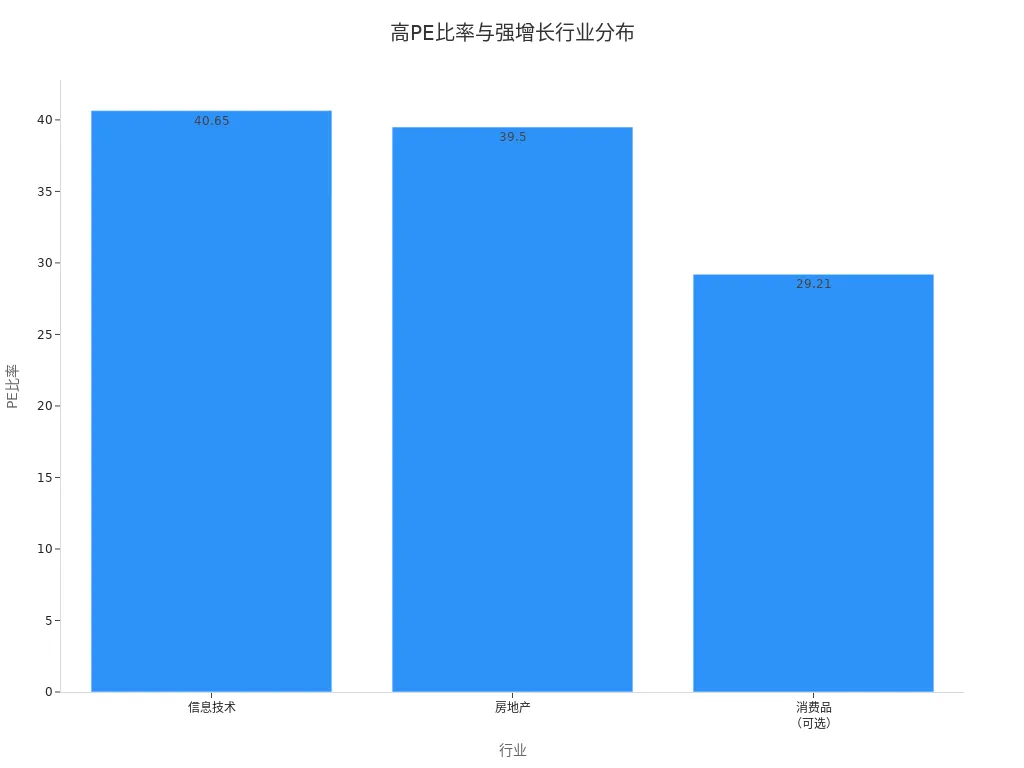
When analyzing high PE stocks, you should combine industry characteristics and company growth potential to avoid making judgments based solely on numbers. This approach allows for a more comprehensive assessment of investment risks and opportunities.
Pitfalls in PE-Based Stock Selection
Pitfalls of Focusing Only on PE
When using the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) for stock selection, you may easily fall into some common pitfalls. Focusing only on the PE value can lead to misjudgments. Below are common misconceptions among investors:
- You may think that a high PE ratio always indicates an overvalued stock. In fact, a high PE sometimes reflects high expectations for future growth and cannot be generalized.
- You may believe that a low PE ratio is always a good opportunity. In reality, a low PE may indicate a lack of growth momentum or unstable financial conditions.
- You may believe that a static PE ratio can accurately reflect a company’s value. In fact, PE is dynamic and influenced by market, industry, and company-specific factors.
- You may overlook that the PE ratio is based on historical earnings, which cannot reflect future growth potential. For companies with no profits, the PE ratio is also inapplicable.
When analyzing, you should be cautious of these pitfalls and avoid making decisions based solely on PE.
Industry Differences
PE ratio standards vary significantly across different industries. You cannot directly compare all companies using the same PE standard. The table below shows the average PE ratios for major industries:
| Industry Name | P/E Ratio |
|---|---|
| Technology | 57.31 |
| Finance | 23.29 |
| Consumer Goods | 19.06 |
You can see that the PE ratio for the technology industry is much higher than that for consumer goods and finance industries. This is because technology companies typically have higher growth expectations. When analyzing, you should compare a company with others in the same industry. Industry growth rates, profit margins, and risk levels all affect the reasonable PE range.
Comprehensive Analysis Suggestions
When selecting stocks, you cannot rely solely on the PE ratio. Professional analysts typically combine multiple financial metrics and market conditions for a comprehensive judgment. You can refer to the following suggestions:
- Combine metrics such as Earnings Per Share (EPS), Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B), Return on Equity (ROE), and Debt-to-Equity Ratio (D/E) to comprehensively assess the company’s financial health.
- Analyze the company’s position in the industry and compare its PE level with other companies in the same industry.
- Focus on the sustainability and growth potential of the company’s earnings. You can use the PEG ratio to incorporate growth expectations into valuation analysis.
- Check non-recurring items in the company’s financial statements to avoid being influenced by one-time gains or losses.
- When evaluating emerging market companies, consider historical average PE and country risk premiums. Inflation and risk levels in different countries affect reasonable valuations.
Only by combining multidimensional data can you more scientifically screen truly promising stocks.
Value Investor’s PE Analysis

Image Source: pexels
Value Investor’s Stock Selection Approach
When learning value investing, you need to understand its core principles. Value investors focus on a stock’s true value rather than short-term market fluctuations. You can grasp the stock selection approach of value investors through the following aspects:
- The essence of value investing is to determine a stock’s intrinsic value through analytical methods, aiming to buy at a price below its true value.
- A stock’s intrinsic value is the core of analysis, and the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) is an important tool for assessing intrinsic value.
- Value investors typically look for stocks with lower PE ratios, as these stocks may be undervalued by the market.
- Long-term holding is a key principle for value investors, and you need to patiently wait for the stock’s value to be realized.
- You can focus on stocks with PE ratios in the bottom 10% of their industry, as they are more likely to be potential stocks.
In practice, you should not only look at the level of the PE ratio. You also need to combine the company’s profitability, growth potential, and industry position. Value investors use multiple financial metrics to comprehensively judge whether a stock is worth investing in.
Combining PE with Fundamentals
When analyzing the PE ratio, you cannot ignore company fundamentals. Value investors combine PE with metrics like earnings growth and Return on Equity (ROE) to comprehensively evaluate a company:
- You can compare the PE ratio with earnings growth. Companies with low PE but fast earnings growth often have greater investment value.
- You should also focus on ROE. A high ROE indicates that the company can effectively use shareholder funds to create profits, reflecting management capability and company competitiveness.
- You can combine metrics like Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B) and Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S) to further determine whether a company is undervalued.
- You need to analyze the company’s financial health, including debt ratios and liquidity, to avoid financial risks.
- You should also focus on industry trends, corporate governance, management quality, and brand reputation, as these qualitative factors affect long-term performance.
In different economic cycles, you should dynamically adjust your judgment of PE. During economic booms, inflated earnings may make stocks appear undervalued; during recessions, declining earnings may make stocks appear overvalued. You can compare PE with historical averages, industry peers, and overall market conditions to make more informed decisions.
You also need to note that the PE ratio’s calculation depends on the company’s reported earnings. Different accounting policies may make PE ratios incomparable. You cannot rely solely on the PE ratio; you must combine other financial and qualitative analyses.
Steps for Screening Potential Stocks
If you want to screen potential stocks like a value investor, you can follow these steps:
- Initial Screening: You can use metrics like low PE, low P/B, low P/S, or high dividend yield to screen stocks with lower valuations.
- Secondary Filtering: You need to check financial health, such as debt ratios, liquidity, and Piotroski F-Score, to eliminate companies with high financial risks.
- Qualitative Assessment: You should analyze management capability, corporate governance, industry competitive landscape, and industry trends. You can also focus on brand reputation and customer satisfaction.
- Intrinsic Value Estimation: You can use methods like discounted cash flow to estimate a company’s intrinsic value, ensuring a sufficient margin of safety in the purchase price.
- Dynamic Adjustment: You need to dynamically adjust screening criteria based on market conditions and economic cycles. You can compare PE with historical averages and industry levels to avoid cyclical misjudgments.
Throughout the screening process, you should combine multiple financial ratios and qualitative analyses. You cannot rely solely on the PE ratio. You also need to focus on the company’s earnings growth, ROE, and industry prospects. This way, you can scientifically screen truly promising stocks like a value investor.
You can refer to the practices of institutional investors, combining the PE ratio with other financial metrics and qualitative factors to enhance the scientific rigor of investment decisions.
Using this method, you can more effectively identify undervalued quality companies. With long-term persistence, value investors can often achieve returns that exceed the market average.
When using the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) for stock selection, you need to analyze rationally. PE is just one of the evaluation tools. You should combine company fundamentals, industry characteristics, and market sentiment to deeply analyze the company’s growth potential and financial health. Do not blindly pursue low PE. You can improve the scientific rigor of investment decisions by regularly monitoring, analyzing industry trends, and assessing management quality. Diversified investments and a long-term perspective are equally important.
FAQ
What is the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE)?
You can use the Price-to-Earnings Ratio (PE) to measure the relationship between a stock’s price and the company’s earnings. PE = Stock Price / Earnings Per Share. You can use it to preliminarily judge whether a stock’s valuation is reasonable.
Are low PE stocks always worth buying?
You cannot judge solely based on a low PE. A low PE may indicate that a company is undervalued, but it could also suggest a lack of growth potential. You also need to combine company fundamental analysis.
Are high PE stocks risky?
When you see a high PE, don’t immediately assume high risk. A high PE sometimes reflects market expectations for future growth. You need to combine industry and company growth potential to judge.
Is PE suitable for comparing all industries?
You cannot compare all industries using the same PE standard. The PE ratios of the tech and finance industries vary significantly. You should compare a company with others in the same industry.
Is selecting stocks based only on PE reliable?
Selecting stocks based solely on PE can easily overlook a company’s financial health and growth potential. You should combine multiple financial metrics and industry analysis to make more scientific investment decisions.
To truly invest like a value investor, you must look beyond the simple Price-to-Earnings (PE) ratio, using it as a starting point to dive into ROE, EPS, and fundamental analysis to identify undervalued gems. Yet, the core challenge remains: high transaction fees and inefficient cross-border funding can drastically reduce the long-term returns achieved through disciplined value investing. Global market access at minimal cost is no longer a luxury—it’s a necessity.
To ensure your value analysis translates into maximized net profit, integrate the financial precision of BiyaPay. We offer zero commission for contract limit orders, a crucial advantage that drastically minimizes the cost of building, maintaining, and rebalancing a long-term portfolio of US and HK equities. This aligns perfectly with the value investor’s focus on capital preservation and long-term compounding. Furthermore, our platform supports the swift, mutual conversion between fiat and digital assets like USDT, providing you with the fastest, most reliable pathway to fund your brokerage accounts for time-sensitive global investment. You can register quickly—in just 3 minutes without requiring an overseas bank account—and gain immediate access to US and Hong Kong Stocks. Leverage our real-time exchange rate checks to maintain transparent control over your funding costs. Open your BiyaPay account today and secure the operational edge your value strategy deserves.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















