- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
How to Complete International Remittances Through Major Canadian Banks

Image Source: unsplash
Completing international remittances through major Canadian banks is not complicated. You only need to follow a few key steps to easily complete the transfer. First, log into your bank account and locate the international remittance option. Next, enter the recipient’s detailed information, such as the SWIFT code and IBAN. Then, select the remittance amount and currency type, ensuring all information is accurate. Finally, confirm and submit the remittance request. The convenience of Canadian international remittances allows you to quickly and securely transfer funds worldwide.
Key Points
- Log into your bank account, find the international remittance option, and ensure the information is accurate.
- When filling out recipient information, verify the SWIFT code and IBAN to avoid errors leading to remittance failure.
- Select the remittance amount and currency type, pay attention to fees and exchange rates, and ensure sufficient account balance.
- Before submitting the remittance, carefully check all information and proceed only after confirming accuracy.
- Save remittance records for future inquiries and to resolve potential issues.
Specific Steps for Canadian International Remittances

Image Source: pexels
Logging into Your Bank Account and Accessing the International Remittance Page
You need to first log into your bank account. Use the bank’s official website or mobile banking application, and enter your username and password to complete the login. After logging in, locate the “International Remittance” option in the menu. Typically, this option is found under the “Transfer” or “Payment” category. Click to enter, and you will see a dedicated page for international remittances. This page will display all the steps and related information required for the remittance.
Tip: If you cannot find the international remittance option, use the bank’s search function and enter “international remittance” for quick navigation.
Adding Recipient Information (SWIFT Code, IBAN, etc.)
On the international remittance page, you need to fill out the recipient’s detailed information. This includes the recipient’s name, bank name, bank address, and the bank’s SWIFT code. The SWIFT code is an international standard code used to identify banks. You can obtain this code from the recipient or their bank.
Additionally, if the recipient’s country uses IBAN (International Bank Account Number), you also need to enter the IBAN. IBAN is typically longer than a regular account number and includes country codes and other identifying information. Ensure all information is accurate, as incorrect information may lead to remittance failure or delays.
Note: When filling out information, it is recommended to carefully verify each item to avoid delays due to input errors.
Selecting the Remittance Amount and Currency Type
After filling out the recipient’s information, you need to select the remittance amount and currency type. Enter the specific amount you wish to send and choose the target currency. Most Canadian banks support multiple currency types, such as USD, EUR, or GBP.
The bank system will calculate the total amount you need to pay based on the current exchange rate. You can review the exchange rate and decide whether to proceed with the remittance immediately. If the exchange rate is unfavorable, you can choose to perform the operation later.
Tip: When selecting the amount, consider fees and exchange rate fluctuations to ensure your account balance is sufficient to cover all costs.
Confirming Remittance Information and Submitting
After selecting the remittance amount and currency type, you need to carefully verify all entered information. Ensure the recipient’s name, bank name, SWIFT code, and IBAN are completely correct. The bank system typically displays a remittance summary, including the remittance amount, fees, exchange rate, and estimated arrival time. You can use this summary to check for any omissions or errors.
Tip: If you find any incorrect information, return immediately to make corrections. Submitting incorrect information may lead to remittance failure or delayed funds.
Once the information is confirmed accurate, click the “Submit” button to complete the remittance request. The bank will send a confirmation notification to your email or phone number. Some banks may also require you to enter a one-time password or use two-factor authentication to ensure transaction security.
Note: Once submitted, funds cannot be withdrawn. Be sure to double-check all information before submitting.
Saving Remittance Records for Future Reference
After completing the remittance, you need to save the related records. These records include the transaction number, remittance date, amount, and recipient information. Most banks provide electronic transaction receipts, which you can download and save to your personal device.
Saving records has obvious benefits. If issues arise with the remittance, such as funds not arriving or incorrect information, these records allow you to quickly contact bank customer service to resolve the problem. Additionally, saving records helps you track remittance history, facilitating future financial management.
Tip: Store records in a secure location, such as an encrypted folder or cloud service, to avoid data loss due to device failure.
If you use mobile banking to complete the remittance, you can directly view the transaction history in the application. Some banks also support exporting transaction records as PDF files for easy printing or sharing.
By following these steps, you can easily complete Canadian international remittances while ensuring transaction security and information integrity.
Key Details for Canadian International Remittances
Fee Calculation Methods and How to Reduce Costs
When conducting Canadian international remittances, fees are a key aspect to focus on. Different banks may have varying fee calculation methods. Typically, fees include fixed charges and percentage-based fees based on the remittance amount. For example, some banks may charge a fixed fee of USD 15 per remittance, while others may charge 0.5% to 1% of the remittance amount.
To reduce fees, you can adopt the following methods:
- Choose Banks or Services with Lower Fees: For example, Wise offers transparent exchange rates and lower fees, suitable for small remittances. In contrast, traditional banks like RBC may charge higher fees.
- Take Advantage of Bank Promotions: Some banks offer fee waivers or discounts during specific periods.
- Avoid Multiple Small Remittances: Consolidating multiple small remittances into a single large remittance can reduce total fee expenses.
Tip: When choosing a remittance service, the level of fees is an important decision factor. By comparing different banks’ fee policies, you can find the most suitable option.
Impact of Exchange Rates and How to Choose the Best Remittance Time
Exchange rates directly affect your remittance costs and the amount received by the recipient. In Canadian international remittances, banks typically offer exchange rates slightly lower than market rates, meaning you may incur additional hidden fees.
To minimize losses due to exchange rates, you can:
- Monitor Real-Time Exchange Rate Fluctuations: Choose times with higher exchange rates for remittances. For example, when market exchange rates fluctuate significantly, you can use the bank’s online tools to check real-time rates and find the optimal remittance time.
- Choose Services Offering Mid-Market Rates: Some providers (e.g., Wise) offer exchange rates close to the mid-market rate, avoiding the exchange rate losses of traditional banks.
- Avoid Remitting on Weekends or Holidays: Exchange rates may be unstable during these periods, and banks may charge additional fees.
Note: The favorability of exchange rates is one of the key factors in choosing a bank. By planning remittance times wisely, you can effectively reduce costs.
Remittance Limits and How to Apply for an Increase
Most Canadian banks set limits on international remittances. These limits may be daily, weekly, or monthly caps on remittance amounts. For example, some banks may set a daily remittance limit of USD 10,000, while others may allow higher amounts.
If your remittance needs exceed the bank’s limit, you can try the following methods:
- Contact Bank Customer Service: You can directly contact the bank to apply for an increase in the remittance limit. Typically, the bank will require additional identity verification or financial proof.
- Split Remittances: If the limit cannot be increased, you can divide large remittances into multiple transactions.
- Choose Services with No Limits: Some third-party remittance platforms may have less stringent limit restrictions, suitable for large remittance needs.
Tip: When applying for a limit increase, preparing relevant documents in advance, such as proof of income or bank statements, can speed up the approval process.
By understanding the key details of fees, exchange rates, and remittance limits, you can better plan Canadian international remittances, saving costs and improving efficiency.
Estimated Arrival Times and Possible Reasons for Delays
After completing a Canadian international remittance, you may be concerned about when the funds will reach the recipient’s account. Typically, international remittances through major Canadian banks take 1 to 5 business days to arrive. The specific time depends on several factors, including the remittance method, the recipient bank’s processing speed, and the countries or regions involved.
Key Factors Affecting Arrival Times
Below are some key factors that may affect arrival times:
- Remittance Method: Remittances via the SWIFT network typically take 2 to 5 business days, while instant remittance services (e.g., Interac e-Transfer Global Payments) may take only minutes to hours.
- Recipient Bank’s Processing Speed: Different banks have varying processing efficiencies. Some banks may require additional time to verify and process international remittances.
- Involved Countries or Regions: If the recipient’s country has a complex banking system or strict regulations, it may cause delays. For example, banks in some developing countries may take longer to complete fund clearing.
- Holidays or Weekends: Banks typically do not process international remittances during holidays or weekends, which may extend arrival times.
Tip: When planning remittances, try to avoid holidays or weekends to minimize unnecessary delays.
How to Handle Possible Delays
If your remittance does not arrive as expected, you can take the following measures:
- Check Remittance Status: Log into your bank account to view transaction records or remittance status. Most banks provide real-time updates.
- Contact Bank Customer Service: If you notice anomalies, contact bank customer service immediately. They can help you confirm the specific location of the funds.
- Provide Complete Remittance Information: Ensure you provided accurate SWIFT codes, IBAN, and recipient information during the remittance. Incorrect information may lead to funds being returned or delayed.
- Be Patient: In some cases, delays may be due to slower international bank clearing processes. Typically, funds will arrive automatically within a few days.
Note: If the remittance does not arrive after 10 business days, contact the bank immediately and provide transaction records for investigation.
By understanding these factors and response methods, you can better plan Canadian international remittances, ensuring funds arrive securely and on time.
Common FAQs
What is a SWIFT Code? How to Obtain It?
A SWIFT code is a unique identifier used by banks for international transfers. It consists of 8 to 11 characters, including bank code, country code, location code, and branch code. Through SWIFT codes, banks can process international remittances quickly and securely.
To obtain a SWIFT code, you can use the following methods:
- Contact the Recipient Bank: Directly ask the recipient bank’s customer service for the SWIFT code.
- Check the Bank’s Website: Most banks provide SWIFT code information on their international remittance pages.
- Review Bank Documents: Bank-provided account information documents typically include the SWIFT code.
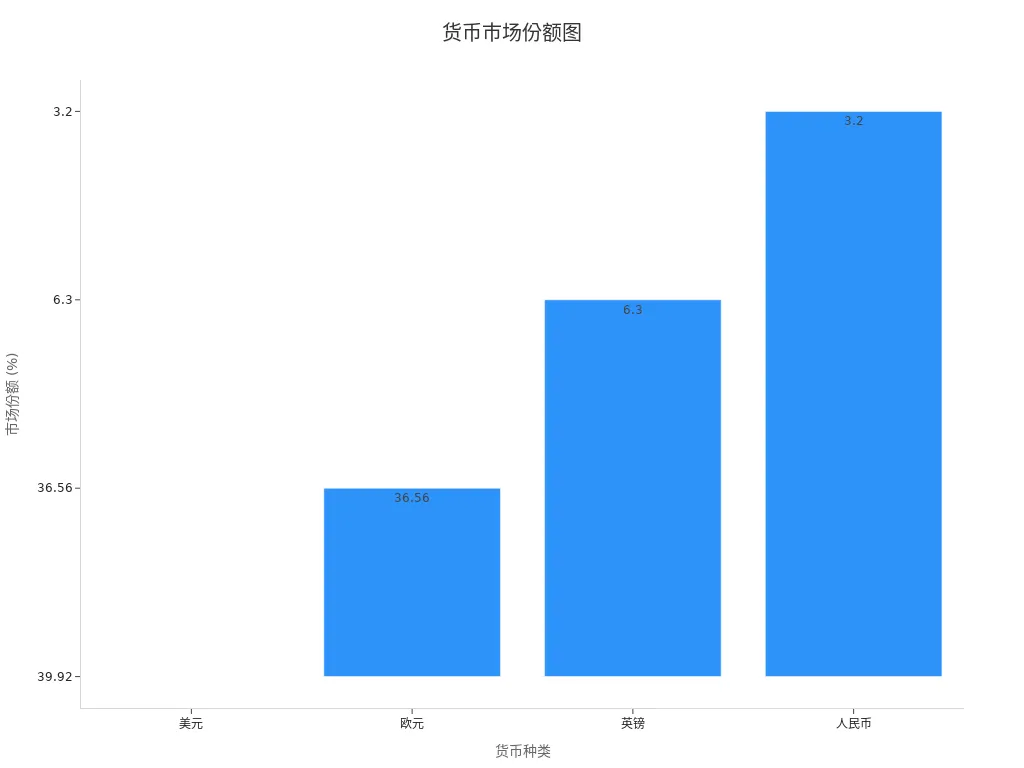
According to statistics, the market share of major currencies supported by the SWIFT network is as follows:
| Currency | Market Share |
|---|---|
| USD | 39.92% |
| EUR | 36.56% |
| GBP | 6.3% |
| RMB | 3.2% |
Tip: When filling out the SWIFT code, ensure it is accurate to avoid remittance failure.
What is the Difference Between IBAN and Account Number?
The main differences between IBAN (International Bank Account Number) and a regular account number lie in their purpose and structure. IBAN is an internationally standardized bank account number designed for cross-border remittances. It includes country codes, bank codes, and account numbers, and is typically longer than a regular account number.
| Feature | IBAN | Regular Account Number |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | International remittances | Domestic remittances |
| Structure | Includes country code, bank code, etc. | Only includes account number |
| Length | Typically longer (up to 34 characters) | Shorter (usually 10-12 characters) |
Note: Canadian banks typically do not use IBAN but instead use a combination of SWIFT codes and regular account numbers.
What to Do If a Remittance Fails or Information is Incorrect?
If a remittance fails or information is incorrect, you can take the following steps:
- Check Remittance Status: Log into your bank account to review transaction records and confirm the reason for the error.
- Contact Bank Customer Service: Provide the transaction number and related information to explain the issue. Bank customer service will assist in identifying and resolving the problem.
- Provide Correct Information: If the error is due to incorrect SWIFT codes or account numbers, provide the correct information promptly. The bank may reprocess the remittance.
- Request a Refund or Re-Remit: If funds have been returned, you can request a refund or initiate a new remittance.
Tip: Save all remittance records, including transaction numbers and recipient information, to facilitate quick issue resolution.
Can International Remittances Be Completed Via Mobile Banking?
Yes, you can complete international remittances via mobile banking. Today, major Canadian banks offer robust mobile banking applications, allowing you to perform international remittances anytime, anywhere. Compared to traditional online banking, mobile banking is more convenient and suits the mobile needs of modern users.
Key Advantages of Mobile Banking
Using mobile banking for international remittances has several notable advantages:
- Operate Anytime, Anywhere: Whether at home, in the office, or traveling, you can complete remittances by opening the mobile banking app.
- User-Friendly Interface: Mobile banking designs are typically more intuitive, suitable for users unfamiliar with complex operations.
- Real-Time Notifications: Many banks send transaction status updates via mobile banking, ensuring you stay informed about remittance progress.
Comparison of Mobile Banking and Online Banking Usage
According to statistical data, user frequency for mobile banking and online banking varies, particularly for transfer and remittance functions:
| Banking Type | Usage Frequency Change | High-Frequency Function Usage Rate | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile Banking | Decreased usage frequency | Transfers and remittances 74.8% | User habits changing, smaller remittance amounts |
| Online Banking | Decreased usage frequency | Transfers and remittances 70.2% | Some users migrating to mobile banking |
As shown in the table, although overall usage frequency for mobile banking has declined, its usage rate for transfer and remittance functions remains high. This indicates that users prefer mobile banking for small international remittances.
Precautions for Using Mobile Banking
When using mobile banking for international remittances, note the following:
- Ensure Network Security: Avoid operating in public Wi-Fi environments to prevent personal information leakage.
- Verify Recipient Information: Before submitting the remittance, carefully check the SWIFT code and account number for accuracy.
- Understand Fees and Exchange Rates: Mobile banking typically displays real-time exchange rates and fees; compare them carefully before confirming.
By completing international remittances via mobile banking, you can enjoy convenience and speed while maintaining control over fund movements. Following these suggestions ensures secure and efficient remittances.
Practical Tips for Improving Canadian International Remittance Efficiency

Image Source: pexels
Preparing All Necessary Information in Advance
Before conducting Canadian international remittances, preparing all necessary information in advance can significantly reduce error rates. You need to ensure the recipient’s name, bank name, SWIFT code, and account number are accurate. Additionally, understanding the remittance amount, currency type, and specific fee calculations is crucial.
Below are suggestions for improving information accuracy:
- Enhance learning and fully understand remittance-related statistical indicators.
- Participate in training or consultation activities offered by banks to gain a comprehensive understanding of the remittance process.
- Proactively contact bank customer service to resolve questions about filling out information, reducing minor errors.
- Establish robust personal financial records to avoid remittance failures due to incomplete information.
Preparing this information in advance not only saves time but also prevents delays or fund returns due to errors.
Using Bank Online Tools for Exchange Rate Comparison
Exchange rates directly impact your remittance costs. Using online tools provided by banks can help you compare exchange rates in real time and choose the best remittance time. Most Canadian banks offer exchange rate lookup functions on their websites or mobile apps.
With these tools, you can:
- View current exchange rates and predict future fluctuation trends.
- Compare exchange rates between different currencies to select the most cost-effective remittance method.
- Set exchange rate alerts to remit immediately when rates reach desired levels.
These tools are convenient and fast, helping you save costs and making your Canadian international remittances more efficient.
Understanding Different Banks’ Fee Policies
Fee policies vary significantly across banks. Understanding these policies can help you choose the most suitable remittance method. Below are some common fee adjustment measures:
- Reduce bank account service fees.
- Lower RMB transfer and remittance fees.
- Eliminate certain bill-related service fees.
- Reduce bank card transaction fees.
The implementation of these measures allows users in many regions to benefit from policy advantages, saving significant costs. By comparing fee standards across different banks, you can choose the bank or platform with the lowest fees, reducing remittance costs.
By preparing information in advance, using online tools, and understanding fee policies, you can significantly improve the efficiency of Canadian international remittances while saving time and costs.
Avoiding Remittances During Holidays or Peak Periods
Conducting international remittances during holidays or peak periods may lead to unnecessary delays and additional fees. Banks and financial institutions typically face higher transaction volumes during these times, slowing processing speeds. Knowing how to avoid these periods can help you complete remittances more efficiently.
Why Do Holidays and Peak Periods Affect Remittances?
- Extended Bank Processing Times: During holidays, many banks have reduced staff, lowering processing capacity. Even if you submit a remittance request, funds may remain pending in the bank’s system longer.
- International Clearing System Restrictions: International remittances require multiple banks and clearing systems to process. If any link is closed for holidays, the entire process may be delayed.
- Increased Exchange Rate Volatility: Market volatility may be higher during holidays and peak periods, leading to unstable exchange rates, which can increase your remittance costs.
Tip: When planning remittances, check the holiday schedules of the target country in advance to avoid submitting requests on these dates.
How to Choose the Best Remittance Times?
- Avoid Weekends and Public Holidays: Most banks do not process international remittances during holidays or weekends. Submitting requests early in the week allows banks more time to process transactions.
- Consider Payday Differences: International remittances involve multiple banking systems across countries. Choosing a time zone where all relevant banks are operational can speed up processing.
- Plan Ahead: If you know holidays or peak periods are approaching, complete remittances a few days in advance to avoid delays.
By choosing optimal remittance times, you can minimize delay risks and ensure funds arrive quickly and securely. Avoiding remittances during holidays or peak periods is a crucial step in improving efficiency.
Completing Canadian international remittances is straightforward. You only need to follow key steps: log into your account, fill out recipient information, select the amount and currency type, and confirm and submit the remittance request. Preparing necessary information in advance is critical, such as SWIFT codes and account numbers. Understanding details like fees, exchange rates, and processing times can help you save costs and improve efficiency.
Choosing the right remittance method for your needs is also important. Whether through traditional banks or third-party platforms, you can find the best solution based on your preferences. By mastering these strategies, you will complete Canadian international remittances more easily.
FAQs
What is a SWIFT Code?
A SWIFT code is an international bank identifier used for cross-border payments. You can obtain it through:
- Contacting the recipient bank’s customer service
- Checking the international remittance page’s website
- Reviewing bank-provided account information documents
Tip: Ensure the SWIFT code is accurate to avoid remittance failures.
What is the Difference Between IBAN and Regular Account Number?
IBAN is an international bank account number designed for cross-border remittances, containing country codes, bank codes, and account information. Regular account numbers are used only for domestic remittances and are shorter. Canadian banks typically do not use IBAN but rely on a combination of SWIFT codes and account numbers.
| Feature | IBAN | Regular Account Number |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Cross-border remittances | Domestic remittances |
| Structure | Includes country code, bank code, etc. | Only includes account numbers |
| Length | Mostly longer (up to 34 characters) | Shorter (4-12 characters) |
What to Do If a Remittance Fails or Information Is Incorrect?
If a remittance fails, you can:
- Review Transaction Records: Check transaction records to confirm the reason for the error.
- Contact Customer Service: Provide the transaction number and details to explain the issue.
- Provide Correct Information: Submit corrected details, if needed, to reprocess or initiate a new remittance.
Tip: Keep all remittance records to aid in quick resolution.
Can International Remittances Be Completed via Mobile Banking?
Yes. Major Canadian banks’ mobile apps support international remittances, allowing operations anytime, anywhere. Mobile banking interfaces are user-friendly, ideal for those unfamiliar with complex processes. Before submitting, ensure network security and verify all information.
Tip: Avoid operating in public Wi-Fi to protect personal information.
How to Check the Arrival Status After a Remittance?
You can check the status through:
- Logging into your bank account to view transaction records.
- Using bank-provided real-time tracking tools.
- Contacting customer service with the transaction number for details.
Tip: Most banks send arrival notifications to your phone or email.
International remittances via Canadian banks are straightforward but incur high fees ($15-50), 1-5 day delays, and risks of SWIFT/IBAN errors. BiyaPay enables investment in U.S. and Hong Kong stocks without an overseas account, simplifying cross-border transfers for family support or investments. Supporting conversions across 30+ fiat currencies and 200+ cryptocurrencies, BiyaPay offers remittance fees as low as 0.5%, covering 190+ countries with 1-2 day delivery. Join BiyaPay now for seamless transfers! Licensed by U.S. MSB and SEC, BiyaPay ensures compliance and real-time exchange rate tracking to optimize timing, with idle funds earning a 5.48% APY via flexible savings. Sign up with BiyaPay for a cost-effective, efficient remittance solution!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.


















