- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Short Iron Butterfly Strategy: A Neutral Profit Approach in Advanced Options Trading

Image Source: unsplash
You can achieve neutral profits through the short iron butterfly strategy when market volatility is low and prices remain stable. This strategy employs a net credit approach, meaning you collect premiums upfront when establishing the position. If the underlying asset’s price stays within a predetermined range at expiration, you will realize the maximum profit. Many investors choose this strategy because it has limited risk, a clear profit structure, and is suitable for those seeking stable cash flow in range-bound markets.
Key Points
- The short iron butterfly strategy is ideal for use in low-volatility, stable-price markets, helping you achieve neutral profits.
- By selling at-the-money call and put options, you can collect a net premium when establishing the position, with maximum profit realized at expiration when the price equals the middle strike price.
- Choosing appropriate strike prices and expiration dates is key to success, ensuring all contracts have the same expiration date to reduce risk.
- When implementing the strategy, setting clear profit targets and stop-loss limits helps you effectively manage risk and lock in gains.
- Closely monitor market changes and adjust or close positions promptly to protect existing profits when volatility increases.
Short Iron Butterfly Strategy Overview

Image Source: unsplash
Definition and Principles
You can achieve neutral profits through the short iron butterfly strategy. This strategy is an advanced options combination, structured with four different options contracts. You simultaneously sell an at-the-money call option and an at-the-money put option, then buy a higher strike call option and a lower strike put option. All contracts have the same expiration date, with the three strike prices equally spaced. You receive a net premium when establishing the position, which is the credit characteristic of the short iron butterfly strategy. The table below can help you understand its structure and risk-reward profile more intuitively:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Strategy Type | The short iron butterfly strategy is a four-part strategy, including a bull put spread and a bear call spread. |
| Options Structure | Short put and short call options have the same strike price, all options have the same expiration date, and the three strike prices are equally spaced. |
| Maximum Profit | Maximum profit is realized when the stock price equals the short options’ strike price at expiration, with all options expiring worthless, and the net credit becomes income. |
| Maximum Risk | Maximum risk is the difference between the lower and middle strike prices minus the net credit received, realized when the stock price exceeds the highest or lowest strike price at expiration. |
Through this structure, you can achieve maximum gains when the market price remains stable, while risk is strictly limited.
Neutral Profit Mechanism
When using the short iron butterfly strategy, you primarily rely on time value decay and the stability of the underlying asset’s price to profit. The specific mechanisms include:
- The sold at-the-money call and put options depreciate over time, especially in low-volatility markets.
- When the underlying asset’s price is close to the middle strike price at expiration, you achieve maximum profit, as all options expire worthless, and the net premium becomes your income.
- The purchased “long wing” options help limit losses in extreme market conditions, ensuring manageable risk.
You can see that the maximum profit range is concentrated around the current price, making it suitable for pursuing stable returns in range-bound markets.
Applicable Markets
The short iron butterfly strategy is most suitable in environments with low price volatility and stable market expectations. You can refer to the following market characteristics to determine if the strategy is appropriate:
- The success rate is typically between 50-70%, especially when you actively manage trades.
- You can increase strategy returns by selling options with overvalued implied volatility.
- Carefully selecting strike prices and expiration dates helps you lock in a more favorable profit range.
- You can further reduce risk and retain existing profits by closing positions early or using hedging techniques.
In the U.S. market, many investors use the short iron butterfly strategy before or after major economic data releases, during periods of declining volatility, to generate stable cash flow.
Strategy Construction
Contract Selection
When constructing the short iron butterfly strategy, you first need to select appropriate options contracts. You should focus on three key elements: strike price, expiration date, and contract type.
- Strike Price Selection: You should center the strike prices around the current underlying asset price, choosing an at-the-money strike as the middle price, then selecting a higher and lower strike price at equal distances. For example, if the underlying asset’s current price is 50 USD, you could choose 48 USD, 50 USD, and 52 USD as the three strike prices.
- Expiration Date Selection: You should choose near-month contracts with good liquidity and faster time value decay. This allows you to collect premiums more quickly while reducing uncertainty during the holding period.
- Contract Type: You need to use both call and put options, ensuring all contracts have the same expiration date.
Tip: You can quickly filter suitable strike prices and expiration dates through the options chain page. Major U.S. brokerage platforms support multi-leg options strategy orders, making it easy to establish positions with a single click.
Operational Steps
You can follow these steps to execute the short iron butterfly strategy on an options trading platform:
- Sell one at-the-money call option and one at-the-money put option (i.e., a short straddle) to establish the base position.
- Buy one call option with a strike price higher than the at-the-money strike (to protect against upside risk).
- Buy one put option with a strike price lower than the at-the-money strike (to protect against downside risk).
- Ensure all options contracts have the same expiration date.
- Before expiration, you can choose to close the entire position or parts of it to realize profits or control risk.
Suppose you choose 50 USD as the middle strike price, selecting 48 USD and 52 USD as the “long wing” strike prices, with all contracts expiring on the same date. You sell the 50 USD call and put options while buying the 52 USD call option and the 48 USD put option. This completes the construction of the short iron butterfly strategy.
Break-Even Points
In practice, you need to clearly calculate the break-even points, which determine whether you can achieve a profit. The short iron butterfly strategy has two break-even points, located above and below the middle strike price. You can refer to the table below:
| Break-Even Point | Calculation Formula |
|---|---|
| B/E #1 | Middle Strike Price - Net Premium Received |
| B/E #2 | Middle Strike Price + Net Premium Received |
| Example | B/E #1 = $50 - $3.73 = $46.27 |
| B/E #2 = $50 + $3.73 = $53.73 |
The higher the net premium received, the wider the break-even range. You can increase the premium received by establishing positions during periods of high implied volatility, thus expanding the profit range. As long as the underlying asset’s price falls between the two break-even points at expiration, you can achieve the maximum profit.
Risk and Reward

Image Source: unsplash
Maximum Profit
When using the short iron butterfly strategy, the maximum profit comes from the net premium received when establishing the position. As long as the underlying asset’s price equals the middle strike price at expiration, all options expire worthless, allowing you to keep the entire premium. The table below illustrates a typical maximum profit calculation:
| Item | Amount |
|---|---|
| Income from Selling Options | $4.00 |
| Income from Selling Options | $4.00 |
| Cost of Buying Options | -$2.00 |
| Cost of Buying Options | -$3.00 |
| Maximum Profit | $3.00 |
You can see that the maximum profit equals the total premium income minus the cost of buying options.
Maximum Loss
In extreme market conditions, you may face the maximum loss. The maximum loss occurs when the underlying asset’s price breaches the highest or lowest strike price. At this point, you need to use the received premium to offset losses from the “long wing” options. The maximum loss calculation formula is as follows:
| Formula Type | Formula |
|---|---|
| Iron Butterfly Maximum Loss | Wing Width - Net Premium Received |
You can effectively reduce the maximum loss by controlling the “wing width” and establishing positions during periods of high premium.
Profit Range
In practice, the profit range depends on whether the underlying asset’s price falls between the two break-even points at expiration. Typical profit range characteristics include:
- You are more likely to achieve maximum profit in low-volatility, stable-price markets.
- Maximum profit occurs when the price equals the central strike price at expiration.
- The strategy is more suitable in neutral market outlooks.
- Experienced traders can typically increase the win rate to 50-70%.
- Time value decay and low volatility help enhance your potential returns.
Short Iron Butterfly Strategy Risk Points
While the short iron butterfly strategy has limited risk, you should still be aware of the following risk points:
- Significant price fluctuations in the underlying asset may lead to the maximum loss.
- A sudden increase in implied volatility can cause adverse option price movements, affecting your returns.
- Insufficient liquidity may increase closing costs, impacting actual profits.
- You need to closely monitor market changes and adjust or hedge positions promptly.
You can effectively control risk and maximize returns by reasonably selecting strike prices, expiration dates, and actively managing positions.
Case Study
Market Example
You can gain a clear understanding of the short iron butterfly strategy’s performance through real market data. The table below shows the strategy’s key parameters and potential returns under different initial stock prices:
| Initial Stock Price | Short Strike Price | Long Strike Price | Total Premium Collected | Total Premium Paid | Net Credit | Maximum Profit Potential | Maximum Loss Potential |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $105.79 | $106 Call, $106 Put | $97 Put, $112 Call | $5.54 | $1.12 | $4.42 | $442 | $158 (Upside), $458 (Downside) |
| $300 | $300 Call, $300 Put | $250 Put, $350 Call | $24.25 | $1.31 | $22.94 | N/A | N/A |
| $74.44 | $300 Call, $300 Put | $250 Put, $350 Call | $3.47 | N/A | N/A | N/A | $153 |
| $752 | $750 Call, $750 Put | $625 Put, $875 Call | $73.55 | $7.40 | $66.15 | $6,615 | $5,885 |
You can see that the higher the net credit, the greater the maximum profit potential. The maximum loss depends on the stock price breaching the “long wing” strike prices. The chart below illustrates the trend of net credit changes under different initial stock prices:
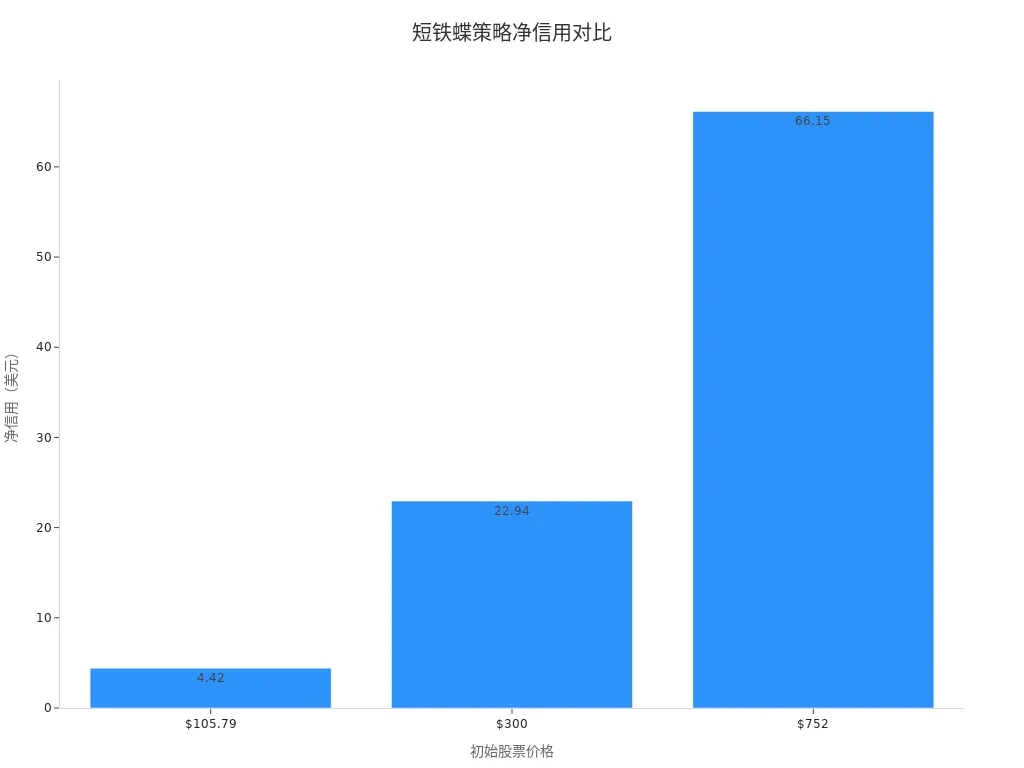
You can use this data to assess the risk and reward distribution across different price ranges.
Strategy Performance
When implementing the short iron butterfly strategy in different market environments, the win rate and returns will vary. The table below summarizes backtest results:
| Market Condition | Win Rate | Risk Management Strategy | Net Average P/L |
|---|---|---|---|
| 25% PT | High | 25% Profit Target | High |
| 50% SL | Low | 50% Stop Loss | High |
| Combined Strategy | High | Combining 25% PT and 50% SL | Medium |
You can see that setting reasonable profit targets and stop-loss points helps improve overall win rates and returns.
- During the 2017-2019 U.S. bull market, the short iron butterfly strategy achieved a win rate of 64.5%.
- In the 2007-2009 bear market, the win rate dropped to 44%.
- Different risk management approaches will affect the final return level.
You can flexibly adjust strategy parameters based on market volatility and your risk tolerance to increase the probability of profit.
Applicable Scenarios and Operations
Applicable Timing
You can consider initiating the short iron butterfly strategy when market volatility is low and prices are stable. Typically, when you have a neutral outlook on the underlying stock and expect it to fluctuate within a narrow range during the option’s life, this strategy is most suitable.
- If the stock price at expiration is within the iron butterfly’s “wings,” you will realize a profit.
- The passage of time has a positive impact, as option values gradually decay.
- Be aware that a sudden increase in implied volatility can negatively affect the strategy, potentially causing option prices to rise and compressing your profit range.
You can choose to enter the market after major economic data releases when market sentiment stabilizes.
Strategy Adjustments
In practice, you should establish a trading plan in advance, clearly defining entry, exit, and adjustment criteria.
- You can set profit targets and maximum loss limits for each trade, allowing you to close positions decisively when targets or stop-loss points are reached.
- When fundamental market changes occur, you should learn to accept small losses rather than blindly adjusting positions.
- If you find yourself adjusting positions two or three times or struggling to manage risk, consider closing the trade and waiting for a better opportunity.
Tip: Good risk management habits can help you achieve long-term stable profits and avoid larger losses due to emotional trading.
Closing and Rolling
When managing the short iron butterfly strategy, you have multiple ways to flexibly respond to market changes.
- You can exit early, closing the entire position before expiration to lock in profits or limit losses.
- If one side of the position shows significant risk exposure, you can close only that side’s options while retaining the rest.
- When market conditions change, you can also “roll” the position by closing the current position and re-establishing a short iron butterfly with new strike prices or expiration dates to better adapt to the new market environment.
These methods help you flexibly adjust in different market conditions, minimizing losses to the greatest extent.
Strategy Comparison
Iron Condor Comparison
When choosing neutral options strategies, you often hesitate between the iron condor and the short iron butterfly strategy. Both strategies are similar in structure, selling options at middle strike prices and buying “long wing” options at the ends to limit risk. You can refer to the table below to understand the main differences between the two:
| Aspect | Iron Condor | Iron Butterfly |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Risk | Wider loss range, limited risk | Narrower, limited risk |
| Maximum Return | Lower premium, limited profit | Higher premium, limited profit |
| Break-Even Points | Farther, wider range | Closer, narrower range |
| Key Dynamics | Lower returns, higher probability | Higher returns, lower probability |
You will find that the iron condor strategy has a wider profit range but lower maximum profit per trade. The short iron butterfly strategy has a narrower profit range but allows you to collect higher premium income. You are better suited to choose the short iron butterfly strategy in extremely low volatility and stable price environments.
Butterfly Comparison
You can also compare the short iron butterfly strategy with the traditional butterfly strategy. The traditional butterfly strategy is typically a net debit structure, requiring you to pay a premium upfront. In contrast, the short iron butterfly strategy is a net credit structure, allowing you to receive a premium when establishing the position. The maximum risk of the butterfly strategy equals the premium paid, while the maximum risk of the short iron butterfly strategy is the “wing width” minus the premium received. You are better suited to choose the short iron butterfly strategy when expecting minimal price fluctuations and aiming to lock in profits upfront.
Pros and Cons Analysis
In practice, you will find that the short iron butterfly strategy has unique advantages and limitations. The table below summarizes common pros and cons:
| Advantage/Disadvantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Limited Risk and Attractive Profit Potential | You can clearly know the maximum risk and profit, with risk limited to the initial cost. |
| Time Decay Benefits | You can benefit from time value decay, especially when prices are stable, with premiums gradually becoming your income. |
| Suitable for Range-Bound Markets | The strategy performs best when you expect prices to stay within a certain range. |
| Limited Profit Potential | Maximum profit is only realized when the price falls within the specified range at expiration. |
| Narrow Profit Range | The profit range is narrow, and profitability decreases with significant price fluctuations. |
| No Benefit from Strong Directional Markets | If the market experiences a significant one-sided move, you cannot gain additional returns. |
When using the short iron butterfly strategy, common mistakes include:
- Choosing incorrect strike prices
- Not using risk management techniques
- Ignoring changes in implied volatility
- Failing to adjust the strategy based on market changes
You can improve the strategy’s success rate by reasonably selecting strike prices, setting stop-loss points, and monitoring volatility. The short iron butterfly strategy is suitable for pursuing stable returns in neutral, low-volatility environments in the U.S. market.
When using the short iron butterfly strategy, you can achieve clear risk definition and stable net premium income.
- You need to monitor market volatility and avoid operating in high-volatility environments, as profit potential is limited, and positions require periodic adjustments.
- You should reasonably select strike prices and expiration dates, balancing the trade range width with net premiums, and closely monitor market signals and liquidity.
- You can adjust the wing width and time value based on your risk tolerance, flexibly managing risk to achieve neutral profits.
FAQ
Is the short iron butterfly strategy suitable for beginners?
You can try the short iron butterfly strategy, but you need to understand the basics of options first. It’s recommended to practice with a demo account to familiarize yourself with the operational process and risk control.
How do I choose appropriate strike prices?
You should center the strike prices around the current underlying asset price, selecting equally spaced high and low strike prices. This allows you to achieve a more reasonable profit range and risk control.
Can I close the strategy before expiration?
You can close the position at any time before expiration. This allows you to lock in existing profits or reduce potential losses. Most U.S. brokerage platforms support early closing operations.
What should I do if the market experiences significant volatility?
You need to closely monitor market changes. If the price approaches the “long wing” strike prices, consider closing the position early or adjusting it to reduce loss risk.
Do I need to pay taxes on the premiums received?
In the U.S. market, premiums received are considered investment income. You need to declare and pay relevant taxes according to U.S. tax laws. It’s recommended to consult a professional tax advisor.
By mastering the short iron butterfly strategy, you’ve learned to secure steady cash flows in low-volatility markets, but high cross-border fees, currency volatility, and complex account setups can limit swift responses to U.S. options markets, especially during declining implied volatility or stable price ranges. Imagine a platform with 0.5% remittance fees, same-day global transfers, and zero-fee limit orders, enabling seamless short iron butterfly execution via one account?
BiyaPay is tailored for options traders, offering instant fiat-to-digital conversions to act on market signals nimbly. With real-time exchange rate query, monitor USD trends and transfer at optimal moments to cut costs. Covering most regions with instant arrivals, it powers rapid allocations to S&P 500 index options (like SPY) or tech stock options. Crucially, trade U.S. and Hong Kong markets through a single account, leveraging zero-fee limit orders for theta decay and breakeven-based strategies.
Whether chasing consistent premium income or mitigating volatility risks, BiyaPay fuels your edge. Sign up now, visit stocks for options prospects—quick setup unlocks cost-effective, data-driven trading. Join global investors and thrive in 2025’s low-volatility markets!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















