- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Comprehensive Guide for Beginners on Fixed Deposits: From Account Opening to Interest Calculation

Image Source: unsplash
Do you always feel that fixed deposits are complicated? You might want to know what documents are needed to open an account, how to choose the right fixed deposit calculation method for yourself, or even worry about potential hidden risks. In fact, fixed deposits are not difficult at all. As long as you follow clear steps and understand each detail, you can easily get started. It’s recommended that you bring your questions and follow the steps to experience the entire process firsthand.
Key Points
- Before opening a fixed deposit, prepare documents like ID and proof of address, compare minimum deposit amounts and offers from different banks, and choose the most suitable bank and account opening method.
- Understand the four types of fixed deposits (time deposit, principal retained with interest withdrawn, regular savings with lump-sum withdrawal, lump-sum deposit with regular interest payments) and select the best option based on your cash flow and financial goals.
- Choosing a fixed interest rate offers stable returns, while a floating rate may yield higher interest but carries greater risk; decide based on your risk tolerance and market expectations.
- Master the interest calculation formula and pay attention to interest payment frequency, taxes, and early withdrawal penalties to accurately estimate actual returns and avoid losses.
- Upon maturity, you can choose to renew, withdraw, or terminate early; each option has pros and cons, so decide carefully based on your financial needs and goals.
Account Opening

Image Source: pexels
Required Documents
If you want to open a fixed deposit account, you first need to prepare basic documents. Most Hong Kong banks will require you to bring the following items:
- Valid identification (e.g., Hong Kong ID or passport)
- Proof of address (e.g., utility bill or bank statement from the last three months)
- Sometimes banks may ask for proof of income (e.g., payslip or tax return)
Tip: Different banks may have different requirements, so it’s best to call and check before opening an account.
Account Opening Steps
Once you have your documents ready, you can follow these steps:
- Choose the bank where you want to open an account, such as HSBC Hong Kong, Bank of China Hong Kong, Hang Seng Bank, etc.
- Visit a bank branch or start the application through the bank’s official website or mobile app.
- Fill in personal information, select the fixed deposit product, and specify the deposit amount.
- Submit documents for the bank to verify.
- Deposit the minimum required amount (generally starting at USD 1,300, calculated at 1 USD = 7.8 HKD).
- Upon completion, you will receive a deposit certificate or electronic notification.
Note: Some banks require “new funds” to qualify for high-interest promotions, meaning you need to deposit funds transferred from another bank.
Online vs. In-Branch
You can choose to open an account in person at a branch or use online banking services. Both methods have their pros and cons:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| In-Branch | Assisted by staff, questions answered | Requires queuing, time-consuming |
| Online | Convenient, available 24/7 | May require mailing documents, delays for issues |
You should note that different banks have varying minimum deposit requirements. Generally, the minimum for fixed deposits is USD 1,300 (approximately HKD 10,000), but some banks may have higher thresholds. It’s best to compare requirements and promotions from several banks before deciding where to open an account.
Deposit Types
When planning to make a fixed deposit, you first need to understand the different deposit types. Each type has its own features and suits different people. You can choose the most suitable option based on your cash flow and financial goals. Below, I’ll introduce the four common types of fixed deposits one by one.
Time Deposit (Lump-Sum Deposit with Lump-Sum Withdrawal)
This is the most popular fixed deposit method. You deposit a lump sum at once and withdraw both principal and interest at maturity.
- The minimum deposit amount is typically USD 10,000 (approximately HKD 78,000, calculated at 1 USD = 7.8 HKD), with slight variations across banks.
- Common terms are 1 year, 2 years, or 3 years.
- Suitable for those with idle cash not needed in the short term.
- Many financial experts suggest splitting large funds into multiple fixed deposits with staggered maturities for greater flexibility. For example, if you have USD 240,000, you can split it into 12 deposits of USD 20,000 each, maturing at different times.
Tip: Interest for lump-sum deposits is typically paid at maturity.
Principal Retained with Interest Withdrawn
You deposit the principal at once but can withdraw interest monthly. This method suits those who want a steady cash flow, such as retirees or people needing regular income.
- The principal is withdrawn at maturity.
- Interest is paid monthly or quarterly, convenient for daily expenses.
Regular Savings with Lump-Sum Withdrawal
You deposit a small fixed amount monthly and withdraw both principal and interest at maturity. This method is ideal for those looking to build savings habits or with steady but modest income.
- Common terms are 1 year, 2 years, or 3 years.
- Suitable for students or recent graduates.
Lump-Sum Deposit with Regular Interest Payments
You deposit the principal at once, but interest is paid periodically. This method is similar to principal retained with interest withdrawn but may differ in interest payment frequency.
- Suitable for those needing regular interest payments without monthly operations.
- Interest may be paid semi-annually or annually.
When choosing a fixed deposit type, consider your cash flow needs and financial goals. Different methods have different advantages, so pick the one that suits you best!
Interest Rate Selection
Fixed Interest Rate
When choosing a fixed deposit, the most common option is a fixed interest rate. A fixed interest rate means your interest remains unchanged regardless of market fluctuations. This method suits those who want stable returns and avoid risks.
- The interest rate remains constant during the deposit or loan period.
- Suitable for those worried about future rate declines.
- You can clearly know how much interest you’ll receive after each calculation.
Currently, fixed interest rates at Hong Kong banks generally range from 2.2% to 3.7%. If you opt for new funds promotions, you may get higher rates. However, these promotions usually apply only to funds transferred from other banks.
Tip: Fixed-rate products make it easier to plan future cash flows, especially for conservative investors.
Floating Interest Rate
A floating interest rate (also called variable rate) adjusts with market rates. If you expect rates to rise in the future, choosing a floating rate may yield higher interest. However, if rates fall, your interest will decrease.
- Rates adjust based on Hong Kong banks’ fixed deposit rate index.
- Floating rate products typically have upper and lower limits, adjusted periodically by banks based on market conditions.
- For example, some life insurance companies’ floating rate products have USD-denominated rates ranging from 4.65% to 9%, but actual rates vary based on market and product terms.
| Bank/Company Name | USD-Denominated Rate Range | Rate Adjustment Method |
|---|---|---|
| Hung Thai Life | 4.65%–9% | Declared rate +0.75% to +2.75%, adjusted by market |
| Chunghwa Post | 4%–6.25% | Predetermined rate calculated in segments |
| Taiwan Life | 6.5%–9% | Declared rate plus 2.0%–2.5% |
Note: Floating rate products may offer higher interest but are more volatile, suitable for those willing to accept some risk and benefit from rising rates.
Interest Rate Comparison
You might wonder whether to choose a fixed or floating rate?
- Fixed rates provide peace of mind, suitable for those seeking stable returns.
- Floating rates suit those willing to accept rate fluctuations and hope to earn more when market rates rise.
- Currently in Hong Kong, the gap between fixed and floating rates is not significant, and long-term interest differences are limited.
- Regular savings with lump-sum withdrawal often use floating rates, offering higher interest than current accounts, ideal for forced savings.
When choosing a rate, keep these points in mind:
- Deposit threshold: Some banks require a minimum deposit of USD 1,300 (approximately HKD 10,000).
- Principal cap: Some promotional rates apply only to certain amounts.
- New funds definition: Typically, only funds transferred from other banks qualify for high-rate promotions.
- Rate fluctuations: Floating rate products adjust with the market, while fixed rates are more stable.
It’s recommended to choose the most suitable rate plan based on your financial goals, cash flow needs, and risk tolerance. When calculating interest, compare terms and promotions from different banks.
Interest Calculation

Image Source: unsplash
Do you want to know how much interest you can earn from a fixed deposit? In fact, calculating interest is not difficult. As long as you master the basic formula and use practical examples, you can easily calculate your actual returns. However, different deposit types, interest payment methods, and early withdrawal terms in the market will affect the final amount you receive. You need to learn to distinguish them to avoid pitfalls.
Calculation Formula
The most commonly used formula for calculating fixed deposit interest is as follows:
Interest = Principal × Annual Interest Rate × Deposit Days ÷ 365
- Principal: The amount you deposit in the bank (e.g., USD 10,000)
- Annual Interest Rate: The bank’s announced fixed deposit annual rate (e.g., 3%)
- Deposit Days: The chosen deposit term (e.g., 1 year = 365 days, half-year = 182 days)
If you choose a “lump-sum deposit with lump-sum withdrawal,” interest is typically paid at maturity.
If you choose “principal retained with interest withdrawn” or “lump-sum deposit with regular interest payments,” the bank will pay interest monthly, quarterly, or annually. Note that the interest payment frequency affects the actual amount you receive.
Tip: Some banks use 360 days as the basis for a year, so check the bank’s terms to avoid calculation errors.
Practical Examples
You might wonder how actual returns differ across deposit types. I’ll break it down with a few examples:
- Suppose you have USD 10,000 for a 1-year fixed deposit at a 3% annual rate, with an exchange rate of 1 USD = 7.8 HKD.
- Lump-Sum Deposit with Lump-Sum Withdrawal
- You deposit USD 10,000 at once and withdraw principal and interest after 1 year.
- Interest = 10,000 × 3% × 365 ÷ 365 = USD 300
- At maturity, you can withdraw USD 10,300.
- Principal Retained with Interest Withdrawn
- You deposit USD 10,000 at once and receive interest monthly.
- Monthly interest = 10,000 × 3% ÷ 12 = USD 25
- After 1 year, you receive USD 300 in total interest, and the USD 10,000 principal is withdrawn at maturity.
- Regular Savings with Lump-Sum Withdrawal
- You deposit USD 1,000 monthly for 12 months at a 3% annual rate.
- Since each deposit has a shorter average holding period, total interest is less than lump-sum deposits.
- Interest = 1,000 × 3% × (12+11+…+1) ÷ 12 ÷ 12
- Actual interest is approximately USD 195 (due to varying deposit durations).
- Lump-Sum Deposit with Regular Interest Payments
- You deposit USD 10,000 at once, and the bank pays interest semi-annually.
- Semi-annual interest = 10,000 × 3% ÷ 2 = USD 150
- After 1 year, you receive two interest payments totaling USD 300, with the principal withdrawn at maturity.
You should know that some income-generating products (e.g., funds) pay distributions based on investment gains or principal. Distributions from investment gains are more stable, while those from principal carry higher risks. Pay attention to the distribution source, as higher distribution amounts don’t always mean better returns. Fund size changes and net asset value fluctuations affect your final amount. You can refer to the company’s website for distribution data over the past 12 months. However, past distributions don’t guarantee future returns.
Note: When calculating interest, don’t just look at the nominal rate; consider distribution sources, fees, and principal changes.
Taxes and Actual Returns
After receiving interest, you also need to consider taxes and other fees.
- In Hong Kong, fixed deposit interest is generally tax-exempt, but overseas products or funds may require tax payments.
- Some banks deduct handling or management fees before paying interest, so ask if there are such charges.
- If you withdraw early, banks typically reduce interest significantly or return only the principal. Read contract terms carefully to understand penalty calculations.
| Item | Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Payment Frequency | Monthly, quarterly, or at maturity |
| Taxes | Hong Kong fixed deposit interest is generally tax-exempt |
| Early Withdrawal | May return only principal or reduced interest |
| Management Fees | Some products deduct management fees |
When calculating interest, include all fees, taxes, and penalties to know exactly how much you’ll receive. Don’t focus only on the nominal rate; the actual amount you get is what matters most.
Tip: Use the bank’s online fixed deposit calculator, inputting principal, rate, and term, to quickly calculate actual returns.
Maturity Options
When your fixed deposit matures, you typically have three options: automatic renewal, withdrawal, or early termination. Each option has different benefits and risks, so choose based on your needs.
Renewal
You can choose automatic renewal, allowing the principal and interest to continue accruing at the bank. This method suits those who don’t need the funds immediately and want to keep earning interest.
- Benefit: No worry about idle funds; interest accumulates automatically.
- Risk: The new term’s rate may be lower than before, and banks may not notify you of rate changes.
- Pitfall: Some banks renew at the lowest rate available. Regularly check bank notifications to avoid missing higher-rate opportunities.
Tip: A week before maturity, check the bank’s latest rates to decide whether to renew.
Withdrawal
You can choose to withdraw the principal and interest at maturity, transferring them to your account. This option suits those with funding needs or seeking higher rates at other banks.
- Benefit: Flexible use of funds for investment or spending.
- Risk: Forgetting to notify the bank may lead to automatic renewal, missing the withdrawal window.
- Pitfall: Some banks require 1–2 days’ notice, or you may need to wait until the next business day to withdraw.
Note: Verify the amount upon withdrawal to ensure both principal and interest are correctly credited.
Early Termination
If you urgently need funds, you can terminate early. However, this option usually involves penalties or interest losses.
- Benefit: Funds are available immediately for urgent needs.
- Risk: Most Hong Kong banks return only the principal upon early termination, with significant or total interest loss.
- Pitfall: Some banks charge fees or calculate interest for the elapsed period at extremely low rates.
| Bank Name | Early Termination Handling | Penalty Terms |
|---|---|---|
| HSBC | Returns principal only, no interest | No additional fees |
| Hang Seng | Returns principal + minimal interest | Interest as low as 0.01% |
| Bank of China Hong Kong | Returns principal only | Requires advance notice, or processing delayed |
Tip: Before terminating early, ask about the bank’s penalty terms and calculate actual losses.
Whichever option you choose, base it on your financial plans and goals. Regularly check bank notifications to avoid missing the best timing.
Tools Comparison
If you want to manage your finances, there are many options available. Fixed deposits, savings insurance, current accounts, funds, bonds, etc., each have different risks and returns. Choose the product that best suits your needs and risk tolerance.
Savings Insurance
You might consider savings insurance, as it offers slightly higher returns than fixed deposits. For single-premium savings insurance, annual rates range from about 2.15% to 2.48%, roughly 1% higher than typical fixed deposits. However, savings insurance has three main risks:
- Credit risk (loss of principal if the insurer goes bankrupt)
- Interest rate risk (policy rates may not keep up if market rates rise)
- Liquidity risk (funds are tied up for longer periods, with early withdrawal causing principal and interest losses)
You can refer to the comparison below:
| Comparison Item | Fixed Deposit | Savings Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Range | Approx. 0.35%–1.05% | Approx. 1.5%–2% |
| Risk | Lowest risk, strong principal protection | Credit, interest rate, and liquidity risks |
| Liquidity | Higher | Lower, requires longer commitment |
| Withdrawal Loss | Interest loss only | Possible principal and interest loss |
| Return Stability | Stable | Higher but not guaranteed |
Tip: If you seek stability and flexibility, fixed deposits are more suitable.
Current Accounts
The biggest advantage of current accounts is that funds can be withdrawn anytime, offering high flexibility. However, returns are typically lower than fixed deposits. If you need funds readily available, current accounts are convenient, but they earn minimal interest.
Check the average expected yields for different terms:
| Product Term | Average Expected Yield |
|---|---|
| 1 month or less | Approx. 3.93% |
| 1–3 months (inclusive) | Approx. 5.10% |
| 3–6 months (inclusive) | Approx. 5.33% |
| 6 months–1 year (inclusive) | Approx. 5.50% |
| Over 1 year | Approx. 5.98% |
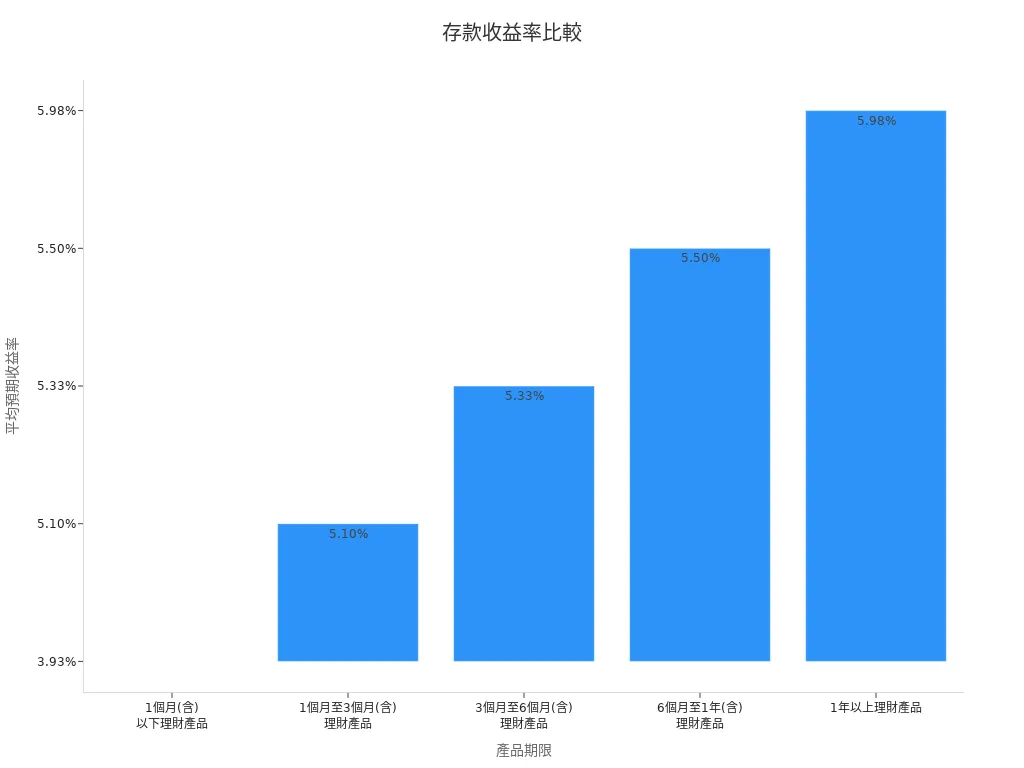
Note: Current accounts suit those needing high liquidity, but for higher interest, consider fixed deposits or other financial products.
Other Financial Products
If you seek higher returns, consider funds or bonds. However, these products carry higher risks and require some investment knowledge. For example, US large-cap stocks have an annualized return of about 10.89% over the past 40 years, but the largest single-year decline was -37.02%. Bonds have lower volatility but also lower returns than stocks.
Below are historical annualized returns and maximum drawdowns for different asset classes:
| Asset Class | Annualized Return (Approx. 40 Years) | Largest Single-Year Decline |
|---|---|---|
| US Large-Cap Stocks | Approx. 10.89% | -37.02% |
| Short-Term Treasuries | Approx. 5.82% | -4.71% |
| Investment-Grade Bonds | Approx. 5.91% | -5.85% |
| High-Yield Bonds | Approx. 8.45% | -21.29% |
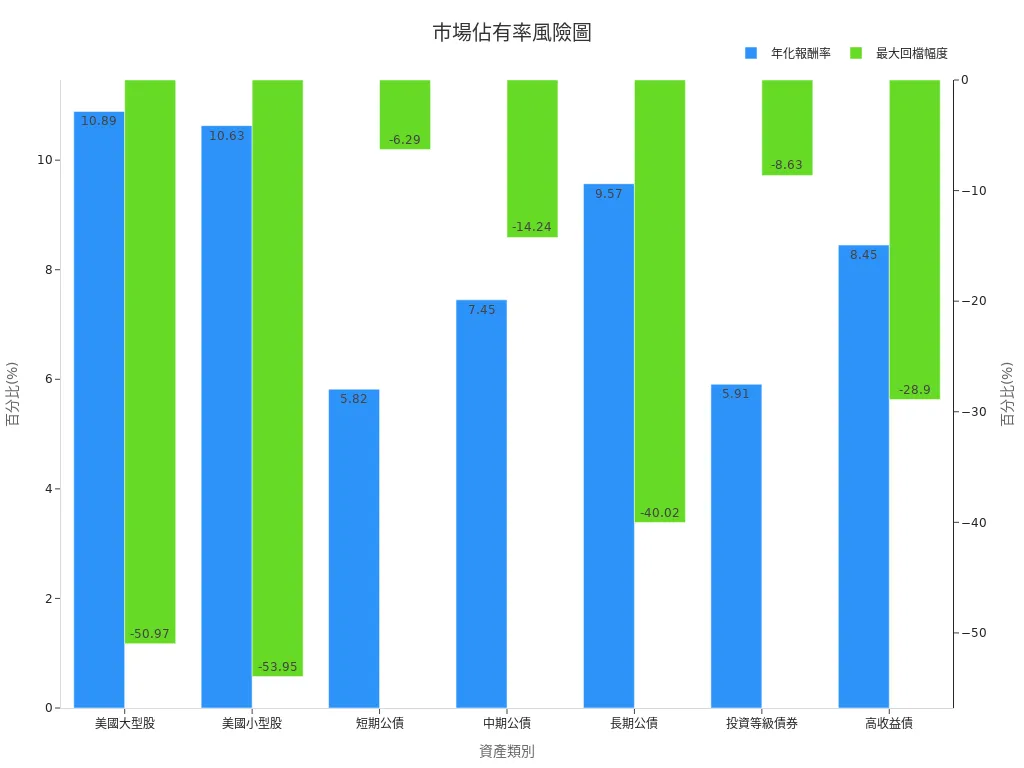
Reminder: Funds and bonds offer high returns but also high risks. Choose based on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
As a beginner seeking capital safety and stable returns, fixed deposits are the simplest and safest choice. Compare rates and promotions from different banks to find the best option.
You should choose the most suitable fixed deposit plan based on your financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. Pay attention to details like rates, maturity options, and early withdrawal terms. Common beginner mistakes include ignoring rate changes, forgetting maturity dates, or misunderstanding penalty terms. Follow the steps in this guide to confidently take your first step in financial management and gradually learn about other financial tools.
FAQ
Can you terminate a fixed deposit early at any time?
You can terminate early, but most Hong Kong banks return only the principal, with significant or total interest loss. Check penalty terms before opening an account.
Is there a minimum deposit requirement for fixed deposits?
Yes. Hong Kong banks generally require a minimum deposit of USD 1,300 (approximately HKD 10,000, calculated at 1 USD = 7.8 HKD). Thresholds vary, so compare banks.
Is interest taxed?
In Hong Kong, fixed deposit interest is generally tax-exempt. For products in mainland China or elsewhere, you may need to pay taxes, so check carefully.
Are funds automatically transferred to your account at maturity?
Not necessarily. Some banks renew automatically, while others transfer funds. Check with the bank before maturity to avoid funds being locked.
Can you open a fixed deposit via online banking?
Yes. Prepare your ID and proof of address, log into a Hong Kong bank’s online platform, and apply conveniently without queuing.
Fixed deposits offer beginners a secure path to stable returns, with clear steps for account opening and interest calculations to kickstart your financial journey. BiyaPay empowers you to expand your wealth-building strategy, enabling investment in U.S. and Hong Kong stocks through one account, bypassing complex setups for these markets. Access a wealth management product with up to 5.48% annualized returns, featuring flexible withdrawals to meet dynamic needs.
BiyaPay’s real-time currency conversions and rate queries keep transfer costs as low as 0.5%, maximizing returns. Regulated by international financial authorities, it ensures secure transactions. Visit BiyaPay today to start investing in U.S. and Hong Kong stocks, complementing fixed deposits for a robust financial plan!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















