- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Weekly vs. Monthly Options: Investment Strategies for Short-Term Flexibility and Long-Term Stability
Image Source: unsplash
When choosing between weekly options and monthly options, you will focus on key factors such as expiration time, premiums, and liquidity. Weekly options expire every week, have lower premiums, and offer more flexible trading, making them suitable for handling short-term market fluctuations. Monthly options expire monthly, have higher premiums, and strong liquidity, making them suitable for long-term holding. The table below shows the significant growth in the market share of weekly options in the U.S. market:
| Time | Short-Term Options Market Share |
|---|---|
| November 2019 | 12% |
| September 2023 | 31% |
| Short-Term Options Growth | From 6.4% to 21.6% |
- Retail investors’ participation rate in short-term expiration options has reached 51%
- 56% of retail options trading volume comes from products with expirations of five days or less
You can analyze investment strategies, combine your own needs, and rationally determine which type of option better suits your investment goals.
Key Points
- Clarify investment goals. Weekly options are suitable for active traders seeking short-term high returns, while monthly options are more suitable for investors focused on long-term stable returns.
- Assess risk appetite. Weekly options are suitable for investors with high risk tolerance, while monthly options are suitable for investors with low risk tolerance.
- Focus on liquidity and transaction costs. Weekly options have frequent trading and higher commission expenses; monthly options have strong liquidity and lower transaction costs.
- Flexibly choose option types. Based on market conditions and personal needs, rationally select weekly or monthly options to enhance portfolio performance.
Selection Considerations
Investment Goals
When formulating an investment strategy analysis, you first need to clarify your investment goals. The investor groups for weekly options and monthly options show significant differences. Weekly options typically attract active traders who aim to capitalize on short-term market fluctuations through frequent trading, pursuing higher returns. If you belong to this group of investors, you can leverage the rapid expiration and lower premiums of weekly options to flexibly adjust positions and maximize income.
Monthly options are more suitable for investors focused on capital preservation and stable income. For example, many retired investors prefer monthly options because they prioritize long-term stability and risk control. The longer holding period and higher liquidity of monthly options provide you with more time to respond to market changes, reducing the pressure from frequent trading.
Tip: You can choose the more suitable option type based on your capital size and return expectations. If you aim to achieve higher returns through short-term operations, weekly options are more attractive. If you pursue long-term steady growth, monthly options are more appropriate.
- Weekly options investors: Active traders, pursuing high-frequency returns
- Monthly options investors: Retired groups, focused on capital preservation and stable income
Risk Appetite
Your risk tolerance directly affects the choice of option type. The time value of weekly options decays quickly, and price fluctuations are more volatile, making them suitable for traders with high risk tolerance. If you can quickly respond to market changes, weekly options can help you capitalize on market fluctuations to achieve higher premiums.
Monthly options are suitable for investors with lower risk tolerance. The longer expiration time gives you more opportunities to adjust strategies, reducing losses due to time decay. You can choose strike prices further from the current market price to lower risk and achieve more stable returns.
The table below shows the differences between weekly and monthly options in terms of liquidity and risk tolerance:
| Option Type | Expiration Time | Premium | Liquidity | Suitable Risk Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weekly Options | Weekly | Low | High | High |
| Monthly Options | Monthly | High | Strong | Low |
- Weekly options are suitable for traders with high risk tolerance, capable of quickly capitalizing on market fluctuations
- Monthly options are suitable for investors with low risk tolerance, offering longer trading time to handle market fluctuations
You can diversify your investment strategy analysis to spread risk across different market conditions, maintaining portfolio balance. Weekly and monthly options each have advantages, and you should choose the option type most suitable for you based on your risk appetite and market judgment.
Weekly Options Investment Strategy Analysis
Image Source: pexels
Definition and Characteristics
In your investment strategy analysis, you will find that weekly options are short-term options, typically expiring weekly. For example, in the U.S. market, SPXW options expire every Friday, while in the Indian market, they expire every Thursday. Weekly options primarily target high-volume stocks or index options, such as Nifty or Bank Nifty. Due to their short expiration periods, weekly options’ premiums are typically lower than monthly options, making them suitable for rapid trading and flexible position adjustments. The table below summarizes the core characteristics of weekly options:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequent Expiration | Expires weekly, suitable for short-term trading |
| Available Securities | High-volume stocks or indices, such as SPXW, Nifty |
| Short-Term | Lasts only a few days, facilitating quick market response |
| Lower Premiums | Low premiums, smaller upfront costs |
| Flexible Strategies | Supports diverse strategies like straddles, strangles, and iron condors |
Suitable Audience
Weekly options are more suitable for active traders and day traders. If you enjoy frequent trading and are adept at capitalizing on short-term market fluctuations, weekly options can help you achieve high-frequency trading goals. For investors looking to leverage market events (such as earnings releases or news announcements) for short-term positioning, weekly options provide an ideal tool. You can flexibly adjust your investment strategy analysis based on market sentiment and technical analysis to enhance return efficiency.
Short-Term Advantages
The greatest advantage of weekly options lies in their flexibility and high responsiveness to market changes. You can use weekly options to quickly capture short-term market fluctuations and adjust positions promptly. SPXW and other weekly options allow you to re-position every week, making them suitable for responding to sudden events or market sentiment changes. Weekly options’ expiration periods range from one day to three months, with lower upfront costs, facilitating diversified investment strategy analysis.
- Weekly options are suitable for trading around upcoming events
- You can precisely time entries based on technical analysis and market sentiment
- Low premiums, transaction costs are manageable
Trading Risks
When investing in weekly options, you need to be aware of their high-risk characteristics. Weekly options’ prices are highly sensitive to market fluctuations, with rapid Theta decay, and if expected volatility does not occur in time, the option value can drop quickly. The table below compares the main risk characteristics of weekly and monthly options:
| Feature | Weekly Options | Monthly Options |
|---|---|---|
| Expiration Date | Every Friday | Last Friday of the Month |
| Lifecycle | Up to one week | Up to one month |
| Price Volatility Sensitivity | High | Low |
| Risk Level | High | Low |
| Theta Decay | Fast | Slow |
| Ideal Audience | Day/Short-Term Traders | Long-Term Investors |
| Liquidity | Lower | Higher |
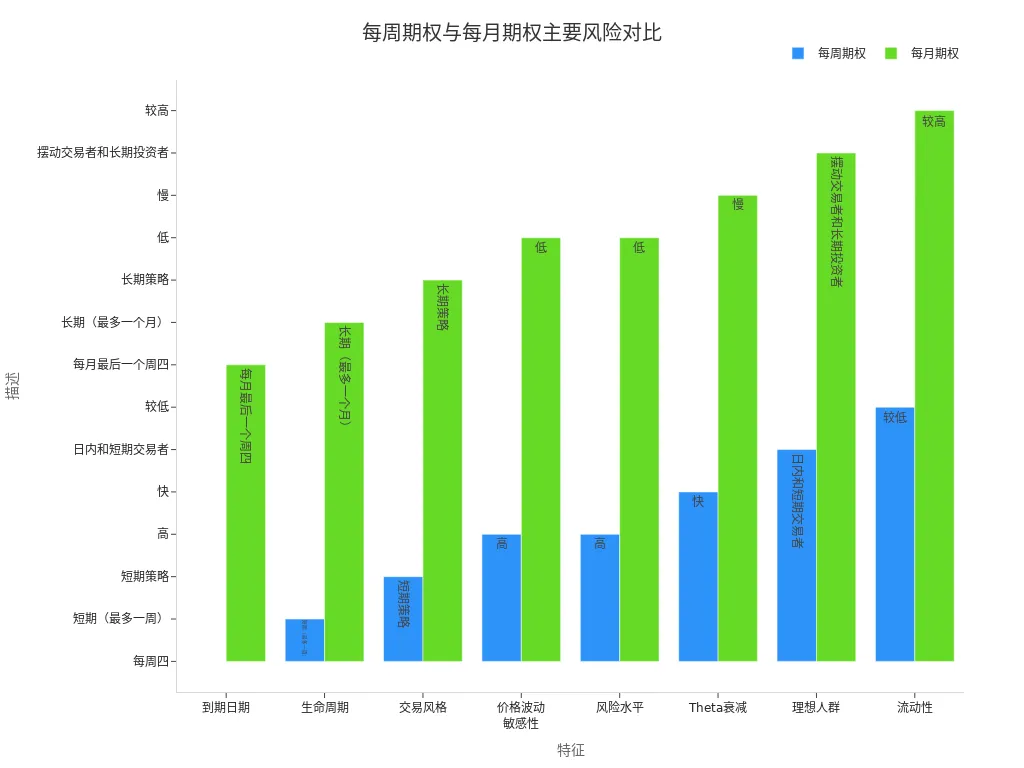
You also need to pay attention to transaction costs. Due to frequent trading, weekly options incur higher commission expenses. For example, monthly options require only one commission, while weekly options may require four commissions per month (in USD). When formulating your investment strategy analysis, you should balance returns and costs, allocating capital reasonably.
Monthly Options Investment Strategy Analysis
Definition and Characteristics
In your investment strategy analysis, you will find that monthly options are standardized options, typically expiring on the last business day of the month. These options are quoted in decimals, with minimum trading units of 0.05 ($5.00) or 0.10 ($10.00), depending on the option price. Monthly options have high liquidity due to their use by a broader range of market participants. You can refer to the table below for a quick overview of the main characteristics of monthly options:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Expiration Date | Expires on the last business day of the month, suitable for asset managers and fund cycles |
| Option Quotation | Quoted in decimals, minimum trading unit of 0.05 ($5.00) or 0.10 ($10.00) |
| Liquidity | High liquidity, diverse market participants |
Monthly options typically expire on the third Friday of the expiration month, providing you with a longer time frame, allowing greater strategic flexibility, including hedging and income-generating strategies.
Suitable Audience
If you prefer long-term holding and stable returns, monthly options are more suitable for your investment strategy analysis. Asset managers, institutional investors, and individuals seeking consistent income through options tend to choose monthly options. You can use monthly options for asset allocation, aligning with fund cycles, or generating stable premium income by selling options.
Long-Term Advantages
Monthly options offer several long-term advantages. You can achieve predictable income streams, reducing reliance on savings and helping manage immediate expenses and long-term financial goals. Monthly options have a lower time decay rate, providing more decision-making time, giving you ample opportunity to adjust your investment strategy analysis. You can diversify holdings to reduce the impact of single market fluctuations, enhancing overall portfolio stability.
- Provides predictable income streams
- Reduces reliance on savings
- Helps manage immediate expenses and long-term financial goals
- Lower time decay rate, offering greater decision-making space
Holding Risks
When holding monthly options, you need to monitor market fluctuations and price changes. Although monthly options have high liquidity, their premiums are higher, and if market trends deviate from expectations, you may face significant losses. You need to regularly evaluate holdings, allocate capital reasonably, and avoid risk concentration due to single events. Monthly options are suitable for investors with lower risk tolerance, but you must remain vigilant and adjust your investment strategy analysis promptly to respond to market changes.
Comparative Analysis

Image Source: pexels
Returns and Risks
When choosing between weekly and monthly options, you first need to focus on the differences in returns and risks. Weekly options, due to their short expiration periods, have lower premium costs, typically ranging from $0.50 to $2.00. You can participate in trading with less capital, requiring only 25-40% of the capital needed for monthly options. The high-frequency trading opportunities of weekly options allow you to quickly capture short-term market fluctuations, especially suitable for leveraging price changes from specific events (such as earnings releases). For example, in the U.S. market, weekly options are the preferred tool for investors capturing short-term fluctuations before Amazon’s earnings releases.
Monthly options have higher premium costs, typically ranging from $2.00 to $5.00. You need to invest more capital but can gain a longer holding period and more stable returns. Monthly options have lower time decay risks, making them suitable for long-term strategies. You can diversify holdings to reduce the impact of single market events on your portfolio. Academic research shows that weekly implied variance outperforms monthly implied variance in predicting weekly realized variance, indicating that weekly options have an advantage in short-term volatility prediction but carry higher risks.
Tip: Weekly options are suitable for those with high risk appetite, pursuing short-term high returns; monthly options are suitable for conservative investors focused on long-term capital preservation.
Liquidity
In actual trading, you will find that liquidity directly affects the efficiency and transaction costs of options trading. Weekly options typically have high trading volumes, especially for the most actively traded stocks in the U.S. market, with weekly options expiring every week and high market participation. The bid-ask spread for weekly options ranges from $0.05 to $0.15, slightly higher than monthly options. Monthly options have bid-ask spreads of $0.02 to $0.10, offering stronger liquidity and lower transaction costs. The table below compares the liquidity characteristics of the two:
| Feature | Weekly Options | Monthly Options |
|---|---|---|
| Premium Cost | $0.50 – $2.00 | $2.00 – $5.00 |
| Capital Required | Less than 25-40% | Standard Amount |
| Transaction Fees | Higher per trade | Lower per trade |
| Bid-Ask Spread | $0.05 – $0.15 | $0.02 – $0.10 |
If a stock lacks weekly options, it usually indicates low market interest in that stock, resulting in thin options trading. When selecting underlying assets, you should prioritize stocks or indices with high trading volumes to ensure sufficient liquidity and lower transaction costs.
Investment Scenarios
When formulating investment strategies, you should choose the appropriate option type based on different market conditions. Weekly options are suitable for the following scenarios:
- You want to capitalize on short-term price fluctuations caused by specific events (such as earnings releases or policy changes).
- You prefer short-term strategies, quickly adjusting positions to capture short-term market opportunities.
- You focus on lower option premiums, pursuing cost efficiency.
Monthly options are more suitable for the following scenarios:
- You pursue long-term stable returns, focusing on capital preservation.
- You need higher liquidity and lower time decay risks.
- You aim to diversify holdings to reduce the impact of single events on your portfolio.
For example, financial advisors in the U.S. market typically recommend using weekly options during earnings release weeks to capture short-term fluctuations, while recommending monthly options for annual or quarterly asset allocation to achieve long-term return goals.
Selection Recommendations
When choosing between weekly and monthly options, you should comprehensively consider the following factors:
- Your investment goals: Short-term high returns or long-term steady growth.
- Your risk tolerance: Whether you can handle high volatility and rapid changes.
- Your capital size: Weekly options require less capital, while monthly options require more investment.
- Your trading experience: Short-term traders are advised to collaborate with experienced professionals to reduce risks.
- Your market judgment: Adjust trading strategies based on market volatility to maximize returns.
Professional Advice: When selecting expiration dates, you need to estimate the time point when your strategy is most likely to be profitable. Weekly options offer up to 52 expiration dates per year, providing abundant trading opportunities, but you should also focus on transaction costs and risk management. Monthly options are suitable for long-term planning, reducing the pressure from frequent trading.
You can flexibly choose weekly or monthly options based on your needs, market conditions, and investment goals to enhance the overall performance of your portfolio.
When choosing between weekly and monthly options, you should make rational decisions based on your capital situation, risk appetite, and investment goals. The table below summarizes the main advantages and disadvantages of the two types of options:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Weekly Options | High flexibility, low premiums, fast time decay | High gamma risk, short lifecycle, lower liquidity |
| Monthly Options | Stable price fluctuations, lower risk, good liquidity | High premiums, slow time decay, less flexibility |
- Clarify investment goals, matching capital and risk tolerance
- Choose the option type that suits your management effort and return expectations
- Continuously monitor the market, adjust strategies promptly, and enhance investment efficiency
FAQ
Can weekly and monthly options be invested in simultaneously?
You can invest in both weekly and monthly options simultaneously. This approach can diversify risks, enhancing the flexibility and stability of your portfolio.
Are the transaction costs for weekly options high?
Weekly options have high trading frequency, leading to higher commission expenses. You need to monitor the fees for each trade and control total costs reasonably.
Are monthly options suitable for short-term trading?
Monthly options have a long holding period, making them suitable for long-term strategies. If you pursue short-term returns, weekly options are more appropriate.
How can I assess the liquidity of weekly or monthly options?
You can check the option’s trading volume and bid-ask spread. Options with high trading volume and narrow bid-ask spreads have better liquidity.
What risks should I be aware of when investing in weekly and monthly options?
You need to focus on market volatility, time value decay, and transaction costs. Allocating capital reasonably and adjusting strategies promptly can help reduce risks.
Whether you lean towards the rapid profit potential of weekly options or the stability offered by monthly options, your ability to execute trades swiftly and manage funding costs directly impacts your success. High-frequency options trading demands exceptional capital mobility, while monthly options require substantial upfront premium management.
To overcome these challenges, consider integrating BiyaPay into your trading toolkit. We offer zero commission for contract limit orders, a crucial advantage that significantly cuts down the execution costs for both periodic short-term strategies and long-term option hedges.
Our platform supports rapid conversion between fiat and digital assets like USDT, ensuring your capital is swiftly and efficiently deployed to meet margin requirements. You can register quickly—in just 3 minutes without needing a foreign bank account—and access US and Hong Kong Stocks to diversify your underlying option assets. Use our real-time exchange rate checks to minimize currency risk and ensure every options trade is managed with maximum cost-effectiveness. Open your account today and gain the financial agility your sophisticated options strategies deserve.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















