- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Common Misconceptions and Solutions for International Remittance Tax Declarations

Image Source: pexels
International remittance tax declarations are crucial for Chinese residents and non-residents with economic transactions in China. They not only provide key data for national macroeconomic decision-making but also help local governments stay informed about the latest developments in foreign-related economies. Declaration subjects include individuals and institutions, and all transaction details must be declared item by item.
If you make errors during declaration, you may face serious consequences. Improper declarations can lead to additional financial losses or even violations of tax laws, resulting in legal liabilities. Correctly understanding international remittance tax policies and completing declarations as required is the best way to avoid these issues.
Basic Provisions of International Remittance Tax Policies
Definition and Scope of International Remittances
International remittances refer to the act of individuals or institutions transferring funds from one country to another through banks or other financial institutions. This behavior typically involves various scenarios such as cross-border transactions, investments, and payment services. To ensure the transparency of fund flows, China has established clear reporting standards for international remittances.
Below are the reporting standards for different types of remittances:
| Type | Reporting Standard (RMB) | Reporting Standard (Foreign Currency) |
|---|---|---|
| Cash Transactions | Above 50,000 RMB | Above $10,000 |
| Corporate Transfers | Above 2 million RMB | Above $200,000 |
| Individual Transfers | Above 500,000 RMB | Above $100,000 |
| Cross-Border Transfers | Above 200,000 RMB | Above $10,000 |
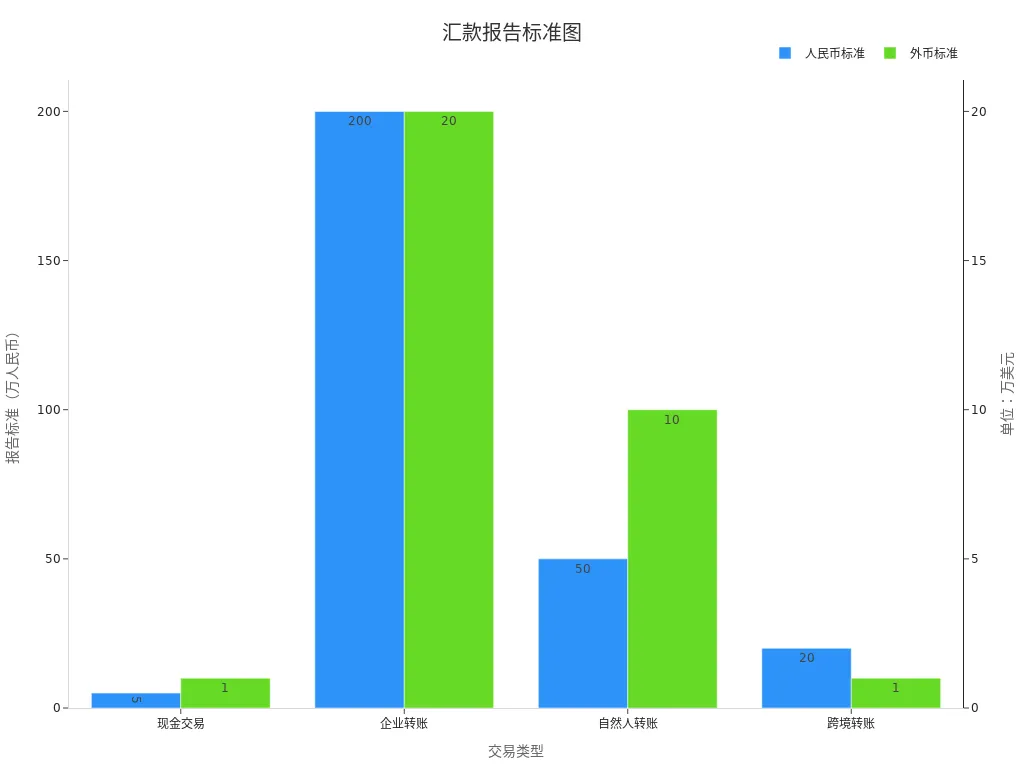
You need to determine whether a tax declaration is required based on the type and amount of your remittance. Whether you are an individual or a business, understanding these standards helps avoid unnecessary legal risks.
Legal Basis and Requirements for Tax Declarations
The implementation of international remittance tax policies has a clear legal basis. Chinese tax authorities ensure the legality and compliance of all cross-border fund flows through the financial and tax big data system. Below are the main requirements and significance of tax declarations:
- Compliance: Declarations ensure that your fund flows comply with Chinese tax law requirements.
- Risk Prevention: Timely declarations can reduce the risk of tax violations and avoid administrative penalties.
- Tax Planning: Proper arrangement of tax matters optimizes tax burden structures and improves economic efficiency.
- Timeliness and Accuracy of Declarations: Verify accounts on time and accurately calculate taxable amounts.
- Enhanced Cooperation with Tax Authority Oversight: Tax authorities use big data technology for precise analysis, improving regulatory efficiency.
You need to complete declarations promptly after a remittance occurs, as required by tax authorities. This is not only a legal obligation but also an important means of protecting your interests.
Specific Provisions on Tax-Exempt Thresholds and Declaration Limits
According to international remittance tax policies, certain remittance activities may qualify for tax exemptions, provided specific conditions are met. For example, when an individual’s annual total international remittance does not exceed a certain threshold, they may be exempt from declaration. However, once the tax-exempt threshold is exceeded, you must declare accurately.
Below are some common tax-exempt thresholds and declaration limits:
- Individual Remittances: Annual total not exceeding $100,000 may be exempt from declaration.
- Corporate Remittances: Single transactions below $200,000 generally do not require declaration.
- Special Cases: Remittances for purposes such as education or medical expenses may enjoy additional tax-exempt policies.
You need to reasonably utilize tax-exempt thresholds based on your specific situation. If you are unsure whether a declaration is required, it is advisable to consult a professional tax advisor.
Common Misconceptions in International Remittance Tax Declarations

Image Source: pexels
Incorrect Declaration of Income Sources
Errors in declaring income sources are one of the most common issues in international remittance tax declarations. You may fail to accurately provide specific details about income sources due to unfamiliarity with declaration requirements. For example, some individuals may mistakenly classify investment income as salary income or label gifted funds as commercial transactions. These errors may trigger further scrutiny from tax authorities and could even result in fines.
To avoid this, you need to carefully verify the classification of income sources. Common income sources include salaries, investment income, gifts, and inheritances. Each income type corresponds to different tax policies and declaration requirements. You can refer to the income classification guidelines provided by tax authorities to ensure the information you provide is accurate.
Additionally, you must ensure the accuracy of bank information during declarations. Below are some common error cases:
- Confusing SWIFT codes with bank codes. For example, mistakenly entering a Hong Kong bank’s branch code as the head office code.
- Ignoring intermediary bank fees. Some agent banks may charge additional fees, causing discrepancies between the declared amount and the actual received amount.
- Non-standard purpose descriptions. Using sensitive terms may trigger anti-money laundering reviews.
These errors can delay the declaration process and may lead to additional financial losses. You need to carefully verify all information before submitting a declaration to ensure accuracy.
Ignoring Conditions for Tax-Exempt Thresholds
Many people overlook the specific conditions for applying tax-exempt thresholds during declarations, leading to unnecessary errors. According to international remittance tax policies, individuals with annual international remittance totals not exceeding $100,000 may be exempt from declaration. However, this policy does not apply in all cases. For example, if your remittance involves commercial transactions, you must declare accurately even if the amount is below the tax-exempt threshold.
You need to pay special attention to the following points:
- Clear Purpose: Remittances for special purposes such as education or medical expenses may qualify for tax exemptions, but relevant supporting documents must be provided.
- Amount Limits: Even if individual remittance amounts are small, cumulative amounts exceeding the tax-exempt threshold require declaration.
- Cross-Border Transactions: Remittances involving cross-border commercial transactions must comply with tax declaration requirements, even if amounts are low.
Reasonably utilizing tax-exempt thresholds can help reduce your tax burden, but you must clearly understand the applicable conditions. If you are unsure whether your situation qualifies for a tax exemption, it is advisable to consult a professional tax advisor.
Misunderstanding International Remittance Tax Policies
Misunderstandings of international remittance tax policies are another major cause of declaration errors. Many people believe that small amounts or clearly defined purposes eliminate the need for declarations. This assumption is incorrect. The core of tax policies lies in the transparency of fund flows, not merely the size of the amount.
Below are some common misconceptions:
- Assuming Small Remittances Don’t Require Declaration: Even small remittances must comply with relevant declaration regulations if they involve cross-border transactions.
- Believing Individual Remittances Are Unregulated: In fact, individual remittances are subject to tax policies, especially for large amounts or special purposes.
- Ignoring Declaration Deadlines: Some believe declarations can be made anytime after a remittance, but tax authorities have strict deadlines, and delayed declarations may result in fines.
To avoid these misconceptions, you need to regularly study and update your knowledge of international remittance tax policies. Tax authority websites and professional tax advisors are reliable sources for accurate information.
Underestimating the Consequences of Delayed or Incorrect Declarations
Delayed or incorrect declarations can lead to serious consequences. You may think these issues are minor oversights, but in reality, they can have profound impacts on individuals and businesses.
First, declaration errors can result in financial losses. For businesses, entering incorrect HS codes during declarations may lead to customs penalties. This not only requires paying fines but may also cause property losses. For example, goods may be detained due to declaration errors, requiring businesses to pay additional storage fees or re-declaration costs. These fees are typically calculated in U.S. dollars, which may strain a business’s financial situation.
Second, delayed declarations can affect customs clearance efficiency. In cross-border transactions, time is critical. If your declaration information is incomplete or submitted late, goods may face delayed clearance. Such delays can lead to customer dissatisfaction or even order cancellations. Business credibility may suffer, requiring additional resources to restore customer relationships.
Additionally, declaration errors can impact long-term business development. Penalized businesses often opt to pay fines and move on, but this may damage their reputation. Tax authorities and customs may subject the business to stricter scrutiny, increasing the complexity of future transactions. You need to recognize that declaration errors are not one-time issues but can have long-term effects on business operations and development.
To avoid these consequences, you need to strictly comply with international remittance tax policy requirements. Ensuring declaration information is accurate and submitted on time is key to protecting your interests. If you are unfamiliar with the declaration process, seeking assistance from a professional tax advisor is advisable.
Analysis of Causes and Consequences of Common Misconceptions
Lack of Understanding of International Remittance Tax Policies
Many people handling international remittances are unclear about the specific requirements of international remittance tax policies. This lack of knowledge may lead you to overlook declaration obligations or mistakenly believe certain remittance activities do not require declaration. For example, some assume small remittances or funds transferred for personal purposes are exempt from tax policies. In reality, tax authorities have clear regulatory requirements for all cross-border fund flows.
Such misunderstandings can lead to serious consequences. Undeclared funds may be investigated by tax authorities or even frozen. You may also face fines or other legal liabilities. To avoid these issues, you need to proactively study relevant policies to ensure your remittance activities are legal and compliant.
Reliance on Non-Professional Advice
During the tax declaration process, many people choose to follow advice from friends or non-professionals. This practice can lead to incorrect declaration decisions. For example, some may suggest splitting remittances to evade declaration requirements or providing inaccurate income source descriptions. These actions not only violate tax laws but may also trigger more severe legal consequences.
Relying on non-professional advice may cause you to miss legitimate tax benefits. For instance, certain remittances for education or medical purposes may qualify for tax exemptions, but require specific supporting documents. Without professional guidance, you may fail to utilize these policies correctly. To avoid these issues, it is advisable to consult professional tax advisors or contact tax authorities directly for accurate information.
Negligence Due to Complex Declaration Processes
The international remittance tax declaration process may involve multiple steps, including filling out income sources, purpose descriptions, and bank information. The complexity of the process can easily lead to confusion and negligence. For example, you may omit necessary documents or make errors when entering bank information. With Hong Kong banks, for instance, many people confuse SWIFT codes with branch codes, leading to declaration failures.
Such negligence can result in financial losses. Declaration errors may cause delays in fund arrivals or even fund seizures. You may also need to pay additional fees or re-declaration costs, which are often calculated in U.S. dollars. To avoid these issues, you need to familiarize yourself with the declaration process in advance and carefully verify all information before submission.
Potential Legal Liabilities and Financial Losses
Errors or delays in international remittance tax declarations can expose you to serious legal liabilities and financial losses. Tax authorities enforce strict oversight of cross-border fund flows, and any non-compliant behavior may trigger legal consequences.
First, failure to declare as required may result in fines or criminal liability. Tax authorities may determine that you engaged in tax evasion, imposing hefty fines or even pursuing criminal charges. For example, in the Huizhou Intermediate People’s Court case (2018) Yue 13 Xing Zhong 361, due to incorrect declarations of cost inputs or R&D expenses, the involved party was found to have caused financial losses of $586,766.50.
| Case | Basis | Finding |
|---|---|---|
| Huizhou Intermediate People’s Court (2018) Yue 13 Xing Zhong 361 | Cost inputs or R&D expenses | Financial loss amount of $586,766.50 |
Second, declaration errors may lead to frozen funds or delayed arrivals. Banks and tax authorities will verify declaration information. If issues are found, your funds may be temporarily frozen until resolved. Such freezes can disrupt your cash flow, particularly in commercial transactions, potentially leading to contract breaches or loss of clients.
Additionally, incorrect declarations may increase the risk of future tax audits. Once flagged by tax authorities for closer monitoring, your subsequent transactions may face stricter scrutiny. This not only increases declaration complexity but may also impact your commercial reputation.
To avoid these consequences, you need to strictly adhere to tax policies, ensuring declaration information is accurate and error-free. If you are unfamiliar with the declaration process, consulting a professional tax advisor is advisable to prevent significant losses from minor errors.
Solutions to Avoid Misconceptions
Image Source: pexels
Specific Steps for Correctly Declaring Income Sources
When declaring income sources, you need to ensure the information is accurate. Below are specific steps to help you complete declarations:
- Confirm the income type. Based on the income classification guide, clearly determine whether your income falls under categories such as salary, investment income, gifts, or inheritances.
- Verify transaction records. Ensure transaction amounts match bank records to avoid declaration failures due to discrepancies.
- Validate invoice information. Confirm the authenticity and legality of invoices through the invoicing platform, ensuring invoice amounts and details align with transaction records.
- Submit declaration documents. When filling out the declaration form, provide detailed explanations of income sources and ensure bank information is accurate.
These steps can help reduce declaration errors and improve efficiency. Verifying the authenticity and consistency of invoices is particularly effective in avoiding tax authority scrutiny.
Recommendations for Reasonably Utilizing Tax-Exempt Thresholds
Tax-exempt thresholds are important tools for reducing tax burdens, but you need to use them wisely. The following recommendations can help you maximize the benefits of tax-exempt thresholds:
- Clear Purpose: If remittances are for education or medical purposes, provide relevant supporting documents to qualify for additional tax exemptions.
- Split Remittances: When the annual total approaches the tax-exempt threshold, consider splitting remittances to stay within the limit.
- Regular Audits: Periodically review annual remittance totals to ensure they do not exceed the tax-exempt threshold.
Reasonably utilizing tax-exempt thresholds not only reduces tax burdens but also helps avoid unnecessary declaration obligations.
Regular Study and Updates on International Remittance Policies
International remittance tax policies may change with the economic environment. You need to regularly study and update your knowledge to ensure your remittance activities remain compliant. Below are some learning recommendations:
- Monitor Tax Authority Websites: Tax authorities periodically release policy updates and declaration guides, which you can access through their official websites.
- Attend Tax Training: Many professional institutions offer tax training courses to help you understand policy details in depth.
- Consult Experts: If you are unsure about policy changes, consult professional tax advisors for accurate advice.
By staying informed, you can keep up with policy changes and avoid declaration errors due to misunderstandings.
The Necessity of Consulting Professional Tax Advisors
Consulting a professional tax advisor during international remittance tax declarations can help you avoid many potential issues. Tax policies are complex and frequently updated, making it difficult for individuals to fully grasp all details. Professional advisors provide accurate information and personalized advice, ensuring your declarations are lawful and compliant.
Why Consult Professional Advisors?
- Policy Interpretation: Advisors are familiar with international remittance tax policies and can help you understand complex legal provisions. For example, they can clarify whether remittances for education or medical purposes qualify for tax exemptions.
- Error Reduction: The declaration process involves multiple components, such as income sources, purpose statements, and bank details. Advisors meticulously review each item to prevent financial losses due to errors.
- Time Efficiency: You may spend hours researching policies and preparing documents, but advisors can complete these tasks quickly, allowing you to focus on other priorities.
How to Choose a Suitable Tax Advisor?
When selecting a tax advisor, consider the following:
- Qualifications: Ensure the advisor holds valid certifications, such as Certified Public Accountant or Tax Practitioner credentials.
- Experience: Prioritize advisors with experience in similar cases, particularly those familiar with Hong Kong bank cross-border remittances.
- Transparent Services: Understand the advisor’s fee structure to avoid hidden costs. Typically, advisor fees are quoted in U.S. dollars, so confirm the exact amount in advance.
Tip: Consulting a tax advisor is particularly crucial if your remittance amounts are large or complex. This not only reduces tax risks but also aids in effective financial planning.
With professional advisors’ assistance, you can complete tax declarations more easily, avoiding issues stemming from policy misunderstandings or operational errors. Hiring an advisor is a worthwhile investment, especially for high-value or complex cross-border remittances.
Considerations for International Remittance Tax Declarations
Comply with Tax Laws to Avoid Tax Evasion
You must strictly comply with tax laws to ensure your international remittance activities are lawful and compliant. According to international remittance tax policies, international remittances are generally considered foreign income and may require personal income tax payments, depending on the remittance purpose. Below are some compliance tips:
- Foreign income may qualify for tax exemptions, but amounts exceeding the threshold must be declared and taxed accurately.
- Correctly declaring income sources is key to lawful tax avoidance. You can reduce tax burdens by scheduling remittances or utilizing tax-exempt thresholds.
- Avoid using false information or concealing income sources, as these actions may lead to severe legal consequences.
By adhering to tax laws, you can protect your financial interests and avoid penalties or criminal liability due to tax evasion.
Retain Relevant Documents and Records
Retaining relevant documents and records is critical in international remittance tax declarations. These documents serve as the basis for declarations and are essential for addressing tax audits. Below are specific measures:
| Compliance Requirement | Specific Actions |
|---|---|
| Organizational Safeguards | Appoint a data security officer and establish a management body, conduct regular risk assessments, and retain reports. |
| Technical Safeguards | Implement encryption, access controls, and data leakage prevention measures. |
| Emergency Response | Develop an emergency response plan for data security incidents, with a clear reporting timeline (report major incidents to regulators within 72 hours). |
You need to properly retain remittance records, invoices, contracts, and other documents, ensuring their authenticity and completeness. Particularly when using Hong Kong banks for cross-border remittances, banks may require detailed transaction records to verify fund sources. By maintaining these documents, you can effectively respond to tax authority audits and reduce compliance risks.
Regularly Check Declaration Status to Ensure No Omissions
Regularly checking declaration status is an important step to avoid omissions. You need to ensure all remittance activities have been declared as required and verify the accuracy of declaration information. Below are some suggestions:
- Regularly log into the tax authority’s declaration system to check if the status shows “completed.”
- Verify that declaration amounts match bank records to avoid failures due to discrepancies.
- Check for missing documents or omitted income source descriptions.
By regularly checking, you can identify issues early and take corrective actions, avoiding fines or other legal consequences due to declaration errors or omissions.
Monitor Changes in International Tax Policies
International tax policies may adjust with changes in the global economic environment. You need to closely monitor these changes to ensure your remittance activities comply with the latest legal requirements. Ignoring policy updates may lead to declaration errors or legal issues.
Below are practical ways to track international tax policy changes:
- Visit Tax Authority Websites Regularly
Tax authorities typically publish the latest policy updates and declaration guides on their websites. You can subscribe to update notifications to receive important information promptly. - Follow Professional Tax Media
Some professional publications and organizations provide in-depth analyses of international remittance tax policies. These resources can help you understand the context and impact of policy changes. - Attend Tax Training or Seminars
Tax authorities and professional institutions often hold training events to explain new policies and declaration processes. Attending these events allows you to ask experts directly and resolve doubts. - Consult Professional Tax Advisors
If you’re confused by policy updates, professional tax advisors can provide tailored advice. They can analyze the specific impact of changes on you and guide you in adjusting your declaration strategy.
Tip: Cross-border remittance policies of Hong Kong banks may be affected by changes in international tax policies. You need to pay special attention to these banks’ announcements to ensure your remittances comply with the latest regulations.
By proactively studying and staying informed about policy updates, you can better protect your financial interests and avoid unnecessary legal risks.
International remittance tax declarations require your utmost attention. Accurate declarations not only mitigate legal risks but also safeguard your financial interests. According to international remittance tax policies, compliance is key to ensuring fund flow transparency.
By consulting tax advisors, you can complete declarations more efficiently and avoid unnecessary errors. Legal compliance is not only a responsibility but also the best way to protect your interests.
FAQ
1. What Basic Documents Are Required for International Remittance Tax Declarations?
You need to prepare the following documents:
- Remittance records
- Proof of income sources (e.g., payslips, investment income statements)
- Relevant purpose documentation (e.g., education or medical invoices)
- Bank information (e.g., SWIFT codes for Hong Kong banks)
Tip: Ensure all documents are authentic and complete to avoid declaration failures.
2. What Are the Consequences of Not Declaring on Time?
Failure to declare on time may result in:
- Fines imposed by tax authorities
- Frozen funds or delayed arrivals
- Increased risk of future tax audits
Recommendation: Regularly check declaration status to ensure timely completion.
3. How Can I Determine If My Remittance Requires Declaration?
To determine if a declaration is required, consider the following criteria:
- Does the remittance amount exceed the tax-exempt threshold (e.g., annual total over $100,000 for individuals)?
- Does the remittance purpose involve commercial transactions?
- Are there other requirements specified by tax authorities?
Note: Even small amounts may require declaration for certain purposes.
4. Can Splitting Remittances Avoid Declaration Obligations?
Splitting remittances cannot evade declaration obligations. Tax authorities review annual totals, not individual transactions. If the cumulative amount exceeds the tax-exempt threshold, you must declare accurately.
Reminder: Attempting to evade declarations may lead to severe legal consequences.
5. How Can I Access the Latest International Remittance Tax Policies?
You can obtain the latest policies through:
- Visiting tax authority websites
- Subscribing to professional tax media
- Consulting tax advisors
Tip: Policies may change with economic conditions, so regular updates are essential.
Cross-border remittance tax declarations often lead to penalties or fund freezes due to misreported income sources, policy misunderstandings, or delays. BiyaPay offers an efficient solution, supporting conversions across 30+ fiat currencies and 200+ cryptocurrencies with remittance fees as low as 0.5%, covering 190+ countries with same-day delivery. BiyaPay ensures fund safety and accelerates processing, simplifying cross-border transactions and complex tax requirements. Join BiyaPay now to optimize your remittance and declaration experience! You can also invest in U.S. and Hong Kong stocks directly on the BiyaPay platform without needing an additional overseas account, enhancing capital efficiency. Idle funds can earn a 5.48% APY through current investment products, backed by BiyaPay’s U.S. MSB and SEC licenses. Sign up with BiyaPay for secure, efficient global remittances!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















