- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
A Simple Guide to SWIFT Meaning and How It Operates

Image Source: pexels
SWIFT stands for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. This network connects more than 11,000 financial institutions in over 200 countries. SWIFT meaning centers on secure communication between banks, not the physical transfer of money. The network helps banks and businesses process international payments safely and quickly. Understanding swift meaning gives users the knowledge to manage international transactions better and avoid errors. Knowing how a swift code works can help people and companies send money abroad with confidence.
Key reasons to understand swift meaning and the swift network:
- SWIFT supports secure, reliable messages between banks.
- It enables fast, accurate international transactions.
- Knowledge of swift code and process helps prevent mistakes.
Key Takeaways
- SWIFT is a global network that helps banks send secure messages to process international payments quickly and safely.
- SWIFT codes act like unique ID cards for banks, ensuring money and messages reach the right place without errors.
- The SWIFT network does not move money itself but sends payment instructions that banks use to complete transfers.
- Most SWIFT payments take 1 to 5 business days and may involve fees and delays depending on banks and countries.
- SWIFT offers strong security, wide global reach, and supports many currencies, but newer alternatives may offer faster or cheaper options.
SWIFT Meaning
What Is SWIFT?
The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication, often called SWIFT, is a global financial messaging system. SWIFT meaning refers to a secure network that allows banks and financial institutions to exchange information about payments and transactions. The acronym SWIFT stands for “Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication.” This organization operates as a cooperative, with ownership shared among its member banks and financial institutions. The headquarters sits in Brussels, Belgium. Central banks from G10 countries, the European Central Bank, and the National Bank of Belgium oversee its operations. A board of directors, elected by shareholders, manages the company and ensures it serves the interests of its members.
SWIFT is not a single entity owned by one organization. Instead, it functions as a cooperative society under Belgian law. Each member bank or financial institution has a say in how the SWIFT network operates. This democratic structure ensures transparency and fairness. The board of directors, made up of representatives from different countries, guides the strategic direction of the network. SWIFT’s governance model helps it remain neutral and focused on the needs of the global financial community.
SWIFT meaning does not involve the actual movement of money. Instead, it provides a secure way for banks to send and receive information about payments, account details, and transaction instructions.
The SWIFT messaging network connects more than 11,000 financial institutions in over 200 countries. It acts as a bridge for the international banking system, making it possible for banks to communicate quickly and safely. The network supports the exchange of payment instructions, account statements, and other financial messages. This global financial messaging system is trusted by banks, businesses, and governments around the world.
SWIFT’s Role in Payments
The main role of SWIFT in payments is to provide a standardized platform for secure communication between banks. SWIFT does not transfer money itself. Instead, it sends messages that contain all the details needed for a payment to take place. These messages include information such as the sender’s and receiver’s account numbers, the amount of money, and the purpose of the payment. Banks use this information to settle payments and reconcile accounts.
The SWIFT network handles a massive volume of messages every day. As of December 2022, it transmitted about 44.8 million FIN messages daily, covering transactions worth around $5 trillion. These messages support a wide range of financial activities, including corporate payments, international wire transfers, interbank settlements, and account reconciliation. The table below shows the types of SWIFT messages and their purposes:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Daily Messages Volume | Approximately 44.8 million FIN messages daily (as of December 2022) |
| Daily Transaction Value | Around $5 trillion in transactions per day |
| Types of SWIFT Messages | MT101, MT103, MT202, MT199, MT900, MT910, MT940, MT942 |
| Purpose of Message Types | - MT101: Bulk transfer requests for corporate payments and treasury operations |
| - MT103: Single customer credit transfers, mainly international wire transfers | |
| - MT202: Interbank settlements and treasury operations | |
| - MT199: Informal communications between banks | |
| - MT900: Debit confirmations for account reconciliation | |
| - MT910: Credit confirmations with transaction details | |
| - MT940: Detailed daily account statements | |
| - MT942: Real-time or intra-day transaction updates for cash flow monitoring | |
| Covered Financial Transactions | Corporate payments, international wire transfers, interbank settlements, account reconciliation, intra-day transaction monitoring |
| System Benefits | Secure, efficient, standardized communication between financial institutions worldwide |
The SWIFT system stands out from traditional money transfer systems. It acts as a secure, standardized messaging platform, not as a payment processor. The table below highlights the differences between the traditional SWIFT system and SWIFT Go, a newer service designed for smaller, frequent payments:
| Feature | Traditional SWIFT System | SWIFT Go System |
|---|---|---|
| Payment Routing | Involves multiple intermediary correspondent banks | Direct transfer between sender’s and recipient’s banks |
| Transaction Type | Large, high-value payments | Low-value, high-frequency payments |
| Cost Structure | Variable fees depending on intermediaries and routes | Fixed, transparent fees |
| Processing Time | Longer, can take several days | Faster, usually within 1-2 business days |
| Tracking | Limited transparency | Real-time tracking with unique tracking code (UETR) |
| Target Users | Corporates and financial institutions | SMEs, freelancers, individuals |
| Security and Standardization | Secure, standardized messaging platform globally trusted | Same secure network with enhancements for accessibility |
| Settlement Process | Multiple banks involved, increasing cost and time | Uses pre-arranged bilateral agreements to reduce steps |
SWIFT meaning centers on its role as a global financial messaging network. It enables banks to communicate across borders, even when they use different currencies or languages. The SWIFT system supports the international banking system by making payments faster, safer, and more reliable. Banks in Hong Kong, for example, use the SWIFT network to send payment instructions to banks in the United States, Europe, or China. This process allows businesses and individuals to move money internationally with confidence.
The society for worldwide interbank financial telecommunications and the society for worldwide interbank financial telecommunication both refer to the same organization. This group has built a global financial messaging network that supports the needs of the international banking system. SWIFT meaning goes beyond just sending messages. It provides the foundation for secure, efficient, and standardized payments worldwide. The global financial messaging system ensures that banks can trust the information they receive, reducing errors and delays in international transactions.
SWIFT Network

Image Source: unsplash
How the SWIFT Network Works
The SWIFT network connects thousands of banks and financial institutions worldwide. This network acts as a secure bridge for sending payment instructions and other financial messages. SWIFT uses advanced encryption and strict security protocols to protect every transaction. The network relies on both logical and physical security measures. These include multi-factor authentication, secure communication channels, and regular audits. SWIFT encrypts messages both in transit and at rest, using strong cryptographic methods. Only authorized users can access the messaging system, which helps prevent fraud and unauthorized access.
The SWIFT network uses unique codes to identify each bank. These codes, called SWIFT codes or BICs, help verify the parties involved in every transaction. This system reduces errors and ensures that messages reach the correct bank. SWIFT also acts as the Registration Authority for several international standards, such as ISO 9362 (BIC), ISO 10383 (Market Identifier Code), and ISO 20022. These standards define how banks format and exchange messages. By following these rules, the SWIFT network ensures that all banks use the same language for financial messaging.
SWIFT maintains a Customer Security Program and a Security Controls Framework. These programs require banks to use preventive measures like intrusion detection systems and role-based access control. This helps protect against cyber threats and data breaches.
The SWIFT network uses the SWIFTNet messaging platform to send messages quickly and securely. The platform supports different types of financial messages, including payment instructions, account statements, and trade confirmations. The network segments traffic, uses firewalls, and monitors for suspicious activity. SWIFT also complies with international standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 and PCI DSS. These steps help keep the financial messaging system safe and reliable.
| Security Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Encryption Standard | AES-256 for end-to-end encryption |
| Communication Protocol | Latest versions of TLS for secure channels |
| Authentication | Digital certificates and multi-factor authentication |
| Network Security | Segmentation, firewalls, intrusion detection systems |
| Access Control | Role-based access and strict user permissions |
The SWIFT network supports international payments by providing a standardized way for banks to communicate. This standardization reduces confusion and speeds up the payment process. Banks in Hong Kong, for example, use the SWIFT network to send payment instructions to banks in the United States or Europe. The network ensures that every message is clear, accurate, and secure.
SWIFT Transaction Process
A SWIFT transaction follows a clear, step-by-step process. The network does not move money directly. Instead, it sends payment instructions between banks. Here is how a typical SWIFT transaction works:
- The sender contacts their bank and provides details for the payment. This includes the recipient’s name, bank, SWIFT code, account number, amount, and currency.
- The sender’s bank checks the information and creates a SWIFT message, often using the MT103 format for international payments.
- The SWIFT network transmits the message securely to the recipient’s bank. If the sender’s bank has a direct relationship with the recipient’s bank, the message goes straight to them.
- If no direct relationship exists, the SWIFT network identifies a correspondent bank to act as an intermediary. The message passes through this bank before reaching the recipient’s bank.
- The recipient’s bank receives the message, verifies the details, and credits the recipient’s account.
- The recipient’s bank sends a confirmation message back through the SWIFT network to the sender’s bank.
SWIFT transactions use Nostro and Vostro accounts to track funds between banks. These mirrored ledgers help banks settle payments accurately.
The time it takes to complete a SWIFT payment depends on several factors. Most SWIFT payments take between 1 and 5 business days. The speed depends on the sender bank’s processing time, the number of intermediary banks, time zone differences, and regulatory checks. Banks may offer expedited SWIFT services for an extra fee. Currency conversion and compliance checks, such as anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) reviews, can also affect the timeline.
- SWIFT payments usually take 1 to 4 business days.
- Intermediary banks add extra time if no direct relationship exists.
- Time zone differences and holidays can cause delays.
- Regulatory checks and currency conversion may extend processing time.
The SWIFT network ensures that every transaction is secure and standardized. The network uses encryption, authentication, and strict access controls to protect data. SWIFT’s global standards, such as ISO 9362 and ISO 20022, help banks exchange messages without confusion. The SWIFT system supports millions of transactions every day, making it a trusted choice for international payments.
SWIFT does not transfer money itself. The network sends payment instructions, which banks use to move funds between accounts. This process makes SWIFT a reliable financial messaging system for global banking.
SWIFT Code

Image Source: pexels
What Is a SWIFT Code?
A swift code, also known as a BIC (Business Identifier Code), acts as a unique identifier for banks and financial institutions worldwide. The swift network uses these codes to make sure every message and payment instruction reaches the correct bank. Each swift code follows a standard format of 8 to 11 characters. This format helps banks avoid confusion and errors during international transactions.
- The first four characters show the bank code. For example, “HSBC” stands for Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation.
- The next two characters represent the country code, such as “HK” for Hong Kong.
- The following two characters indicate the location or city code.
- The last three characters, which are optional, identify a specific branch. If the code ends with “XXX,” it usually means the main office.
A swift code works like a global identity card for banks. It ensures that funds and messages go to the right place. The swift system assigns these codes under the ISO 9362 standard, making them trusted worldwide.
A swift code helps banks route payments accurately and securely, reducing the risk of misdirected funds.
How SWIFT Codes Are Used
Banks use swift codes in international wire transfers to identify the sending and receiving institutions. When someone in Hong Kong wants to send money to a friend in the United States, the sender’s bank uses the swift code to direct the payment to the correct bank and branch. This process helps prevent errors and speeds up the transfer.
Swift codes play a key role in the swift network by enabling secure communication between banks. They allow banks to send payment instructions, account details, and other messages with confidence. The swift code, combined with the recipient’s account number, ensures that funds reach the intended person or business.
Common mistakes with swift codes include typing errors, incorrect formatting, or using the wrong branch code. These mistakes can cause delays, rejected payments, or extra fees. To avoid problems, people should double-check the swift code before sending money. Banks and payment platforms often provide tools to verify swift codes.
| Segment | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Code | Identifies the bank | HSBC |
| Country Code | Shows the country | HK |
| Location Code | Points to the city or region | HH |
| Branch Code | Optional, for specific branches | XXX |
The swift network relies on swift codes to keep international payments safe, fast, and accurate. These codes help banks in Hong Kong and around the world connect and move money across borders.
Who Uses SWIFT
Financial Institutions
The SWIFT network connects more than 11,000 financial institutions in over 200 countries and territories. Banks in Hong Kong and around the world rely on SWIFT for secure messaging and international bank transfers. The main users of SWIFT are supervised financial institutions. These include banks, eligible securities broker-dealers, and regulated investment management companies. Supervised financial institutions have full rights to send and receive all types of messages on the SWIFT network. Other users, such as non-supervised entities and closed user groups, have limited access to SWIFT messaging services.
- Supervised financial institutions:
- Banks
- Securities broker-dealers
- Regulated investment management institutions
These institutions use SWIFT for global bank transfers, international money transfer, and cross-border payments. SWIFT helps them process international transfers quickly and securely. The network also supports compliance with regulations and helps prevent financial crimes.
Common Uses for Payments
SWIFT plays a key role in international payments and international transfers. The network processes both local currency transfers and international wire transfers. For example, a bank in Hong Kong can use SWIFT to send a payment in USD to a bank in the United States or a payment in EUR to a bank in China. SWIFT payments include both local transfers, where the currency matches the destination country, and international bank transfers, where the currency is different.
Corporations and governments also use SWIFT for many financial operations. Corporations connect to SWIFT to manage treasury functions and reduce costs. Governments and financial intelligence units use SWIFT data to trace transactions and enforce sanctions. SWIFT supports compliance with international laws and helps track suspicious activity.
| User Type | Common SWIFT Uses |
|---|---|
| Banks | International bank transfers, cross-border payments |
| Corporations | Treasury operations, international money transfer |
| Governments | Sanctions enforcement, financial crime tracking |
SWIFT payment instructions help banks move funds securely. The network supports international payments, swift payments, and cross-border payments for many users. SWIFT acts as the backbone for secure, standardized, and compliant financial messaging worldwide.
Benefits and Alternatives
Advantages of SWIFT
The swift network offers several important advantages for international payments.
- Global reach: The swift network connects over 11,000 banks in more than 200 countries. This allows users to send payments almost anywhere in the world.
- Standardized processes: The use of swift codes and BICs helps reduce errors and makes payment workflows easier.
- Secure transactions: The swift network uses advanced encryption and follows strict banking standards to keep information safe.
- Multiple currencies: Swift supports payments in over 160 currencies, making cross-border payments simpler.
- Transparent fees: The network provides clear information about costs, so users know what to expect.
- Real-time tracking: Swift offers updates on payment status, which helps users follow their transactions.
- Compliance: The swift network supports anti-money laundering and know-your-customer rules, helping banks meet global regulations.
The swift network stands out for its global connectivity and secure cross-border payments, making it a trusted choice for banks and businesses.
Drawbacks and Costs
While swift has many strengths, it also has some drawbacks.
- Fees can be high, especially for payments to certain countries or in less common currencies.
- The process often involves several banks, which can add extra charges and slow down the payment.
- Users may face limited visibility, as not all swift payments offer real-time tracking.
- The system requires banks to have trained staff and technical support, which increases operational costs.
- Security risks exist, even with strong protections, as cyber threats continue to evolve.
| Bank | Typical SWIFT Fee Range (USD) | Notes on Fees and Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| HSBC Hong Kong | $7 - $25 | Fees vary by amount and destination. |
| Hang Seng Bank | $10 - $30 | Extra charges for urgent or large payments. |
| Bank of China (HK) | $8 - $28 | Currency conversion fees may apply. |
Swift Go offers a solution for smaller payments, with transparent fees and no deductions from the transfer amount. However, traditional swift transfers may still involve multiple fees and deductions.
Alternatives to SWIFT
Several alternatives to swift now exist for international and cross-border payments.
- Fintech platforms like Tilli Software, Chimoney, and PayQuicker provide real-time processing, lower costs, and better tracking.
- Blockchain networks such as Ripple and Stellar allow near-instant payments by removing intermediaries.
- Regional systems like SEPA in Europe and real-time payment networks in some countries offer fast, low-cost transfers but have limited reach.
| Payment System | Speed | Cost | Geographic Scope | Notes / Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SWIFT | 1-5 business days | High ($50-$100+) | Global | Most widely used, but slower and costly |
| SEPA | ~1 business day | Low | Europe | Fast euro payments, limited to Europe |
| Real-Time | Seconds | Low | Limited cross-border | Instant, but not yet global |
| Fintech | Near real-time | Low | Expanding globally | User-friendly, transparent, and cost-effective |
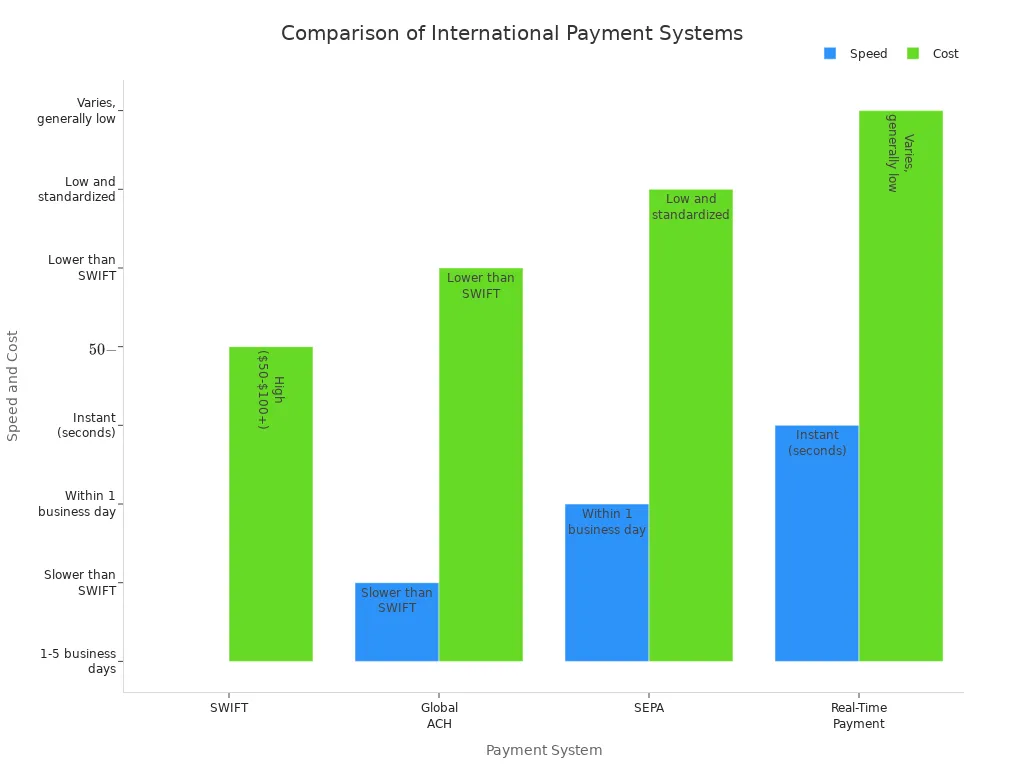
New technologies like blockchain and stablecoins continue to improve speed, security, and transparency. The swift network is also updating its services to stay competitive, but users now have more choices for secure, fast, and affordable cross-border payments.
SWIFT connects over 11,000 financial institutions, providing secure and standardized messaging for global payments. The network does not move funds but sends payment instructions using SWIFT codes, which help reduce errors and speed up transfers. Anyone sending money abroad should check fees, verify the SWIFT code, and consider alternatives for cost and speed. SWIFT remains essential for international finance, supporting secure transactions and adapting to new technologies.
SWIFT’s strong security, global reach, and ongoing innovation make it a trusted foundation for cross-border payments.
FAQ
What does a SWIFT code look like?
A SWIFT code has 8 or 11 characters. The code includes letters and numbers. For example, HSBC Hong Kong’s main office uses “HSBCHKHHXXX.” Each part of the code shows the bank, country, city, and branch.
How long does a SWIFT transfer take?
A SWIFT transfer usually takes 1 to 4 business days. The time depends on the banks involved, the number of intermediary banks, and regulatory checks. Delays may happen during holidays or if extra verification is needed.
Are there fees for using SWIFT transfers?
Yes, banks charge fees for SWIFT transfers. For example, a Hong Kong bank may charge $7 to $25 USD per transfer. Extra fees may apply if the payment uses multiple intermediary banks or needs currency conversion. Check the latest USD exchange rates for accurate costs.
Can individuals use SWIFT for personal transfers?
Individuals can use SWIFT for sending money abroad. Most banks in Hong Kong offer this service. The sender needs the recipient’s name, account number, and SWIFT code. SWIFT helps ensure the payment reaches the correct bank safely.
While SWIFT remains a trusted backbone for international banking, businesses and individuals often struggle with high fees, multiple intermediaries, and transfer delays of up to 5 days. That’s where BiyaPay offers a modern alternative. With real-time exchange rates, international transfers starting at just 0.5%, and support for both fiat and digital currencies, BiyaPay makes cross-border payments faster, more affordable, and more transparent. Same-day transfers are also available, giving you confidence and speed when moving money internationally.
Don’t let costly and slow processes hold back your global transactions. Discover smarter payments today with BiyaPay.
Get started in just minutes — register with BiyaPay.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















