- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Golden Opportunities in Earnings Season: Understanding Company Earnings and EPS to Catch Signals of Stock Price Increases!
In the stock market, earnings are one of the important indicators for evaluating a company’s financial health. In particular, earnings per share (EPS) is widely used as a core data for measuring a company’s profitability and shareholder returns. This article will provide a detailed analysis of the definition of earnings, calculation methods, the relationship between dividends and EPS, and the impact of earnings season on stock prices, helping investors better understand this key concept and make rational investment decisions.
When analyzing company earnings and formulating investment strategies in the global market, efficient fund management and convenient trade execution are of great importance. As a multi - asset wallet platform supporting US and Hong Kong stock trading, BiyaPay’s fast fund - in and fund - out services can help investors respond more efficiently to market changes and improve investment efficiency.

What is Company Earnings?
Earnings usually refer to the amount of money a company earns from selling products or providing services, after deducting costs and expenses. In financial reports, earnings are an important indicator for measuring a company’s profitability. Usually, terms such as earnings, profit, net income, and bottom line are interchangeable and are used to refer to the economic benefits generated by a company.
Earnings are crucial for shareholders and investors because they directly reflect the company’s operating conditions and future profit - making potential. Higher earnings usually mean that the company has a place in the market and can effectively create returns for shareholders. However, earnings alone are not sufficient to comprehensively evaluate a company. Especially among different industries and companies, a simple number may not fully represent the company’s true profitability.
In the stock market, earnings per share (EPS) is the most commonly used important indicator for measuring a company’s earnings. It helps investors compare the performance of different companies through the profit per share.
What is Earnings per Share (EPS) and How to Calculate It?
Earnings per share (EPS) refers to the net profit per common share that a company earns during a specific period (usually a quarter or a fiscal year). EPS is an important indicator used by investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s profitability and is often used for comparing different companies within the same industry.
The formula for calculating EPS:
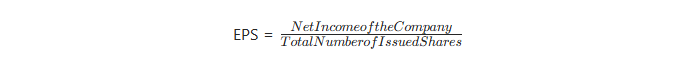
For example, if a company’s net profit is $10 million and the company has issued 10 million common shares, then the EPS is $1.
The importance of EPS lies in its ability to help investors understand the distribution of a company’s earnings and evaluate the company’s earnings growth potential accordingly. For example, if a company has a relatively high EPS, it usually means that its earnings performance is strong, attracting the attention of investors and driving the stock price up.
It should be noted that EPS may vary depending on whether the company has carried out share buy - backs, is involved in special projects, etc. Therefore, when analyzing EPS, investors should pay attention to the adjusted EPS, that is, the net profit after deducting non - recurring expenses and revenues.
How Much Impact Does Earnings Season Have on Dividends and Stock Prices?
Every year, listed companies release financial reports, which list in detail the company’s financial situation in a fiscal quarter or year, including core data such as profit, revenue, and earnings per share (EPS). During earnings season, investors and analysts usually pay close attention to these figures, especially the difference between the company’s actual profit and analysts’ predicted profit.
When a company releases its financial report, if the actual profit is higher than expected, it usually leads to an increase in the stock price because it is considered a sign of the company’s good financial condition. Conversely, if the actual profit is lower than analysts’ consensus earnings estimates, it may lead to a decline in the stock price, especially when there are large changes in earnings expectations, and the stock price will be more volatile.
As a part of the company’s profit paid to shareholders, dividends are also closely related to the company’s earnings. If a company’s EPS increases and it continues to issue stable dividends, shareholders will see higher returns, which may attract more investors to buy the stock.
What Impact Do Dividends and Profits Have on Shareholders?
Dividends are directly related to a company’s earnings. Usually, a company decides whether to pay dividends and how much to pay according to its own earnings situation. For mature companies, paying dividends is a common way to return profits to shareholders; while for growth - oriented companies, they may use most of their earnings for business expansion and reinvestment instead of distributing dividends.
- Dividend Payment and Earnings Distribution: Generally speaking, the proportion of dividend payment is closely related to the company’s profitability level. If the company’s earnings grow, shareholders may receive more dividends; while when the company’s profit is unstable or it faces operating difficulties, dividends may be reduced or suspended.
- The Impact of Dividend Payment on Stock Prices: Dividends usually enhance investors’ confidence. Especially when the market is highly volatile, stable dividend payments provide investors with additional returns. The stability of such dividend payments can also help the stock price rise. However, after the dividend is paid, the stock price will be adjusted downward accordingly based on the amount of the dividend paid. For example, a company that pays a $2 dividend will usually drop by $2 on the ex - dividend date.
- Reinvestment and Shareholder Returns: Compared with paying dividends, many growth - oriented companies choose to use their profits for business expansion, such as research and development, market expansion, etc. This reinvestment strategy may not directly benefit shareholders in the short term, but if it can bring long - term growth and earnings, shareholders will ultimately receive higher returns.
How to Evaluate a Company’s Investment Value Using Earnings and EPS?
When choosing investment targets, earnings and EPS are two crucial indicators. Investors can evaluate whether a company has long - term investment value by analyzing these two data.
- Steady Growth of Earnings: Over the long term, steadily growing earnings usually indicate that a company has strong market competitiveness and management capabilities. Especially in periods of high economic uncertainty, stable earnings will provide continuous financial support for the company and enhance shareholders’ confidence.
- Continuous Growth of EPS: Investors should pay attention to whether EPS shows a continuous growth trend. If a company can steadily increase its EPS over multiple quarters or years, it usually means that its profitability is constantly strengthening and it may become a worthy long - term investment target.
- Comparison with Peer Companies: EPS helps in comparing companies within the same industry. By comparing the differences in EPS among various companies, investors can determine which company has greater profit - making potential and competitiveness.
- Comprehensive Consideration of Other Financial Indicators: Although EPS and earnings are important indicators for evaluating a company’s profitability, they alone cannot determine investment decisions. Investors should comprehensively evaluate the company’s financial health by combining other financial indicators, such as net profit, gross profit margin, and debt - to - asset ratio.
Understanding Earnings and EPS to Make More Precise Investment Decisions
Dividends and earnings per share (EPS) are important tools for understanding a company’s financial health and evaluating its future profit - making potential. Steady earnings usually support the rise of stock prices, and EPS is a core indicator for investors and analysts to evaluate a company’s profitability. By in - depth understanding of these financial data, investors can make more precise investment decisions.
In actual investment, using a flexible and efficient asset management platform can further enhance the investment experience. As a wallet platform supporting global multi - asset trading, BiyaPay provides trading functions for the US stock, Hong Kong stock, and digital currency markets, helping investors quickly obtain dividend income and efficiently manage their assets. Through BiyaPay, you can easily trade US stock options, access investment opportunities in global stock markets and digital currencies, and maximize asset allocation and returns.
lity
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















