- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Leverage or Liquidation? Master Margin Trading for Steady Returns

Image Source: pexels
Have you ever hesitated in margin trading, worried that an impulsive move could lead to liquidation? Choosing the right margin buying approach and scientifically managing risks can help you achieve stable profits in the “leverage or liquidation” dilemma. You need to master practical strategies to protect your capital safety amidst market fluctuations.
Key Takeaways
- Choose the appropriate margin mode. Full margin suits traders pursuing capital efficiency, while isolated margin better controls risks.
- Set reasonable stop-loss and take-profit levels. Scientific stop-loss settings protect capital, while take-profits lock in profits.
- Dynamically adjust position management. Flexibly adjust capital allocation per trade based on market fluctuations to reduce liquidation risks.
- Diversify investments and hedge risks. Allocate funds to different assets to reduce the impact of single market fluctuations on the overall account.
- Adhere to capital management principles. Control the risk of each trade to ensure individual losses do not jeopardize overall account safety.
Basic Principles and Risks

Image Source: pexels
Introduction to Margin Trading
In margin trading, you can borrow funds from a broker to invest beyond your own capital. This approach allows you to open larger positions with less capital. For example, with $1,000 in capital, using 10:1 leverage, you can manage assets worth $10,000. This gives you the opportunity for higher returns but also comes with greater risks.
Leverage and Risk Amplification
Leverage amplifies your investment outcomes. You control larger market positions with smaller capital. For every 1% market price fluctuation, your profit or loss is magnified by the leverage ratio. For instance, a 3% market drop could result in a $30 loss instead of $3.
- Leverage trading amplifies potential profits and losses.
- You can take on greater risks with less capital.
- Losses also increase rapidly with higher leverage ratios.
Liquidation Mechanism
In the “leverage or liquidation” choice, liquidation is a risk you must be vigilant about. Liquidation is typically triggered by the following reasons:
- Your margin level is too low to support current positions.
- Severe market fluctuations cause significant price changes in a short time.
- You lack a reasonable trading plan and underestimate risks.
- Positions are too large, exceeding your risk tolerance.
Once liquidated, you may lose nearly all your capital and feel frustrated or guilty. Liquidation can also alter your trading behavior and strategies, impacting subsequent decisions.
Margin Buying Methods
Full Margin vs. Isolated Margin
In margin trading, you often need to choose between full margin (cross margin) and isolated margin. Full margin allows you to use all available margin in your account to support all positions, enhancing capital efficiency but increasing risks. Isolated margin allocates separate margin for each position, effectively controlling the risk of individual trades and protecting your capital. The table below shows the main differences between the two modes:
| Feature | Cross Margin (Full Margin) | Isolated Margin |
|---|---|---|
| Risk Management Approach | Flexibly allocates risk, suitable for traders with high risk tolerance | Precisely controls risk, suitable for traders seeking capital protection |
| Capital Efficiency | Maximizes capital use, supports multiple positions, but higher risk | Isolates risk for each position, preventing major losses |
| Flexibility and Precision | Flexibly adjusts positions and leverage to adapt to market changes | Precisely manages individual position risks |
| Liquidity and Management | Uses all margin to reduce liquidation likelihood | Isolates risks to protect the account from cascading liquidations |
| Trading Goal Alignment | Suits traders pursuing efficient capital use | Suits traders prioritizing discipline and risk control |
You can choose the appropriate mode based on your trading goals and risk appetite. Experienced traders often opt for full margin to maximize capital efficiency. Beginners or risk-averse investors prefer isolated margin for better risk control.
Leverage Ratio Selection
The leverage ratio determines how much you can amplify profits and risks. Choosing high leverage offers the potential for higher returns but significantly increases liquidation probability. Data shows that in 2021, the total liquidated positions on centralized exchanges in mainland China reached nearly $80 billion, averaging over $200 million daily. Many traders were automatically liquidated due to insufficient collateral. When trading in high-volatility markets like Bitcoin futures, you must cautiously select leverage ratios to avoid falling into the “leverage or liquidation” trap.
- High leverage suits short-term experts but carries extreme risks.
- Low leverage is better for conservative investors, with lower liquidation probability.
- You should flexibly adjust leverage based on your risk tolerance and market conditions.
Combined Strategies
You can combine full and isolated margin modes, flexibly apply different leverage ratios, and develop personalized trading strategies. For example, you can use isolated margin for main positions to control individual trade risks and full margin for auxiliary positions to improve capital efficiency. You can also adjust leverage ratios based on market volatility to reduce liquidation risks. A reasonable combination of margin buying methods helps you achieve stable returns in the “leverage or liquidation” choice.
Leverage or Liquidation: Stable Strategies
Position Management
In margin trading, position management is key to achieving stable returns. Reasonably allocating capital per trade can effectively reduce liquidation risks. You can refer to the following three common position management methods:
| Method | Description | Risk Management Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Fractional Position Sizing | Risks a fixed 1-2% of total account value per trade. | Limits potential losses per trade. |
| Volatility-Based Position Sizing | Adjusts investment size based on market volatility, increasing investment in low volatility and reducing it in high volatility. | Reduces risk exposure in volatile markets. |
| Kelly Criterion Position Sizing | Calculates optimal trade size based on win rate and odds. | Improves trading success rate and capital protection. |
You can choose fixed fractional position sizing, risking only 1-2% of your account per trade to protect capital even during consecutive losses. Volatility-based sizing automatically reduces investment during sharp market fluctuations, avoiding liquidation due to rapid price changes. The Kelly Criterion helps you scientifically calculate the optimal capital allocation per trade based on historical win rates and odds.
Dynamically adjusting positions helps you adapt to market changes. You can flexibly adjust risk and return levels based on current market conditions. This reduces emotional decision-making, improving trading consistency and stability. In the “leverage or liquidation” choice, position management is the most fundamental and effective risk control tool.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit
In margin trading, stop-loss and take-profit settings directly impact your final returns and risks. Scientifically setting stop-loss prevents excessive losses in a single trade, protecting your capital. Take-profit helps you lock in profits, avoiding missed opportunities due to greed.
| Evidence Type | Impact | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Stop-Loss Orders | Price Cascading | Execution of stop-loss orders causes rapid exchange rate changes, forming trends. |
| Take-Profit Orders | Negative Feedback Trading | Take-profit orders do not trigger price cascades and have minimal impact on exchange rates. |
| Statistical Tests | Greater and Longer-Lasting Reactions | Empirical tests show stop-loss orders have a significantly greater impact than take-profit orders. |
You can choose different stop-loss and take-profit tools based on market conditions. For example, in an uptrend, you can use ATR trailing stops or Parabolic SAR to let stop-loss dynamically follow price increases. In range-bound markets, you can use Bollinger Bands or Donchian Channels to set entry and exit points based on ranges. High-volatility markets suit Chandelier Exit or volatility-based stops, setting wider stop-loss ranges to absorb price fluctuations.
Many professional traders set a 1:3 risk-reward ratio. If you risk 50 points per trade aiming for 150 points, you only need a 33% win rate to achieve long-term profitability. When trading in mainland China, regularly adjust stop-loss based on the ATR indicator to maintain alignment with market volatility. This maximizes capital and profit protection in the “leverage or liquidation” process.
Diversification and Hedging
In margin trading, diversification and risk hedging are equally important. Diversification reduces the impact of single market or asset fluctuations on your overall account. You can allocate funds to different asset classes or trading instruments to lower liquidation probability.
- You can actively monitor foreign exchange risks, especially during periods of geopolitical tensions, tariff changes, or rising inflation pressures. This protects your cash flow and return stability.
- Market makers’ gamma exposure significantly affects spot market volatility. Short gamma exposure increases market volatility, while positive gamma exposure helps reduce it.
- You can use hedging strategies, such as buying and selling correlated assets, to reduce risks from single market fluctuations.
When conducting margin trading in mainland China, diversification and hedging strategies help maintain account stability during high-volatility periods. Combining position management with stop-loss and take-profit settings forms a comprehensive risk control system. This allows you to achieve stable long-term returns in the “leverage or liquidation” choice.
Risk Control Methods
Capital Management
In margin trading, capital management determines account safety. Scientifically allocating funds can reduce liquidation risks. You can adopt the following common capital allocation models:
- Risk-Based Allocation: You allocate funds based on maximum drawdown limits, position size control, and daily loss thresholds. This ensures individual losses do not jeopardize overall account safety.
- Performance-Based Allocation: You tie capital allocation to trading results, dynamically adjusting risk exposure based on monthly profit targets and three-month rolling performance evaluations.
You can also improve long-term trading success through the following methods:
- Strictly control position size per trade, typically 1-2% of account capital.
- Set stop-loss before entering trades, clarifying maximum risk.
- Adjust position size based on market volatility.
- Gradually increase positions during clear trends and reduce them after consecutive losses.
- Track maximum drawdown levels to maintain risk consistency.
Adhering to capital management principles effectively protects your capital, reducing liquidation risks from single trade losses.
Emotions and Discipline
In high-leverage trading, emotions and discipline directly impact risk control effectiveness. The table below shows common psychological factors and their effects:
| Psychological Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Emotional Triggers | Fear and greed can lead to impulsive decisions, impairing judgment. |
| Lack of Risk Framework | Relying on emotions rather than probability analysis increases losses. |
| Cognitive Biases | Overconfidence and confirmation bias cause you to overlook risk management. |
| Stress and Mental Fatigue | Prolonged stress impairs judgment, increasing risk management failure probability. |
You can maintain trading discipline through the following methods:
- Review and log trades at fixed times daily.
- Take regular breaks to avoid mental fatigue.
- Continuously monitor position sizes and track win-loss ratios.
- Adjust risk ratios per trade during market volatility.
- Practice meditation and mindfulness to reduce impulsive decisions.
- Identify and log emotional triggers to support rational decision-making.
By building good trading habits, you can maintain stable performance in the complex environment of mainland China’s markets.
Warning and Liquidation Lines
When using leverage, warning and liquidation lines are critical tools for protecting your account. Major trading platforms automatically monitor your margin levels, triggering liquidation mechanisms. You should focus on the following points:
- Liquidation is the process of a platform forcibly closing your leveraged positions when margin is insufficient.
- Liquidation events can occur anytime, especially with high leverage (e.g., 100x, 50x, 25x), which carries higher risks.
- Prices often move toward liquidity pools, leading to concentrated liquidation events.
- You can set reference prices, trading volume thresholds, and volatility thresholds to identify potential risks early.
By reasonably setting warning and liquidation lines, you can take proactive measures to avoid passive account liquidation. This allows you to better control risks and achieve stable returns in mainland China’s markets.
Case Studies

Image Source: pexels
Stable Returns Case Study
When adopting stable strategies in the U.S. stock market, you can see the advantages of long-term returns. From 2000-2021, the performance of value stocks, growth stocks, and the broad market across economic cycles is as follows:
| Period | Value Stocks Performance | Growth Stocks Performance | Broad Market Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000-2002 | Declined 39% | Declined 56% | Declined 46% |
| 2007-2009 | Declined 54% | N/A | Declined 49% |
| 2020-2021 | Returned 35% | Returned 20% | Returned 27% |
You can observe that stable strategies incur smaller losses during market downturns and recover faster during upswings. Quality stocks outperformed growth stocks and the broad market after the financial crisis. The chart below shows the performance of these three stock types across economic cycles:
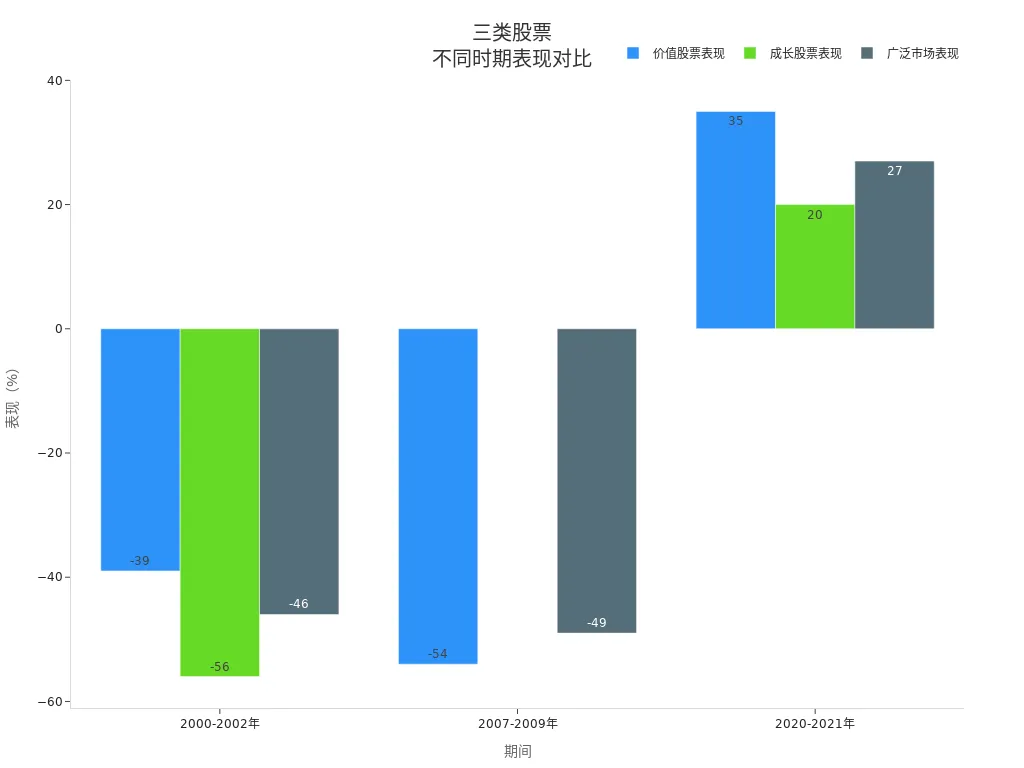
By choosing diversified investments and low leverage, you can effectively reduce liquidation risks and achieve stable long-term returns.
Liquidation Lessons
In margin trading, common causes of liquidation include impulsive trading, overpursuing quick profits, and lack of risk management. Novice investors often make mistakes due to unfamiliarity with market volatility and the impact of high leverage. Common errors leading to liquidation include:
- Impulsive trading without rational analysis.
- Overusing high leverage, ignoring risks.
- Failing to monitor accounts in time or set stop-losses.
- Not maintaining sufficient margin buffers.
If you ignore these risks, you are prone to forced liquidation during sharp market fluctuations, potentially losing all your capital. You can reduce liquidation probability by setting stop-loss orders, diversifying investments, and regularly monitoring your account.
Strategy Comparison
In the “leverage or liquidation” choice, the long-term performance of stable versus aggressive strategies differs significantly. The table below compares the volatility of the two strategies:
| Strategy Type | Median Volatility | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Conservative | 7% | 2009 data |
| Aggressive | 26% | Aggressive median volatility is nearly 4 times that of conservative |
| 2023 | Aggressive median volatility is 2.1 times that of conservative | |
| Past Five Years | Aggressive strategies carry higher risks than conservative ones |
When adopting aggressive strategies, you may achieve higher returns, but volatility and potential losses are greater. High-risk strategies have a Sharpe ratio of 0.63, far higher than the global equity average of 0.34, but stable strategies perform better on a risk-adjusted basis. If you pursue stable returns, prioritize diversified investments, low leverage, and strict risk management.
To achieve stable returns, scientifically selecting margin buying methods and risk management is critical. You can refer to the following methods:
- Choose a suitable trading platform, focusing on fees and leverage options.
- Use a demo account to familiarize yourself with platform features.
- Diversify trading strategies to reduce risks.
- Combine hedging and other investment strategies to enhance stability.
- Start with small investments and gradually scale up trading.
The table below shows research findings on scientific margin strategies and risk management:
| Study Title | Key Findings |
|---|---|
| Countercyclical and Risk-Sensitive Margin Strategies | Countercyclical strategies optimize loss distribution |
| Margin Trading Volatility and Stock Price Crash Risk | Margin trading volatility correlates with future crash risks |
| Margin Buying, Short Selling, and Chinese Stock Return Volatility | Margin trading activity positively correlates with return volatility innovations |
By adhering to rational operations and combining scientific methods, you can achieve the goal of “leveraging without liquidation” in mainland China’s markets.
FAQ
What are the main risks of margin trading?
When conducting margin trading in mainland China, the main risks include liquidation, market volatility, and amplified losses from leverage. You need to strictly manage positions and stop-losses to protect your capital.
It’s recommended to assess risks before each trade and avoid blindly increasing leverage.
How do I choose the appropriate leverage ratio?
You can choose leverage ratios based on your risk tolerance and market volatility. Beginners should use leverage below 5x. High leverage offers higher returns but increases liquidation probability.
| Leverage Ratio | Liquidation Risk | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|
| 1-5x | Low | Beginners, conservative traders |
| 6-20x | Medium | Experienced traders |
| Above 20x | High | Aggressive traders |
What’s the difference between full margin and isolated margin?
In full margin mode, all positions share the account’s margin, carrying higher risks. Isolated margin allocates separate margin per position, effectively controlling individual trade risks. You can choose based on your trading goals.
If you prioritize capital safety, consider using isolated margin first.
How can I avoid liquidation?
You can set stop-losses, diversify investments, and control the capital proportion per trade. Regularly check margin levels and top up funds promptly. Scientific risk management is key to avoiding liquidation.
How do I choose a margin trading platform in mainland China?
You should prioritize platform security, trading fees (in USD), leverage options, and customer service. It’s recommended to use a demo account to familiarize yourself with platform features before live trading.
The choice between “leverage or liquidation” is not binary; the key to achieving stable returns lies in scientifically chosen margin modes, strict position sizing, and stop-loss/take-profit discipline. Whether you opt for cross-margin for capital efficiency or isolated margin for single-trade risk control, an efficient, low-cost global trading channel is vital for mitigating systemic risk and enhancing fund security.
BiyaPay is dedicated to providing you with this essential infrastructure. We enable seamless conversion between fiat and digital currencies (like USDT), helping you secure fast funding that bypasses complex channels. Deposits can arrive as quickly as the same day, ensuring you never miss a trading opportunity and allowing efficient connection to high-liquidity markets like US stocks. For margin users involved in high-frequency trading, our stocks platform offers the low-cost benefit of zero fees on contract limit orders for position building, alongside the convenience of managing global assets through a single account. Moreover, our Real-Time Exchange Rate Query tool lets you stay on top of currency dynamics and avoid hidden losses. Crucially, BiyaPay international remittance fees are as low as 0.5%, which can save you up to 90% compared to traditional banks.
Ready to open an account in 3 minutes for zero barriers to global investment, and ensure you “leverage without liquidating” with lower costs and higher efficiency? Click to register with BiyaPay and begin your secure leveraged trading journey.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















