- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Low-Priced Stocks Investment Guide: A Market Arena of Opportunities and Pitfalls

Image Source: pexels
When considering a low-priced stock investment guide, you need to fully recognize the high volatility and high risks of low-priced stocks. You should focus on the company’s fundamentals, analyze liquidity, and observe market sentiment. If you cannot tolerate sharp price fluctuations or risks arising from information opacity, you should carefully select your investment targets. Rational analysis and effective risk management can help you make more informed decisions in complex markets.
Key Points
- Low-priced stocks have high volatility and high risks, so you need to assess your own risk tolerance before investing.
- Focus on the company’s fundamentals and financial metrics, such as price-to-earnings ratio and price-to-book ratio, to help determine whether a stock is undervalued.
- Market sentiment and macroeconomic changes can affect the performance of low-priced stocks, requiring timely adjustments to your investment strategy.
- Establish risk control strategies and set stop-loss points to avoid significant losses due to market fluctuations.
- Diversify investments across different assets and industries to reduce the risk of a single investment and enhance overall return potential.
Definition and Current State
Low-Priced Stock Criteria
When learning about low-priced stocks, you first need to understand their definition. Low-priced stocks typically refer to stocks with a lower per-share price, but the specific criteria vary by market. Many investors are easily influenced by nominal prices, believing that low-priced stocks are cheaper and have greater potential. You can refer to the following points to understand the reasons behind the formation of low-priced stocks:
- Individual investors prefer low-priced stocks, while institutional investors tend to favor high-priced stocks.
- Listed companies maintain stock prices within a reasonable range to attract small investors.
- Low-priced stocks are more likely to attract noise traders, enhancing market liquidity.
These phenomena indicate that low-priced stocks are not just about low prices but also reflect investment styles and market structures.
Market Distribution
When analyzing low-priced stocks, you can find that they are widely distributed in the Chinese mainland market. Many emerging companies have lower stock prices due to limited financial history. You can refer to the table below to understand the market characteristics of low-priced stocks:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Volatility | Daily price fluctuations of 5% to 20% |
| Trading Volume | Average daily volume of 100,000 to 500,000 shares |
| Reporting Requirements | Fewer compared to major exchanges |
| Bid-Ask Spread | Typically between 5% and 15% |
These data indicate that low-priced stocks have lower trading activity and information transparency, requiring extra attention to liquidity and risks during investment.
Characteristics
When studying the low-priced stock investment guide, you will find that low-priced stocks have unique market characteristics. Recently, industry disclosure guidelines require specific industry companies to provide more detailed information, enhancing transparency and reducing price synchronicity. Nasdaq has also adjusted its listing standards, raising minimum liquidity requirements, accelerating the delisting process for low-market-cap companies. These changes help curb market manipulation and protect investor interests.
When selecting low-priced stocks, you must pay attention to company disclosures and changes in market regulations to help you avoid potential risks.
Low-Priced Stock Investment Guide: Opportunity Analysis

Image Source: unsplash
High Return Potential
When learning the low-priced stock investment guide, you will find that low-priced stocks are often undervalued due to market sentiment or short-term events. Many investors believe low-priced stocks are risky, but in fact, some low-priced stocks have extremely high return potential. In the U.S. market, many successful investment cases stem from in-depth analysis and long-term holding of low-priced stocks. For example, Magellan Fund achieved an average annual growth rate of 15.87% through quantitative screening and fundamental analysis. Berkshire Hathaway focused on acquiring undervalued companies, with its stock price growing from $19 per share to over $600,000. You can refer to the table below to understand the strategies and results of these investment cases:
| Investment Case | Strategy Description | Result Description |
|---|---|---|
| Magellan Fund | Seek high-quality growth stocks using quantitative screening and fundamental analysis. | Since its inception in 1963, it achieved an average annual growth rate of 15.87%, with a cumulative return of 813,364%. |
| Berkshire Hathaway | Acquire undervalued companies, focusing on strong fundamentals and growth potential. | Stock price grew from $19 per share in 1965 to over $600,000 recently, demonstrating the success of long-term value investing. |
| Sequoia Fund | Focus on concentrated value investment strategies in domestic mid- and large-cap companies. | From 1986 to 2024, it achieved a return of 5,163% (annualized 11.14%), surpassing the S&P 500’s 4,654% (annualized 10.84%). |
| The Prudent Speculator | Invest in undervalued stocks through broad diversification, adopting a “buy low, sell high” strategy. | Evolved from a small newsletter into a wealth management firm managing nearly $1 billion, maintaining a value-oriented investment foundation. |
When analyzing low-priced stocks, you can combine metrics such as price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, dividend yield, and price-to-earnings growth ratio to determine whether a stock is undervalued. The table below shows common triggers for undervaluation:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E) | Compares stock price to the company’s actual profits; a lower P/E suggests the stock may be undervalued. |
| Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B) | Compares stock price to the company’s total asset value; a P/B between 0 and 1 may indicate the company is undervalued. |
| Dividend Yield | The ratio of a company’s annual dividend to its current stock price; a higher ratio may suggest undervaluation, but beware of risks from falling stock prices. |
| Price-to-Earnings Growth Ratio (PEG) | Considers the company’s future earnings potential; a PEG below 1 typically indicates the stock is undervalued. |
In practice, you can use these metrics to screen for low-priced stocks with high return potential, increasing your investment success rate.
Market Sentiment Impact
When using the low-priced stock investment guide, you need to pay attention to the impact of market sentiment on low-priced stocks. Market sentiment fluctuations can lead to sharp price changes in low-priced stocks. Short-term events, news reports, or macroeconomic changes can trigger investor panic or optimism, affecting stock prices. You can observe that rising interest rates increase borrowing costs, making expansion and investment more expensive, which may pressure low-priced stock performance. In a high-inflation environment, companies with thin profit margins struggle to raise prices, increasing pressure on low-priced stocks. During economic growth, increased consumer spending may boost low-priced stock performance; during recessions, their risks increase.
- Rising interest rates increase borrowing costs, affecting company expansion and investment.
- In a high-inflation environment, companies with thin profit margins struggle to raise prices, increasing pressure on low-priced stocks.
- Economic growth helps improve company profitability, benefiting low-priced stocks; recessions increase their risks.
When investing in low-priced stocks, you need to closely monitor macroeconomic changes and market sentiment, adjusting your investment strategy in a timely manner.
Industry and Growth Potential
When selecting low-priced stocks, you can analyze industry development and company growth potential. Some industries have a high concentration of low-priced stocks with strong growth potential. In the U.S. market, the technology sector is characterized by innovative products and services, offering significant return potential. The healthcare sector is similarly driven by innovation, attracting investor attention. Modular construction, as an emerging industry, shows strong growth potential, suitable for investors seeking low-priced stocks.
- Technology Sector: Innovative products and services align with market trends, offering significant return potential.
- Healthcare Sector: Driven by innovation, attracting investor attention.
- Modular Construction: An emerging industry with strong growth potential.
When applying the low-priced stock investment guide, you can prioritize these industries, combining company fundamentals, industry position, and growth potential to screen for quality low-priced stocks. This approach can increase your investment success rate and reduce risks.
Risks and Pitfalls
Image Source: unsplash
Volatility and Liquidity Risks
When focusing on low-priced stocks, you first need to address their extremely high price volatility and liquidity risks. Low-priced stocks can experience sharp daily price changes, far exceeding those of mid- and high-priced stocks. The table below shows the average daily volatility of some low-priced and high-priced stocks in the U.S. market:
| Stock Ticker | Company Name | Average Daily Volatility % | Average Daily Volatility $ |
|---|---|---|---|
| HOOD | Robinhood Markets Inc. | 5.42% | $4.94 |
| PLTR | Palantir Technologies Inc. | 4.33% | $6.63 |
| AMD | Advanced Micro Devices Inc. | 3.48% | $4.95 |
| TSLA | Tesla Inc. | 3.55% | $12.79 |
| NVDA | NVIDIA Corporation | 2.52% | $4.22 |
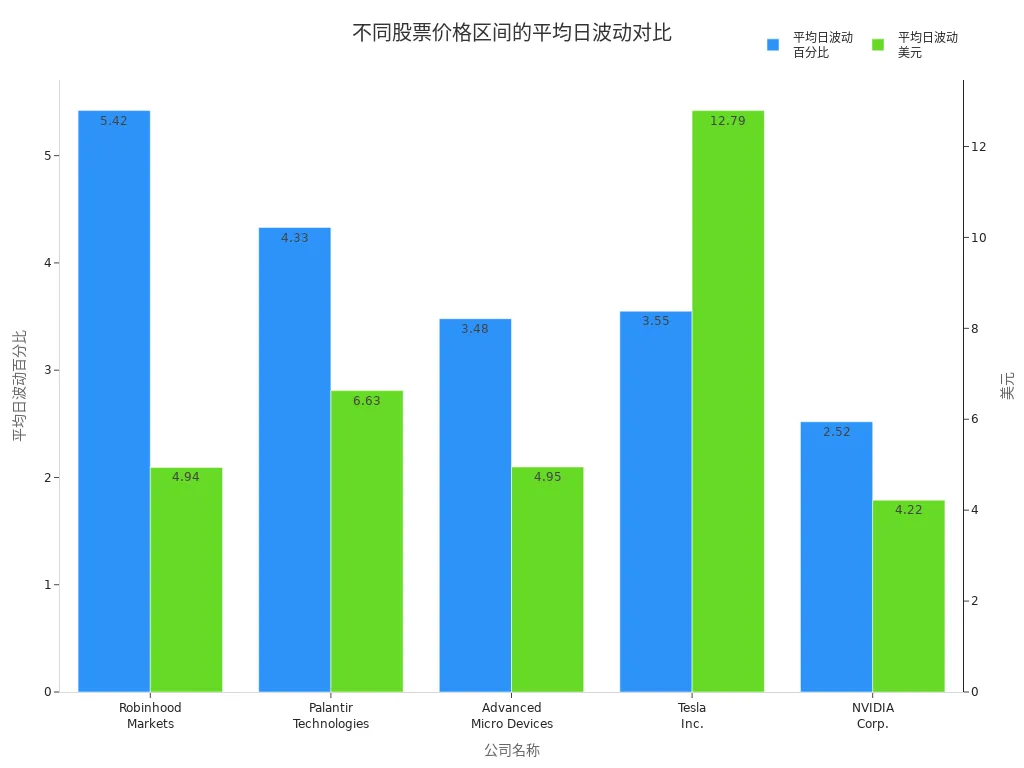
You can see that low-priced stocks have significantly higher volatility than high-priced stocks. Liquidity risks are particularly pronounced during market stress periods. Historically, the U.S. market has experienced liquidity dry-ups multiple times:
- During the 1987 stock market crash, investors suffered significant losses as low-priced stock liquidity rapidly disappeared, accelerating price declines.
- In 1998, during the Long-Term Capital Management collapse, leveraged investors’ sell-offs exacerbated asset price declines, impairing market functionality.
- In the 2008 financial crisis, market makers’ capacity was overwhelmed, causing sharp price drops in low-priced stocks.
In the low-priced stock investment guide, you should pay special attention to liquidity risks. Studies show that stocks with higher liquidity risks experience larger price drops during financial crises. You need to be cautious, as low-priced stocks may be difficult to sell during market turmoil, leading to amplified losses.
When investing in low-priced stocks, you must assess trading volume and bid-ask spreads to avoid significant losses during liquidity dry-ups.
Fundamental Deterioration
When selecting low-priced stocks, you must pay attention to changes in the company’s fundamentals. Many low-priced stock companies have unstable financial conditions, making their performance prone to deterioration. Data shows that approximately 25% of low-priced stocks experience significant fundamental deterioration within a year, considered “trap stocks” by the market. The table below shows related statistics:
| Statistic | Description |
|---|---|
| 25% | Half of the market’s value stocks are considered traps within a year. |
You may encounter the following issues:
- The company’s profitability continues to decline, leading to prolonged stock price stagnation.
- The balance sheet deteriorates, with increasing debt pressure.
- Negative operating cash flow makes it difficult to sustain normal operations.
In the low-priced stock investment guide, you should regularly track the company’s financial reports, focusing on key metrics such as profitability, debt, and cash flow. Many investors make the mistake of holding losing stocks for too long, neglecting to rebalance their portfolios or making decisions without a financial plan. These behaviors increase the risk of losses.
You must stay rational, cut losses in a timely manner, and avoid long-term losses due to deteriorating performance.
Delisting Risk
When investing in low-priced stocks, you also need to be wary of delisting risks. In the U.S. market, low-priced stocks face the possibility of being forcibly delisted by exchanges due to sustained stock prices below $1 per share, corporate governance issues, or abnormal financial reports. The following are common delisting warning signals:
- Stock price plummets, falling below $1 per share.
- The company announces privatization, voluntarily delisting.
- Multiple reverse stock splits, indicating operational difficulties.
- Abnormal financial ratios, with continuous reporting issues.
- Large-scale sell-offs by institutional investors.
- Corporate governance violations, facing regulatory penalties.
- The company ignores exchange warnings.
In the low-priced stock investment guide, you should closely monitor these signals. After delisting, stocks may become untradeable on mainstream platforms, further reducing liquidity and making it difficult for investors to recover losses.
You should regularly check company announcements and exchange warnings, adjusting your investment strategy in a timely manner to avoid delisting risks.
Market Manipulation
In the low-priced stock market, you also need to guard against market manipulation. Due to their smaller market capitalization and limited trading volume, low-priced stocks are more susceptible to manipulation. Regulatory reports indicate that the following phenomena are common in manipulated low-priced stocks:
- Abnormal price fluctuations: Sudden surges or drops in stock prices without news or fundamental support.
- Abnormal trading volume: Trading volume spikes, far exceeding the average daily level by 200-300%.
- Coordinated trading patterns: Multiple accounts placing identical orders simultaneously, indicating manipulative behavior.
When investing, you should be vigilant about these signals. Many investors fall into traps set by manipulators due to overconfidence or following market sentiment. Panic selling and blind trend-following are common mistakes.
You should maintain independent judgment, combining company fundamentals and market regulatory information to avoid becoming a victim of market manipulation.
Identifying Quality Stocks
Financial Metrics
When screening for quality low-priced stocks, you can focus on several key financial metrics. The price-to-earnings ratio (P/E Ratio) can help you determine whether a company is undervalued. If the P/E ratio is below the industry average, the company may present an investment opportunity. The price-to-book ratio (P/B Ratio) reflects the relationship between the stock price and book value. A P/B below 1 typically indicates that the company’s asset value exceeds its market pricing. The debt-to-equity ratio (D/E Ratio) shows the company’s debt level. A lower D/E ratio indicates a more stable financial position. Companies with positive free cash flow (FCF) have surplus cash after paying operational and investment expenses. Profitability growth and stability are also important. You can prioritize companies with sustained profit growth that is not yet reflected in their stock prices.
- P/E ratio below industry average
- P/B ratio below 1
- Low debt-to-equity ratio
- Positive free cash flow
- Sustained and stable profit growth
These metrics can help you initially screen for low-priced stocks with strong financial health.
Industry Position
When analyzing a company’s industry position, you can focus on its competitiveness within the sector. Industry-leading companies typically have stronger market share and brand influence. You can evaluate a company’s growth potential through its industry ranking, market share changes, and innovation capabilities. In the U.S. market, leading companies in the technology and healthcare sectors often exhibit higher growth potential. You can review industry reports to understand a company’s performance in its niche. If a company holds a leading position in its industry, it has greater future development potential and a higher likelihood of stock price appreciation.
You can prioritize industry leaders or companies with innovative capabilities to enhance investment safety and return potential.
Corporate Governance
When evaluating quality low-priced stocks, you cannot overlook the corporate governance structure. Good corporate governance helps enhance stock price stability. The table below shows the impact of governance factors on company performance:
| Influencing Factor | Result Description |
|---|---|
| Board Governance | Shows a significant positive correlation with stock price stability. |
| Information Disclosure | Positively contributes to stock price stability, with financing constraints playing a partial mediating role. |
| Shareholder Structure | The impact of information disclosure on stock price stability varies significantly across companies with different ownership structures and financial conditions. |
| High-Tech Companies | The positive impact of board governance on stock prices is more pronounced in high-tech companies. |
| Institutional Ownership Ratio | The impact of board governance on stock prices is more significant in companies with higher institutional ownership. |
You can assess a company’s long-term stability by reviewing its annual reports, governance structure, and disclosure practices. A strong governance structure helps companies navigate market changes and protect investor interests.
Investment Recommendations
Risk Control
When investing in low-priced stocks, you need to establish clear risk control strategies. You can set a maximum loss ratio to ensure each investment does not jeopardize your overall financial safety. You should monitor the company’s financial condition and market fluctuations, adjusting your holdings in a timely manner. You can use stop-loss orders to automatically sell when the price falls to a preset point, reducing losses. You should regularly review your investment decisions to avoid emotional trading. In the U.S. market, many investors limit single investment losses to within 10%.
Remember that risk control is key to protecting your capital. Only with controlled risks can you pursue long-term stable returns.
Capital Management
When allocating investment capital, you should prioritize capital preservation. You can diversify your funds across different ETFs to reduce overall volatility. You can adopt linear programming methods, prioritizing low-volatility ETFs and avoiding high-risk products. You can also diversify risks further by investing in international markets. In practice, you can refer to the following capital management recommendations:
- Protect initial investments to avoid significant losses.
- Diversify investments across different ETFs and international markets.
- Prioritize low-risk ETFs, reducing the proportion of high-volatility products.
- Regularly adjust your portfolio to maintain capital safety.
You should remain cautious in capital management, allocating funds rationally to achieve capital preservation and moderate returns in low-priced stock investments.
Diversification and Stop-Loss
When building your investment portfolio, you can reduce risks through diversification. You can allocate funds to different asset classes, industries, and regions to minimize the impact of underperforming single assets. You can use stop-loss orders to automatically sell during market fluctuations, protecting your capital. Diversification also helps you capture global growth opportunities, enhancing overall returns. You can refer to diversification strategies in the U.S. market, where many investors allocate across technology, healthcare, consumer goods, and other sectors.
- Diversification reduces overall risk and volatility.
- Stop-loss orders protect capital and avoid significant losses.
- Multi-industry and multi-region allocations capture growth opportunities.
You should adhere to the principles of diversification and stop-loss to effectively control risks and achieve steady growth in low-priced stock investments.
Suitable Investors
Risk Tolerance
When considering investing in low-priced stocks, you need to have a high risk tolerance. Low-priced stocks experience significant price fluctuations, which may lead to substantial losses. You must be able to accept the unpredictability and sharp price changes during the investment process. Risk tolerance determines how much volatility and loss you are willing to endure to pursue higher returns. Many investors choose low-priced stocks because they can tolerate high risks and aim for higher returns. If you prefer stable and safe investments, low-priced stocks may not be suitable for you.
- You need to accept the possibility of sharp price fluctuations.
- You must be mentally prepared to face potential significant losses.
- You are suitable for low-priced stock investments if you are willing to take high risks for high returns.
Experience Requirements
When trading low-priced stocks, experience is crucial. Low-priced stocks are often traded in over-the-counter markets with low information transparency and poor liquidity. You need to master chart pattern analysis, as traditional analysis methods may not apply. You should have substantial practical experience to identify price manipulation and fraudulent behavior. The trading environment for low-priced stocks is complex, and only experienced investors can effectively manage various risks. If you are new to investing, it is advisable to learn the basics and gain practical experience before considering low-priced stock investments.
- You need to understand chart patterns and market behavior.
- You must have the ability to address price manipulation and fraud.
- You are suitable for low-priced stock investments if you have extensive trading experience and market analysis skills.
Investment Horizon
When choosing to invest in low-priced stocks, the investment horizon is also important. The time span of your investment affects your risk and return. A longer investment horizon allows you to tolerate more risks and achieve higher potential returns. Short-term investors prefer safer assets, as market downturns require quick liquidation, increasing loss risks. If you have a longer investment horizon, your portfolio has more time to recover from fluctuations. The table below shows the impact of investment horizon on risk and return:
| Investment Horizon | Risk Level | Return Potential | Suitable Investors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-Term (Within 1 Year) | Low | Low | Conservative Investors |
| Medium-Term (1-5 Years) | Medium | Medium | Balanced Investors |
| Long-Term (Over 5 Years) | High | High | Aggressive Investors |
You can choose an appropriate investment horizon based on your investment goals and time availability. If you have long-term plans, low-priced stocks may be more suitable, as you have more time to navigate market fluctuations and achieve compound growth.
In low-priced stock investments, you will encounter various opportunities and risks. Recent studies indicate that a slowing labor market, uneven corporate earnings, and rising inflationary pressures may increase investment challenges, but valuation resets in the technology sector and better-than-expected earnings from some companies also present new opportunities. Professional analysts recommend that you can balance risk and return through diversified asset allocation. You should combine your risk tolerance and investment goals, analyze rationally, participate cautiously in low-priced stock investments, and continuously improve your market analysis skills.
FAQ
What are the main risks of investing in low-priced stocks?
You will encounter risks such as high volatility, poor liquidity, and information opacity. Some companies may face delisting or performance deterioration. You should closely monitor company announcements and financial conditions.
You can identify risk signals in a timely manner by reviewing company annual reports and market reports.
How to determine if a low-priced stock is undervalued?
You can analyze metrics such as price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, and PEG. A lower P/E and P/B may indicate undervaluation. You should combine the company’s profitability and industry position for a comprehensive judgment.
| Metric | Reference Value |
|---|---|
| Price-to-Earnings Ratio | Below industry average |
| Price-to-Book Ratio | Below 1 |
| PEG | Below 1 |
What experience is required for investing in low-priced stocks?
You need to master fundamental analysis and chart pattern recognition. You must have the ability to identify price manipulation and abnormal trading. Extensive market experience can help you avoid common pitfalls.
- You can read more investment books.
- You can practice with simulated trading.
Are low-priced stocks suitable for long-term holding?
You can hold some quality low-priced stocks long-term but should regularly review their performance. Long-term holding can mitigate short-term fluctuations, but the company’s fundamentals must continue to improve. You should set stop-loss points to protect your capital.
You should choose a holding period based on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
How to diversify risks in low-priced stock investments?
You can allocate funds across different industries and regions. You can choose U.S. market ETFs or diversified stock portfolios. Diversification can reduce losses caused by the volatility of a single asset.
- You can regularly adjust your portfolio.
- You can focus on global market opportunities.
By mastering the low-price stock investment guide, you’ve learned to spot high-return potential while dodging high-volatility traps, but high cross-border fees, currency volatility, and offshore account complexities can limit seizing U.S. penny stock opportunities, especially for swift responses to market sentiment or portfolio tweaks. Imagine a platform with 0.5% remittance fees, same-day global transfers, and contract limit orders with zero fees, enabling seamless low-price stock strategies via one account?
BiyaPay is tailored for penny stock investors, offering instant fiat-to-digital conversions to act on market signals nimbly. With real-time exchange rate query, monitor USD trends and transfer at optimal moments to cut costs. Covering most regions with instant arrivals, it powers rapid allocations to S&P 600 SmallCap ETFs (like IJR) or high-potential penny stocks. Crucially, trade U.S. and Hong Kong markets through a single account, leveraging contract limit orders with zero fees for P/E or P/B-based limit strategies.
Whether chasing undervaluation plays or mitigating liquidity risks, BiyaPay fuels your precision. Sign up now, visit stocks for U.S. prospects—quick setup unlocks cost-effective, data-driven investing. Join global investors and profit in 2025’s market swings!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















