- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
What is Investing? Core Concepts and Practical Guide for Investors

Image Source: pexels
You often hear the word “investment,” but do you know how it differs from saving, spending, or speculation? Investment involves putting money into assets with intrinsic value, hoping to generate future cash flow or asset appreciation. Saving focuses more on safety, typically depositing money into low-interest accounts. Speculation involves high risk in pursuit of short-term gains from price fluctuations. See the table below:
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Saving | Safely storing money for future use, typically in low-interest accounts. |
| Investment | Allocating capital to assets with intrinsic value to generate cash flow or appreciation. |
| Speculation | Betting on significant asset appreciation, often influenced by market behavior rather than intrinsic value. |
You need to focus on the core concepts of investment, such as risk and return, asset allocation, and investment strategies, which are crucial foundations for achieving wealth growth.
Key Takeaways
- Investment differs from saving and speculation. Investment focuses on the intrinsic value of assets, aiming to achieve wealth appreciation.
- Understand the relationship between risk and return. High returns often come with high risks, so choose assets that match your risk tolerance.
- Asset allocation is a key strategy for reducing risk. Spreading funds across different asset types can improve long-term returns.
- The compound interest effect is a powerful tool in investing. The earlier you start investing, the more pronounced the effect of compounding, making time your best friend.
- Regularly evaluate and rebalance your portfolio. Staying aligned with market changes and personal goals ensures the effectiveness of your investment strategy.
Investment Definition

Image Source: pexels
Purpose of Investment
The core purpose of your investment is to achieve wealth appreciation and secure future financial needs. Investing is not just about making money “grow” but also about preparing for significant life goals. Many financial institutions believe that the essence of investment lies in capital raising and advisory services, helping individuals and businesses achieve effective capital allocation. See the table below:
| Definition | Core Purpose |
|---|---|
| Investment banking involves providing merger and acquisition advice and various capital-raising strategies. | Capital raising and advisory services |
| Corporate financing transactions involve helping clients raise funds in capital markets and providing merger and acquisition advice. | Capital raising and advisory services |
You can see that investment serves not only individuals but also provides funding support and professional advice for businesses and institutions.
Difference Between Investment and Speculation
You need to clearly distinguish between investment and speculation. Investment focuses on economic fundamentals, emphasizing the intrinsic value of assets. You typically opt for long-term holding with measurable risks. Speculation focuses more on short-term price fluctuations, with shorter operation cycles and higher risks and uncertainties. Common differences include:
- Investment focuses on economic fundamentals, while speculation focuses on price fluctuations.
- Investment typically has a longer time horizon, while speculation leans toward short-term operations.
- Investment risks are generally measurable, while speculation comes with greater uncertainty and potential losses.
When making decisions, you should clarify whether your actions are investment or speculation, which helps you manage risks and expectations.
Investment Goals
Your investment goals can vary widely. Common goals for individual investors include:
- Personal wealth accumulation
- Retirement savings
- Education funding
- Purchasing a car or house
- Starting a business
- Leaving a legacy
Institutional investors may focus on:
- Achieving specific investment return targets
- Managing pension, endowment, or insurance fund portfolios
- Maintaining purchasing power
Different asset classes suit different goals. For example, cash is suitable for short-term goals like buying a house or education expenses; stocks are suitable for long-term growth, and young investors can allocate more to stocks; bonds are suitable for investors with lower risk tolerance nearing major financial goals, offering stable income and lower volatility. You should set clear investment goals based on your needs and risk tolerance.
Core Investment Concepts
To become an excellent investor, you must understand the core concepts of investment. These concepts help you make informed decisions in practice. Below, I will explain each key point in detail.
Risk and Return
When investing, you always face a trade-off between risk and return. High returns typically come with high risks, while low risks mean limited returns. You can understand the risk-return relationship of different assets through the following points:
- Stocks generally offer higher returns but come with greater volatility and risk.
- Bonds typically provide lower returns with less volatility, acting as a stabilizing force in a diversified portfolio.
- Real estate returns and risks vary depending on market conditions and specific investments.
You can refer to the table below to understand the average annual returns in the U.S. market over different periods:
| Period | Average Annual Return |
|---|---|
| Past 10 years | 11.01% |
| Past 20 years | 8.87% |
| Past 30 years | 9.33% |
| Past 40 years | 9.83% |
| Since 1928 | 8.55% |
| Since 1957 | 8.00% |
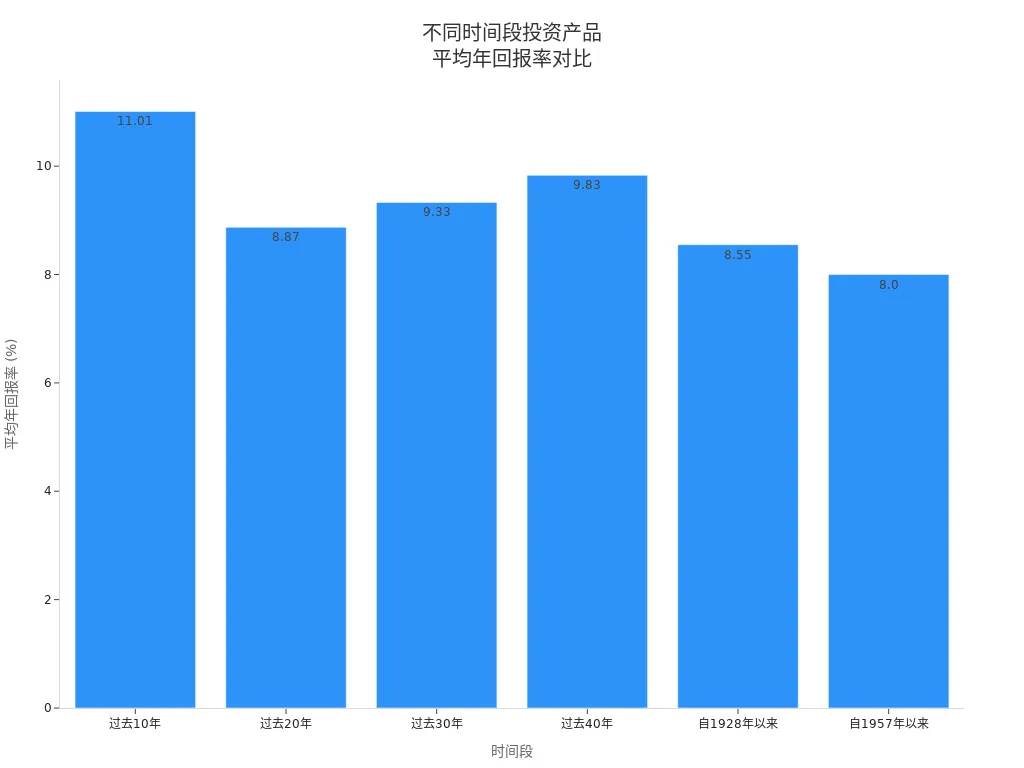
You need to choose the appropriate asset type based on your risk tolerance. One of the core investment concepts is learning to balance risk and return.
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is one of the core investment concepts. You need to spread your funds across different types and risk levels of financial assets. This can reduce overall risk and improve long-term returns. Academic research shows that asset allocation significantly contributes to a portfolio’s long-term returns. See the table below:
| Evidence Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Contribution of asset allocation to time-series returns | Approximately 75%, lower than other institutional investors. |
| Contribution of asset allocation to cross-sectional performance | On average, only about 10%, significantly lower than other institutional environments. |
| Similarity of passive risk | Passive return levels of university endowments are similar, indicating that active decisions are the main source of performance differences. |
You can choose from various asset allocation models:
- Strategic asset allocation: Setting an ideal asset mix and periodically rebalancing.
- Tactical asset allocation: Making short-term adjustments based on market conditions to seize opportunities or avoid risks.
- Dynamic asset allocation: Continuously adjusting the asset mix to respond to economic and market changes.
- Core-satellite approach: Combining passive and active investing, with the core being stable, low-cost investments and the satellite being investments seeking higher returns.
In practice, you can choose the appropriate asset allocation method based on your goals and market conditions. Asset allocation is a core investment concept that directly impacts your investment outcomes.
Investment Horizon
The investment horizon is a core investment concept you need to focus on. The longer the investment horizon, the more certain risks diminish. For example, historical data shows that the annualized standard deviation ratio of the HML factor decreases over time. See the table below:
| Investment Factor | One-Year Standard Deviation | Long-Term Standard Deviation | Risk Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOM | High | Low | Decreases |
| RMW | Low | High | Increases |
| HML | Medium | Low | Decreases |
| LIQ | Medium | High | Increases |
If you choose long-term investment, you can typically reduce certain risks and achieve more stable returns. The core investment concept requires you to set a reasonable investment horizon based on your goals.
Compound Interest Effect
The compound interest effect is the most fascinating part of the core investment concepts. The returns you earn each year generate new returns, creating a “snowball” effect. Compounding allows your investment to grow exponentially; the longer the time, the faster the growth. You can see the difference in total returns from starting investments at different ages in the table below:
| Scenario | Age to Start | Investment Amount | Total at Retirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 20 | $1,000 | $32,000 |
| 2 | 30 | $1,000 | $16,000 |
| 3 | 40 | $1,000 | $8,000 |
| 4 | 25 | $30,000 over 20 years | $160,300 |
| 5 | 45 | $30,000 over 20 years | $49,970 |
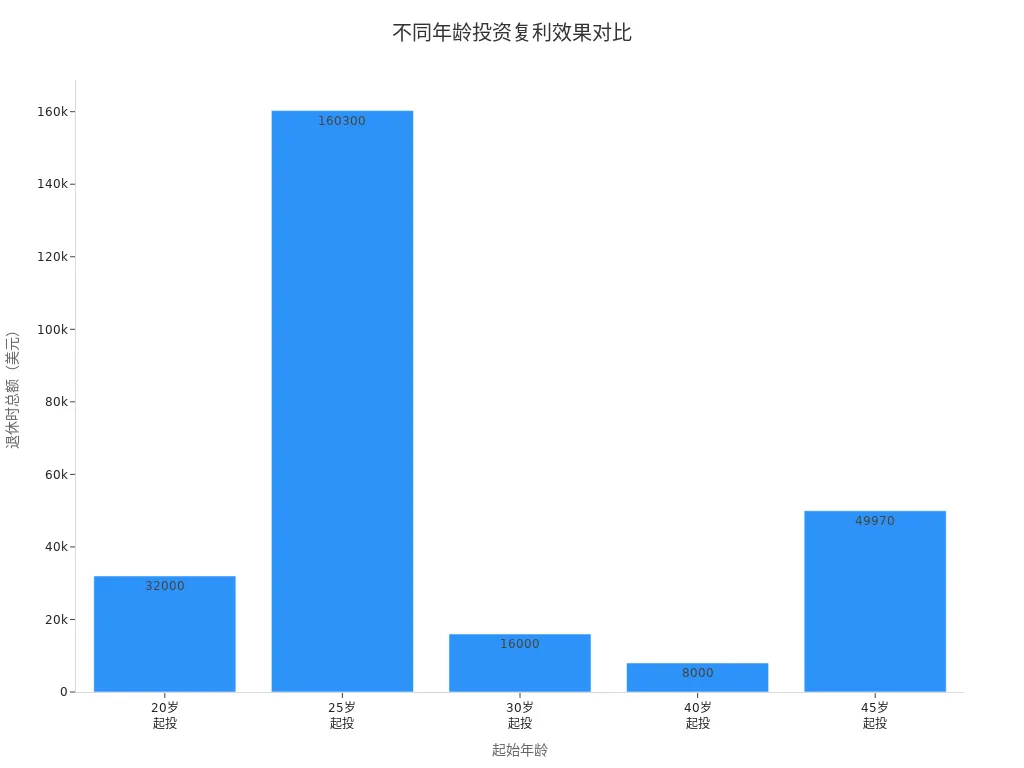
The earlier you start investing, the more pronounced the compound interest effect. The core investment concept reminds you that time is your best friend.
Diversification
Diversification is one of the core investment concepts. You can reduce specific risks by holding a variety of assets that are not perfectly correlated. Modern portfolio theory suggests that the lower the correlation coefficient, the better the diversification effect. If you hold only perfectly correlated assets, risk increases. Diversification can help you minimize losses during market downturns. See the table below:
| Portfolio Type | Pre-Crisis Performance | Post-Crisis Performance | Diversification Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cross-Asset Diversified Portfolio | High | High | Significant |
| Internationally Diversified Portfolio | Medium | Low | Reduced |
| S&P 500 Index | High | High | Significant |
Through diversification, you can make your portfolio more robust. The core investment concept emphasizes that diversification is a key method for reducing risk and achieving long-term goals.
Practical Guide

Image Source: unsplash
Risk Assessment
Before investing, you need to understand your risk tolerance. You can assess your risk preferences and investment goals by completing a risk tolerance questionnaire, investor profile questionnaires, or similar methods. Common approaches include:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Tolerance Questionnaire | Quantifying your risk tolerance through professional questionnaires. |
| Investment Risk Tolerance | Answering key questions to determine how much risk you can bear. |
| Investor Profile Questionnaire | For example, Schwab’s intelligent portfolio questionnaire helps you understand your investment style. |
| Personal Risk Tolerance Measurement | Combining your willingness and actual ability to comprehensively assess risk tolerance levels. |
You can combine these methods to find the investment direction that suits you.
Investment Strategies
You can choose active or passive investing. Active investing relies on the judgment of investment managers to pursue returns above the market average. Passive investing tracks market indices, with lower fees and risks. Performance in different market environments is as follows:
| Period | Active Investing Performance | Passive Investing Performance |
|---|---|---|
| 2000-2009 | 9/10 times | 1/10 times |
| 1990s | 5/10 times | 5/10 times |
| Past 35 years | 17 times | 18 times |
- Passive investing is suitable for long-term holding with low fees, ideal for most investors.
- Active investing sometimes performs better in small-cap or international markets but relies on manager expertise and carries higher risks.
Asset Allocation Case Study
You can enhance investment returns by optimizing asset allocation. Here is a practical case study:
| Portfolio Type | Initial Value (USD) | Value After 6 Months (USD) | Annualized Growth Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Original Portfolio | 100,000 | 102,135.72 | N/A |
| Optimized Portfolio | 100,000 | 104,743 | 4.65 |
You can see that scientific asset allocation can effectively boost returns.
Investment Tool Selection
You can choose investment tools such as stocks, bonds, funds, or ETFs through licensed banks in Hong Kong, U.S. brokers, or other channels. You should select tools based on your risk preferences and investment goals, diversifying investments to reduce risk.
Controlling Investment Costs
You need to pay attention to management and transaction fees. Over the long term, fees significantly impact returns. For example, over a 30-year period:
| Fee Type | Impact on $100,000 Investment (30 Years) |
|---|---|
| No Fees | $761,230 |
| 1% Annual Fee | $574,353 |
| Difference | $186,877 |
A 1% annual fee difference could result in nearly $190,000 less in earnings. You should prioritize low-fee products for more significant long-term compounding effects.
Investment Management
Regular Evaluation
You need to regularly evaluate your portfolio to ensure it aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. Financial advisors recommend the following practices:
- Maintain communication with your investment advisor to obtain timely professional advice.
- Periodically review your investment policy to adapt to market and personal goal changes.
- Conduct a Request for Proposal (RFP) for investment services every 3 to 5 years to evaluate the performance and service quality of advisors.
Regular evaluation helps you identify issues in your portfolio, adjust strategies promptly, and avoid losses due to market changes.
Rebalancing
Portfolio rebalancing is a crucial tool for managing risk. You need to periodically adjust your asset allocation to return to the originally set proportions. Professional investors recommend rebalancing annually. This effectively controls risk and maintains portfolio stability. Vanguard’s research shows that annual rebalancing performs best in risk-adjusted returns, increasing approximately 0.51% in risk-adjusted returns annually. You only need to check asset proportions annually and buy or sell assets as needed to keep your portfolio healthy.
Market Trends
When investing, you should pay attention to market trends and economic cycles. Inflation reduces real returns, and many investors choose real estate, natural resources, or precious metals to hedge risks. During economic recessions, bonds and consumer goods stocks typically perform better; during recoveries, stock markets offer higher returns, with technology and industrial stocks favored. The emergence of new technologies also brings new investment opportunities but increases volatility. Economic cycles are divided into four stages: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough. By analyzing historical and current data, you can determine the market stage, adjust your investment strategy promptly, and optimize performance.
Learning from Experience
You can gain valuable insights from the experiences of successful investors:
- Develop a clear financial plan to lay the foundation for investing.
- Stick to your investment strategy and avoid changing it due to short-term fluctuations.
- Build a habit of regular saving to accumulate long-term capital.
- Diversify investments to reduce risks from single assets.
- Choose low-fee investment products to control costs.
- Pay attention to taxes and account types to improve investment efficiency.
By continuously learning and summarizing experiences, you can make your investment journey more robust and efficient.
To become an excellent investor, you need to understand core concepts such as risk and return, asset allocation, and diversification. You can continuously improve through the following methods:
- Understand your personal risk tolerance and regularly review and rebalance your portfolio.
- Diversify investments to avoid emotional decisions and blindly chasing high returns.
- Utilize investor education resources and investment clubs to continuously learn new knowledge.
Common pitfalls include investing in a single asset, trying to predict the market, and being tempted by high returns. You should focus on long-term goals, dynamically adjust strategies, and balance risk and return.
FAQ
What is the difference between investing and saving?
When you deposit money into a savings account, you primarily seek safety and liquidity. When you invest, the goal is to grow your capital, taking on certain risks to achieve higher returns.
Can I invest in only one asset?
Investing in a single asset carries high risks. By diversifying across multiple assets, you can reduce the likelihood of losses and make your portfolio more stable.
How much money do I need to start investing?
You can start investing with very little money. For example, many U.S. ETFs allow you to buy with less than USD 100. You don’t need a large amount of capital.
How long does it take to see returns from investing?
The time it takes to see returns depends on the asset type. When investing in stocks or funds, it typically takes several years to see significant growth.
Will investing always lead to losses?
There is a possibility of losses when investing, but through diversification and long-term holding, you can reduce risks. With proper planning, the likelihood of losses decreases.
By grasping investment’s core concepts and practical strategies, you’ve unlocked the power of risk-reward balance, asset allocation, and compounding, but high cross-border fees, currency volatility, and offshore account complexities can limit deploying U.S. or global assets, especially when swiftly responding to market trends or rebalancing portfolios. Imagine a platform with 0.5% remittance fees, same-day global transfers, and contract limit orders with zero fees, enabling seamless wealth-building via one account?
BiyaPay is tailored for investors, offering instant fiat-to-digital conversions to seize market opportunities nimbly. With real-time exchange rate query, monitor USD trends and transfer at optimal moments to cut costs. Covering most regions with instant arrivals, it powers rapid allocations to S&P 500 ETFs (like VOO) or low-fee bond funds. Crucially, trade U.S. and Hong Kong markets through a single account, leveraging contract limit orders with zero fees for risk-reward-based limit strategies.
Whether chasing long-term compounding or optimizing allocations, BiyaPay fuels your success. Sign up now, visit stocks for global prospects—quick setup unlocks cost-effective, data-driven investing. Join global investors and lead in 2025’s wealth-building journey!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















