- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
A Complete Guide to the Cost of Living in Malaysia

Image Source: pexels
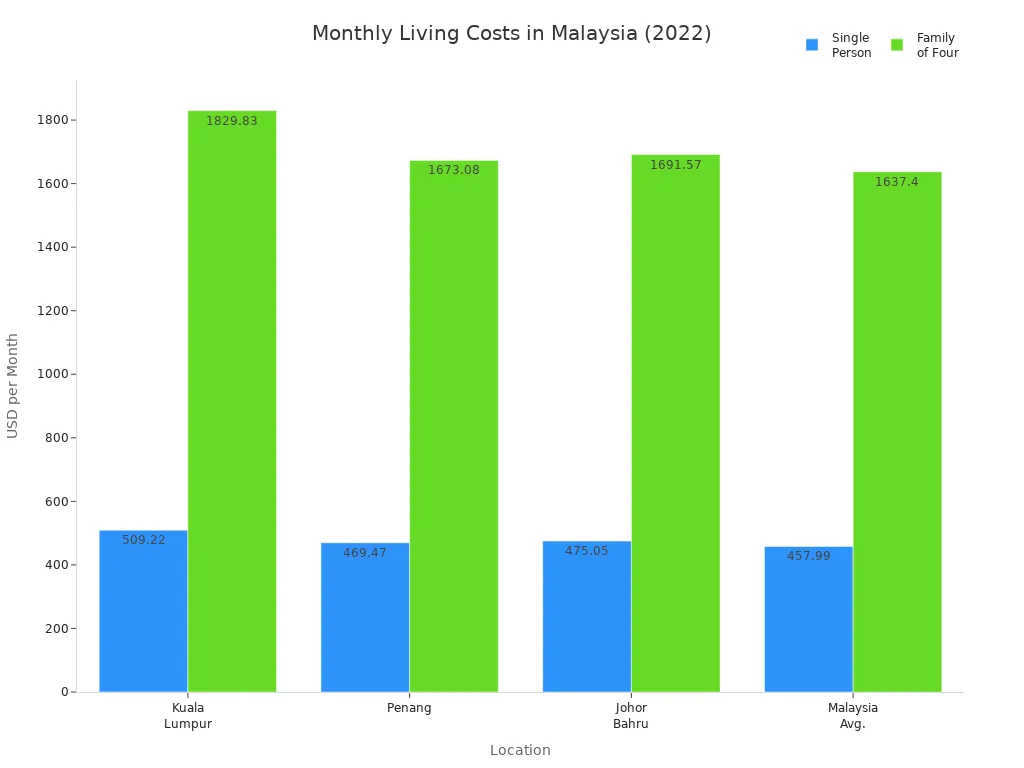
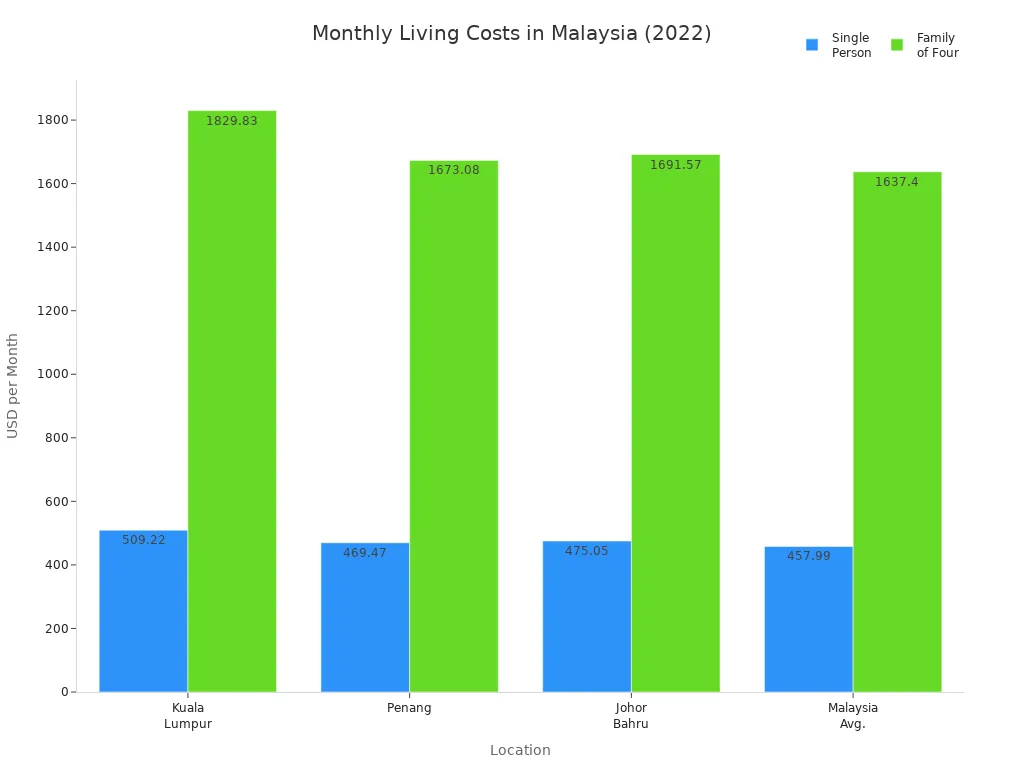
Wondering how much you need to live comfortably in Malaysia? For a single person, the average monthly cost sits around $458. Couples spend about $700–$850, while a family of four usually pays between $1,200 and $1,400 each month in big cities like Kuala Lumpur. Check out the table below for a quick look:
| Household Type | Average Monthly Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Single | 458 |
| Couple | 700–850 |
| Family of Four | 1,200–1,400 |
You’ll find the cost of living in Malaysia much lower than in the UK or US, where prices often double or even triple. Most of your budget goes to food, housing, and daily needs. With a cost of living index of 30.0, Malaysia stands out for its affordability in Southeast Asia.
Key Takeaways
- Living in Malaysia is affordable, with monthly costs around $458 for singles and up to $1,400 for families in big cities.
- Rent and food are the largest expenses, but cooking at home and using public transport can save you money.
- You can choose from short-term or long-term housing options, with rents varying by city and location.
- Public transport is cheap and reliable, so owning a car is not necessary in major cities.
- Tracking your expenses and planning your budget helps you live comfortably and save money in Malaysia.
Cost of Living Overview
Average Monthly Expenses
When you look at the cost of living in Malaysia, you will notice that your money goes a lot further here than in many other countries. The average cost in Malaysia for a single person ranges from RM 2,000 to RM 3,500 each month. If you are a couple, you might spend up to RM 10,000. For a family of four, the monthly cost is around RM 10,084. These numbers cover your main expenses like rent, food, utilities, and transportation.
Here’s a breakdown of what you might spend each month in Kuala Lumpur:
| Expense Category | Single Person (RM) | Couple (Estimated RM) | Family of Four (RM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rent (1-bedroom apartment) | 1,532 - 2,452 | N/A | 2,679 - 4,539 (3-bedroom apartment) |
| Utilities (Electricity, Water, Garbage) | 257 | ~400 (estimated) | 257 (per apartment, likely similar) |
| Internet & Mobile Phone | 153 (108 + 46) | ~153 (shared) | 153 (shared) |
| Food (per meal) | Breakfast: 10 | ~20 (2x single) | Breakfast: 40 (4x10) |
| Lunch: 15 | ~30 | Lunch: 60 | |
| Dinner: 15-20 | ~30-40 | Dinner: 60-80 | |
| Transportation (monthly pass) | 50 | ~100 (2x single) | 50 (family may use multiple passes) |
| Childcare (per child) | N/A | N/A | 1,133 (preschool) |
| Total Monthly Cost (excluding rent) | 2,549 | ~4,000 (estimated) | 9,053 |
You can see that rent is usually the biggest part of your budget. Utilities and internet are quite affordable. Food costs depend on whether you eat out or cook at home. If you have children, childcare will add to your monthly expenses.
Tip: If you want to save more, try cooking at home and using public transport. Many expats say these two changes help lower their cost of living in Malaysia.
International Comparison
You might wonder how the average cost in Malaysia stacks up against other countries. The answer might surprise you. Malaysia offers one of the lowest costs of living in the region. Let’s look at the numbers:
| Country | Average Monthly Expenses (USD) |
|---|---|
| United States | 2,504 |
| Thailand | 877 |
| United Kingdom | 2,390 |
| Singapore | 5,821 |
Malaysia’s average monthly expenses are much lower than those in the US, UK, and Singapore. Even compared to Thailand, Malaysia remains very competitive. The cost of living index for Malaysia is 31.7, which is far below Singapore’s 78.0 and the UK’s 90.8.
Many expats choose Malaysia because they get great value for their money. Surveys show that expat satisfaction rates are high, especially for those who want a comfortable lifestyle without spending a fortune. Malaysia often ranks among the top countries for affordability and quality of life.
Note: The cost of living in Malaysia can change depending on your lifestyle and the city you choose. Kuala Lumpur and Penang are popular with expats, but smaller cities can be even more affordable.
Housing Costs
Image Source: unsplash
Renting in Major Cities
When you look for accommodation in Malaysia, you will notice that the cost of accommodation depends a lot on the city and the type of place you choose. In Kuala Lumpur, the cost of renting a modest one-bedroom apartment outside the city center starts at about $430 USD (RM2,000) per month. If you want a nicer apartment in a good location, the monthly rent can go up to $750 USD (RM3,500) or more. In Penang and Johor Bahru, rental prices are rising, but you can still find options that fit different budgets.
Here’s a quick look at average monthly rent in major cities (using 1 USD ≈ RM4.65):
| City | Average Monthly Rental Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Kuala Lumpur | $430+ for modest 1-bedroom; $750+ for nicer units |
| Penang | Prices rising; varies by area |
| Johor Bahru | Prices rising; varies by area |
Tip: You can often save money by choosing accommodation a bit farther from the city center.
Buying Property
If you plan to stay in Malaysia for a long time, you might think about buying property. The cost of accommodation for buyers depends on the state and whether you are a foreigner. For example, in Kuala Lumpur, foreigners need to buy property worth at least $215,000 USD (RM1 million). In Penang, the minimum price for landed property is even higher. You also need to pay fees like stamp duty, legal fees, and sometimes agent fees.
When you sell property, you may have to pay Real Property Gains Tax (RPGT). The rate depends on how long you own the property. If you sell within three years, the tax is 30%. After six years, foreigners pay 10%.
Note: Always check the latest rules before buying, as property laws and taxes can change.
Short vs Long-Term Options
You can choose between short-term and long-term accommodation in Malaysia. Short-term rentals, like those on Airbnb, let you stay from one night up to three months. These options give you flexibility and often cost less than hotels. Long-term rentals usually offer better value if you plan to stay for several months or more. For example, in Kuala Lumpur, a studio apartment can cost $320–$860 USD (RM1,500–RM4,000) per month for long-term stays.
| Location | Studio (Serviced Apartment) | Entire House (Double-story) |
|---|---|---|
| Kuala Lumpur | $320–$860 | $860–$1,500 |
| Penang | $340–$470 | $430–$860 |
| Selangor | $70–$540 | $430–$860 |
Short-term rentals are great for travelers or people who want to try out different neighborhoods. Long-term rentals help you save on the cost of accommodation if you plan to settle down.
Food and Groceries
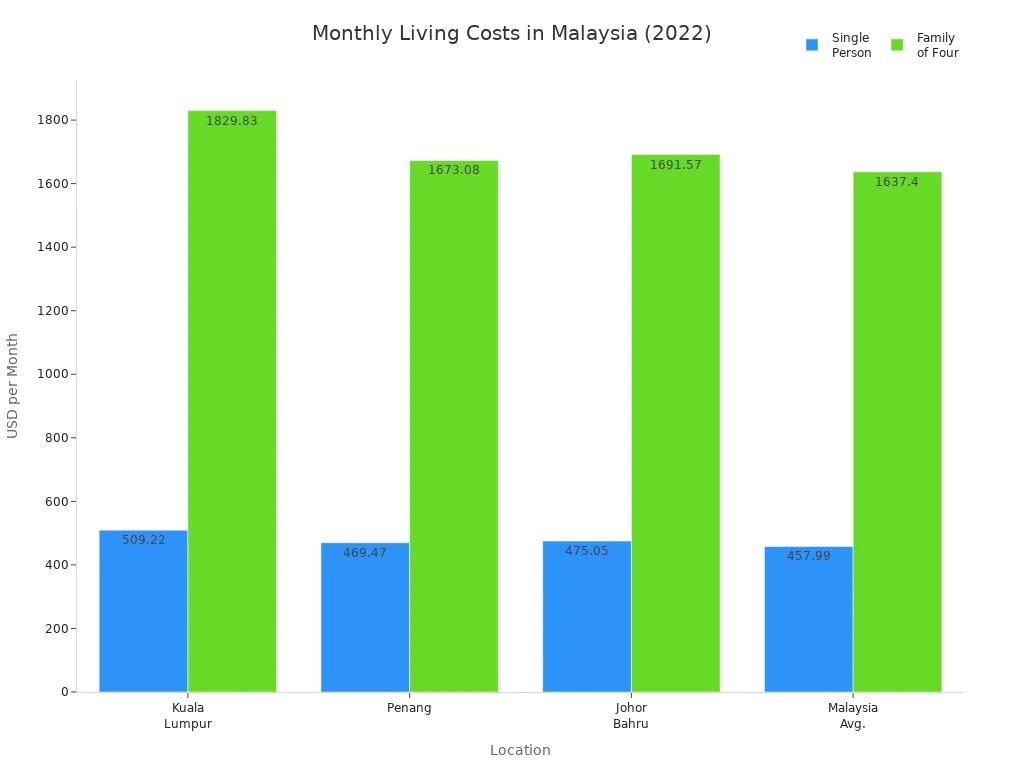
Image Source: unsplash
Grocery Prices
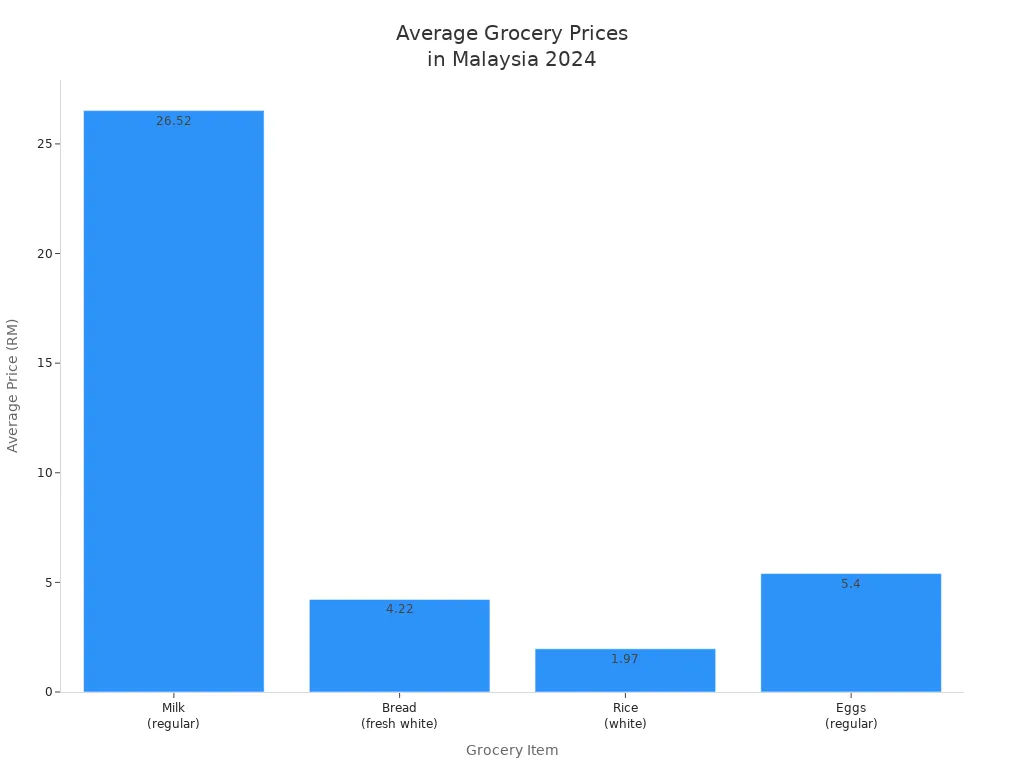
When you shop for basic groceries in Malaysia, you will notice that prices are much lower than in the US. You can find fresh milk, bread, rice, and eggs at local supermarkets or wet markets. Here is a table showing the average prices in 2024. The exchange rate is about 1 USD = 4.65 RM.
| Item | Average Price (RM) | Average Price (USD) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk (regular) | 29.14 | $6.27 | 1 gallon |
| Bread (fresh white) | 4.22 | $0.91 | 1 lb |
| Rice (white) | 2.80 | $0.60 | 1 lb |
| Eggs (regular) | 7.92 | $1.70 | 12 eggs |
You can see that food prices for these items are quite affordable. In the US, you might pay double for the same groceries.
Tip: Shopping at local markets often gives you fresher produce and better deals than big supermarkets.
Eating Out
Eating out in Malaysia is a big part of daily life. You can grab a meal at a street stall for less than $1. Local restaurants usually charge between $3.60 and $7.20 per person. If you want Western food like pizza or burgers, expect to pay $3.60 to $12 or more. International or mid-range restaurants cost about $7.20 to $14.40 per meal. Fine dining starts at $14.40 and goes up from there. Penang is famous for tasty and cheap local food, while Kuala Lumpur has more options for international cuisine.
| Restaurant Type | Average Cost per Person (USD) |
|---|---|
| Street Food / Local Stalls | Less than $1 |
| Local Malaysian Restaurants | $3.60 - $7.20 |
| Western Food (Pizza, Burgers, Spaghetti) | $3.60 - $12+ |
| Mid-range / International | $7.20 - $14.40 |
| Fine Dining | $14.40+ |
Monthly Food Budget
Your monthly food budget in Malaysia depends on your lifestyle. If you cook at home and eat local food, you can save a lot. Here is a guide to what you might spend each month:
| Household Type | Typical Monthly Food Budget (USD) | Notes on Lifestyle and Food Choices |
|---|---|---|
| Single Person | $86 - $129 | Local groceries, simple meals |
| Couple | $430 | Mix of groceries, eating out, alcohol |
| Family | $645 | Groceries, eating out, some international food |
If you love eating out or prefer international food, your budget will be higher. Many expats say that Malaysia offers great value for both groceries and dining out.
Transportation
Getting around in Malaysia is easy and affordable. You have many options for transport in malaysia, from public buses and trains to owning a car or taking a quick flight between cities. Let’s look at what you can expect for the cost of transport in malaysia.
Public Transport
Public transport in malaysia is reliable and covers most big cities. You can use local buses, trains like the KTM and LRT, taxis, or ride-hailing apps such as Grab. Most people find public transport in malaysia cheap and convenient. Here’s a quick look at what you might pay:
| Transportation Mode | Average Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Local Buses | $0.20 - $1 | Common within cities |
| Trains (KTM, LRT) | $0.30 - $1.50 | Efficient, many routes |
| Taxis | $2 - $5 | Short rides, negotiate fare |
| Ride-hailing (Grab) | Varies by distance | Easy to book, good value |
Tip: If you want to save money, use buses and trains for daily travel. They are safe and help you avoid traffic jams.
Car Ownership
Some people prefer to drive in malaysia, especially if they live outside city centers. Owning a car gives you more freedom, but the cost of transport goes up. Here’s a breakdown of what you might spend each month if you own a car:
| Expense Category | Estimated Monthly Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Car Loan Instalment | $683 | Based on a typical loan for a mid-range car |
| Fuel (Petrol) | $41 | For about 1,200 km per month |
| Parking | $127 | Includes work, home, and leisure spots |
| Toll | $26 | For daily commutes |
| Insurance | $51 | Comprehensive coverage |
| Road Tax | $7 | Annual fee divided monthly |
| Maintenance | $27 | Regular service and repairs |
| Tyres | $19 | Replacement every three years |
| Car Wash | $17 | Weekly cleaning |
| Total | $998 |
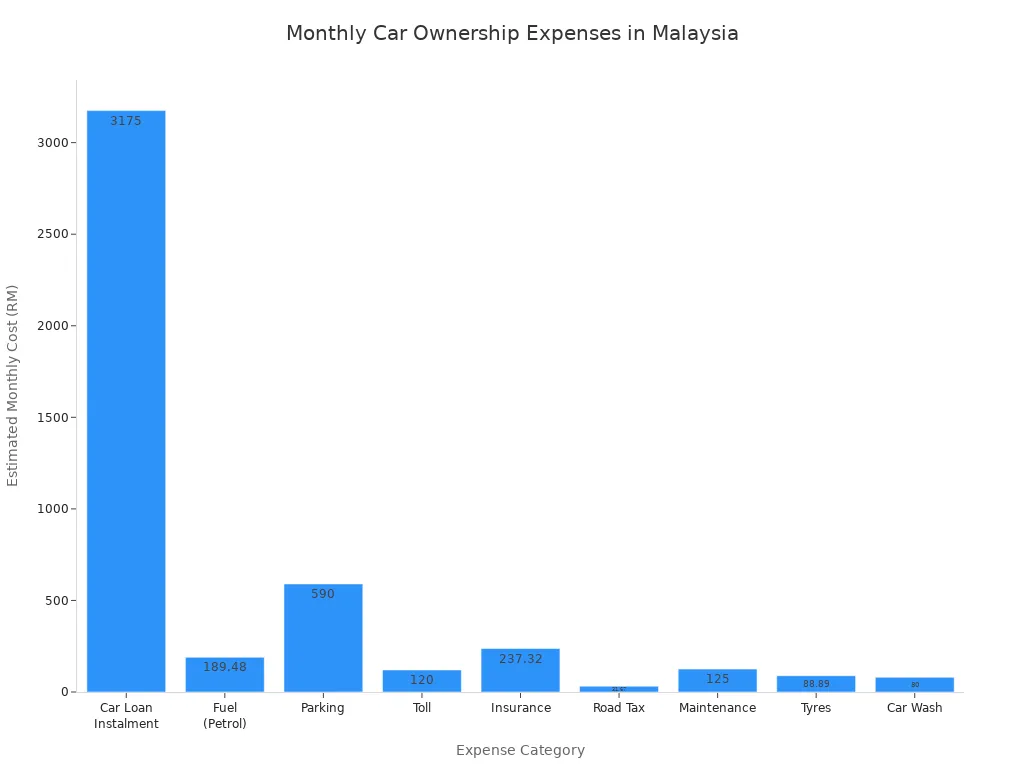
You can see that the cost of transport in malaysia is much higher if you own a car. Many people choose public transport in malaysia to avoid these extra costs.
Domestic Travel
Traveling between cities in malaysia is simple. You can take a bus, train, or even a domestic flight. Buses and trains are affordable, while flights save time for longer trips. Here’s what you might pay:
| Transportation Mode | Average Cost (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Intercity Buses | $5 - $20 | Good for longer distances |
| Intercity Trains | Under $1 (short trips) | $5 - $20 for longer trips |
| Domestic Flights | Higher, varies | Best for fast travel between cities |
| City Taxi Rides | $2 - $5 | Typical city fare |
| Ride-hailing (Grab) | Varies by distance | Available in most cities |
You can plan your trips based on your budget and how fast you want to get there. Many people use buses and trains for the best value.
Note: The cost of transport in malaysia changes by city and travel style. Always check the latest prices before you go.
Utilities and Internet
Utility Bills
When you live in malaysia, you will find that utility bills are quite reasonable. Most people pay for electricity, water, and garbage collection each month. If you rent an apartment, your landlord may include some of these costs in your rent. For a typical apartment in a city like Kuala Lumpur, you can expect to pay about $55–$90 USD per month for electricity. Air conditioning can push your bill higher, especially during hot months. Water bills are usually low, often less than $5 USD per month. Garbage collection is often included in your rent or maintenance fees.
If you use gas for cooking, you will buy gas cylinders. One cylinder costs about $6–$8 USD and can last a month or more, depending on how much you cook. Many apartments in malaysia use electric stoves, so you might not need to worry about gas at all.
Tip: Turn off lights and air conditioning when you leave a room. This simple habit helps you save money on your electricity bill in malaysia.
Internet and Mobile
Staying connected in malaysia is easy and affordable. You can choose from many internet and mobile plans. Most homes use fiber broadband. Entry-level fiber plans (30–50 Mbps) cost about $17–$19 USD per month. If you want faster speeds, a 100 Mbps plan is around $28 USD, and a 300 Mbps plan is about $32 USD. Gigabit plans are available for heavy users and cost $75–$86 USD per month.
Mobile phone plans in malaysia are also budget-friendly. Prepaid daily passes start at just $0.20–$0.65 USD. A monthly prepaid bundle with 20 GB of data costs about $6.50 USD. Unlimited data plans range from $7.50–$12 USD per month, but speeds may slow down after you use a certain amount. Postpaid plans with unlimited calls and 40–50 GB of data cost $13–$17 USD per month. If you have a family, you can get a shareable plan for four lines with 1 TB of data for about $28 USD per month.
Here’s a quick look at typical internet and mobile costs in malaysia:
| Service Type | Plan Description | Average Monthly Cost (USD) | Data/Speed Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Broadband | Entry-level fiber (30–50 Mbps) | 17–19 | Unlimited usage |
| Fixed Broadband | Mid-tier (100 Mbps) | 28 | Unlimited usage |
| Fixed Broadband | Higher-tier (300 Mbps) | 32 | Unlimited usage |
| Fixed Broadband | Gigabit plans | 75–86 | Unlimited usage |
| Mobile Prepaid | Daily 1 GB pass | 0.20–0.65 | Daily validity |
| Mobile Prepaid | Monthly 20 GB bundle | 6.50 | Monthly validity |
| Mobile Prepaid | Unlimited data plans | 7.50–12 | Speed capped after quota |
| Mobile Postpaid | Unlimited calls + 40–50 GB data | 13–17 | Monthly billing |
| Family Shareable | 4 lines sharing 1 TB data | 28 | Monthly billing |
| Typical Resident | Home broadband + mobile | 28–34 | Combined |
Note: Most apartments in malaysia have good internet coverage. You can sign up for a plan online or at a local store. Many expats say the internet speed in malaysia is fast enough for work, streaming, and video calls.
Healthcare
When you live in malaysia, you will notice that the healthcare system gives you many choices. You can use public hospitals or private clinics, and each option has its own benefits and costs. Let’s break down what you need to know about the cost of healthcare in malaysia.
Public vs Private
Public healthcare in malaysia is very affordable because the government pays most of the bill. You might pay as little as $0.22 USD (RM1) for a visit to a general doctor and $1.10 USD (RM5) for a specialist. These low fees make public hospitals popular, but you may have to wait longer for treatment. Private healthcare costs more, but you get faster service and more choices for doctors. Here’s a quick look at the differences:
| Healthcare Sector | Consultation Fee (General Practitioner) | Consultation Fee (Specialist) | Funding Source | Payment Method | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Healthcare | $0.22 | $1.10 | Government subsidies | Minimal fees | Longer waiting times due to high demand |
| Private Healthcare | $6.45 - $27 | $17.20 - $50.50 | Out-of-pocket/insurance | Upfront payment | Shorter waits, more provider options, higher cost |
You can see that the cost of healthcare in private clinics is much higher than in public hospitals. Many people choose private care when they want quick service or special treatments.
Insurance
Health insurance helps you manage the cost of healthcare in malaysia, especially if you use private hospitals. Local insurance plans are cheaper but have lower coverage limits. Expat insurance plans cost more but cover more services and higher bills. Some plans even reward you for healthy habits. Here’s a look at monthly premiums for different providers:
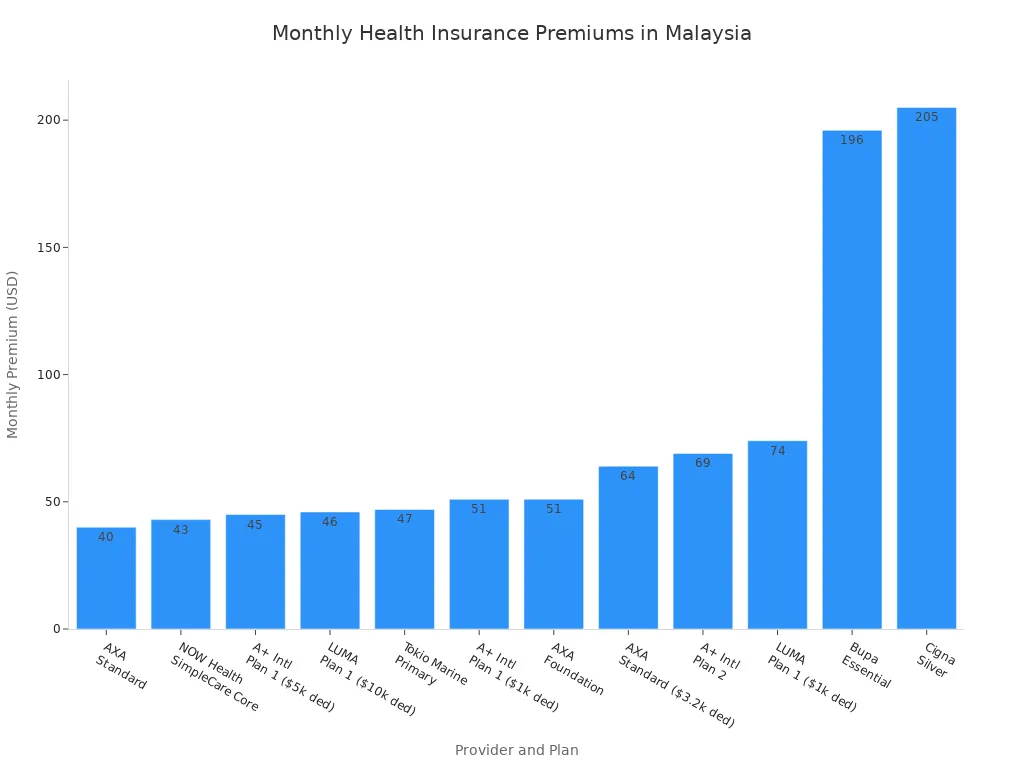
Most local plans cover up to $280,000 USD per year, while expat plans can go up to $1,000,000 USD or more. Monthly premiums range from $40 to over $200 USD. You should pick a plan that fits your needs and budget.
Common Expenses
When you use healthcare in malaysia, you may pay out-of-pocket for some things, even with insurance. Here are the most common expenses:
- Consultation fees for doctors and specialists
- Medications and prescriptions
- Medical procedures and surgeries
- Diagnostic tests like blood work or X-rays
- Medical appliances such as implants or lenses
If you have a serious illness, you might also spend on travel, accommodation, or special food. Private hospitals often charge more for supplies and services, so your cost of healthcare can add up quickly. Insurance helps, but you may still have to pay for things not covered by your plan.
Tip: Always check what your insurance covers before you get treatment. This helps you avoid surprise bills and manage your cost of healthcare in malaysia.
Education
Public and Private Schools
When you move to malaysia with kids, you will want to know about the education system. Public schools in malaysia teach in Malay and follow the national curriculum. Most expat families choose private schools because they offer English instruction and smaller class sizes. The cost of education at private schools is higher than public schools, but many parents feel it is worth it for the extra support and activities.
Here’s a quick look at average annual tuition fees for private schools:
| School Type | Level | Average Annual Tuition Fee (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Private Schools | Primary | $3,860 – $3,975 |
| Private Schools | Secondary | $4,615 – $5,210 |
Public schools charge very little, but private schools can add up. You should also plan for extra costs like uniforms, books, and activities. The cost of education in malaysia depends on your choices and your child’s needs.
International Schools
International schools in malaysia attract families from all over the world. These schools offer British, American, or IB programs. You will find international schools in cities like Kuala Lumpur, Johor Bahru, and Penang. The cost of education at these schools ranges from $645 to over $6,450 per year. Some cities, such as Ipoh-Perak and Kuching, have international schools with median fees as low as $2,725 per year. This is much lower than in cities like Beijing or Singapore.
International schools often have extra fees for enrollment, uniforms, and after-school clubs. When you compare the cost of education in malaysia to other Asian countries, you will see that malaysia offers great value for international education.
Tip: Always ask about hidden fees before you enroll your child. This helps you plan your budget and avoid surprises.
Higher Education
Malaysia is a popular place for higher education. You can choose between public and private universities. Public universities charge lower tuition fees, but private universities offer more programs in English. The cost of education for a bachelor’s degree at a public university is about $2,365 to $5,320 per year. Private universities charge between $1,720 and $10,750 per year. Some private programs can cost up to $23,655 for a full degree.
| Institution Type | Annual Tuition Fee Range (USD) |
|---|---|
| Public Universities | $2,365 – $5,320 |
| Private Universities | $1,720 – $10,750 |
You should also think about living expenses, which can add to the total cost of education. Many students in malaysia say the quality of education is high, and the cost is much lower than in the US or UK.
Other Expenses
Entertainment
You will find plenty of ways to have fun in Malaysia without spending a fortune. Whether you love going to the movies, hitting the gym, or enjoying a night out, you can keep your entertainment budget in check. Here’s a quick look at what you might pay each month for popular activities:
| Entertainment Activity | Average Cost (USD) | Typical Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Gym Membership | $34 | $17 - $54 |
| Cinema Ticket (International Release) | $4.30 | $3.20 - $5.60 |
| 2 Movie Tickets | $8.20 | — |
| Cocktail Drink in Downtown Club | $9.50 | — |
| Monthly Gym (Business District) | $46 | — |
You can see that a night at the movies or a gym membership costs much less than in many other countries. If you enjoy nightlife, a cocktail in a downtown club will set you back about $9.50. Many locals and expats say Malaysia offers great value for entertainment.
Tip: Local festivals and outdoor events are often free or very affordable, so you can enjoy the culture without breaking your budget.
Shopping
Shopping in Malaysia is a favorite pastime for many. You will find everything from luxury malls to bustling street markets. Prices for clothes, electronics, and daily goods are usually lower than in the US. International brands often cost more, but local products and markets offer bargains. If you love fashion, you can pick up a pair of jeans for about $25–$40 or a summer dress for $20–$35. Electronics like smartphones and laptops are sometimes pricier due to import duties, so check prices before you buy.
- Local markets: Great for fresh produce, snacks, and souvenirs.
- Shopping malls: Air-conditioned comfort with a wide range of brands.
- Street vendors: Perfect for unique finds and local crafts.
Note: Bargaining is common at markets, so don’t be shy to ask for a better price.
Taxes
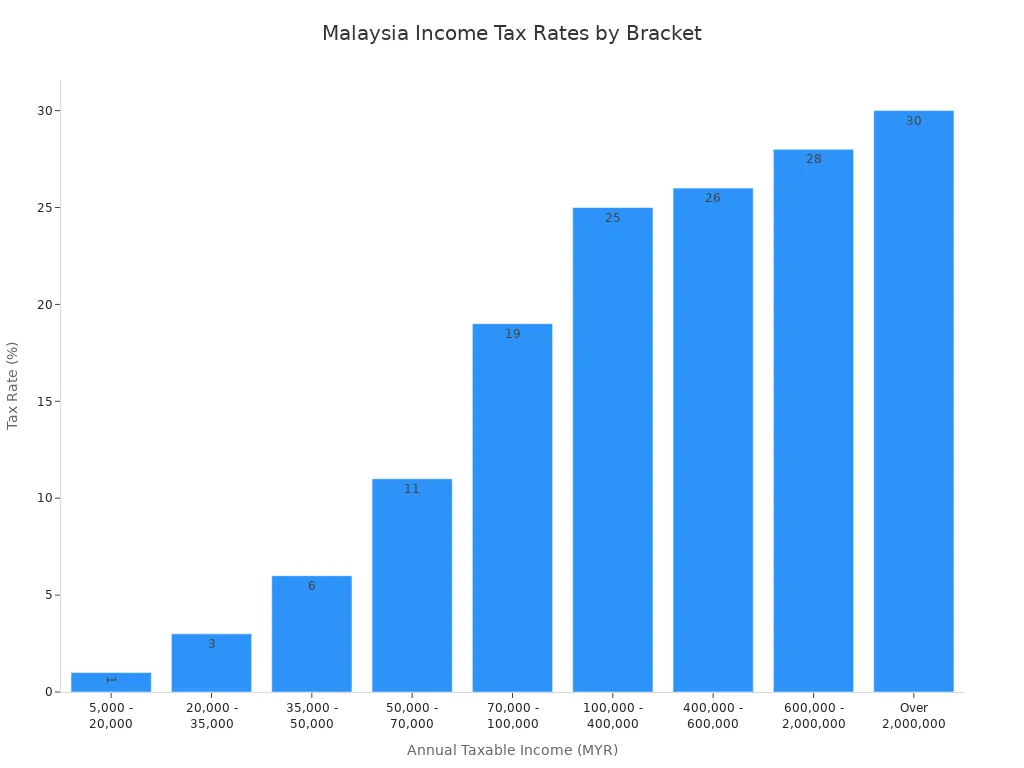
You need to know about taxes if you plan to live or work in Malaysia. The country uses a territorial tax system, so you pay tax only on income earned in Malaysia. Foreign-sourced income is exempt until 2026. Residents pay progressive income tax rates up to 30%, while non-residents pay a flat 30%. Here’s a summary of the main taxes:
| Tax Type | Description | Typical Rates / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Income Tax | Tax on income earned by individuals | Up to 30% for residents; flat 30% for non-residents |
| Sales and Service Tax | Tax on goods and services | Sales tax: 5%-10%; Service tax: 6% |
| Real Property Gains Tax | Tax on gains from property sales | 0%-30% depending on ownership period and residency |
| Stamp Duty | Duty on property transfers and documents | 1%-3% based on transaction value |
| Tourism Tax | Tax on hotel stays for foreigners | Fixed $2.15 per room per night |
If you sell property, the Real Property Gains Tax can reach 30% if you sell within three years. After six years, the rate drops to 10% for foreigners. Always check the latest tax rules, as they can change.
Tip: If you join the Malaysia My Second Home (MM2H) program, you may have special tax considerations. Ask a tax advisor for details.
Budgeting Tips
Saving Money
Living in malaysia gives you many ways to save money every day. You can shop at local markets for fresh fruits and vegetables. These places often have better prices than big supermarkets. Try eating at food stalls or small restaurants. Local dishes cost less and taste great. If you use public transport, you will spend less than driving a car. Many people in malaysia also save by turning off lights and air conditioning when they leave a room. You can look for discounts and deals online before you shop or eat out. Some stores and restaurants offer special prices on certain days.
Tip: Bring your own reusable bag when you shop. Many stores in malaysia charge extra for plastic bags.
Sample Budgets
You might wonder how much you need each month. Here are some sample budgets to help you plan. These numbers use an exchange rate of 1 USD = 4.65 RM.
| Household Type | Rent (USD) | Food (USD) | Transport (USD) | Utilities (USD) | Other (USD) | Total (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | 430 | 100 | 30 | 60 | 50 | 670 |
| Couple | 650 | 200 | 60 | 80 | 80 | 1,070 |
| Family of Four | 1,000 | 350 | 100 | 100 | 150 | 1,700 |
These budgets show you can live well in malaysia without spending a lot.
Expense Tracking
Keeping track of your spending helps you stay on budget. You can use a notebook or a simple spreadsheet. Many people in malaysia use free apps like Mint, Spendee, or Money Lover. These tools let you see where your money goes each month. Set a goal for saving, and check your progress often. If you notice you spend too much in one area, you can make changes right away.
Note: Review your expenses every week. Small changes can help you save more in malaysia.
You now have a clear picture of daily life in malaysia. You can find affordable housing, food, and transportation. If you plan to move, check the latest prices and compare options. Research schools and education choices early. Many expats say malaysia offers great value and a friendly community. Use this guide as your starting point. Good planning helps you enjoy malaysia and get the most from your education journey.
FAQ
How much money do you need to live comfortably in Malaysia?
You can live well on about $700–$1,000 USD per month as a single person. Couples and families will need more. This covers rent, food, utilities, and transport. The exchange rate is about 1 USD = 4.65 RM.
Can foreigners rent or buy property in Malaysia?
Yes, you can rent or buy property. Renting is simple and flexible. If you want to buy, you must meet minimum price rules. For example, in Kuala Lumpur, you need to buy property worth at least $215,000 USD.
Is healthcare expensive for expats in Malaysia?
Healthcare costs less than in the US or UK. Public hospitals charge very little. Private clinics cost more but offer faster service. Many expats buy health insurance for extra peace of mind.
What is the average cost of eating out in Malaysia?
You can eat at local food stalls for less than $1 USD per meal. Restaurants charge $3–$7 USD for local dishes. Western or international food costs more. Eating out often will raise your monthly budget.
Do you need a car to get around in Malaysia?
You do not need a car in big cities. Public transport is cheap and easy to use. Buses, trains, and ride-hailing apps like Grab work well. If you live outside the city, a car may help you get around.
Living affordably in Malaysia is a major draw, but managing international payments—like sending money home or paying overseas bills—can come with high fees and delays. BiyaPay offers a seamless solution with same-day international transfers and remittance fees as low as 0.5%. It supports real-time exchange rate queries for 30+ fiat and 200+ digital currencies, ensuring transparent pricing with no hidden costs. Pay in 190+ countries with 40+ currencies using Biya EasyCard, compatible with Amazon, eBay, and PayPal, all with no annual fee. For instance, use it to pay international school fees or shop on Amazon while living in Kuala Lumpur, avoiding hefty conversion fees. Complement your budget-conscious lifestyle with BiyaPay’s cost-effective global payments—register in minutes at BiyaPay for hassle-free transactions.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















