- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
FHA Loan Process Explained and How to Apply Successfully

Image Source: pexels
The FHA loan process helps you buy a home with support from the federal housing administration. You start by checking if you meet eligibility rules, then gather documents, choose a lender, fill out your application, complete an appraisal, go through underwriting, and finish with closing. Many first-time homebuyers use FHA loans because you need a lower credit score and a smaller down payment.
| Loan Type | Percentage of First-Time Homebuyers (Jan 2021) |
|---|---|
| Conventional Loans | 59% |
| FHA-Insured Loans | 24% |
You may find several benefits with an FHA loan:
- Easier qualification standards from the federal housing administration
- Lower down payments and closing costs
- Fixed interest rates for steady payments
- Assumable loans for future resale
If you want to apply for an FHA loan, understanding the benefits and requirements can help you succeed.
Key Takeaways
- FHA loans help many people buy homes with lower credit scores and smaller down payments than conventional loans.
- You must meet FHA rules for credit score, income, employment, and property type to qualify for an FHA loan.
- Prepare all required documents and shop around with FHA-approved lenders to find the best loan terms.
- The FHA loan process includes application, appraisal, underwriting, and closing, usually taking about 43 days.
- Avoid common mistakes by checking your credit, maintaining stable finances, and understanding FHA mortgage insurance costs.
FHA Loan Basics
What Is an FHA Loan
You may wonder what makes an FHA loan different from other home loans. The U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development defines an FHA loan as a loan insurance program managed by the Federal Housing Administration. This program helps you buy a home by providing mortgage insurance to lenders. If you cannot make your payments, the insurance protects the lender from losses. The FHA program aims to make homeownership possible for more people by offering flexible qualification standards compared to conventional home loans.
FHA home loans allow you to qualify with a lower credit score and a smaller down payment. You can use an FHA loan to buy a house, refinance your current mortgage, or even make repairs to your home. The federal housing administration sets rules for these loans, but you work with FHA-approved lenders to apply.
Note: FHA home loans require you to use the property as your primary residence. You cannot use them for investment or vacation homes.
Who Should Consider an FHA Loan
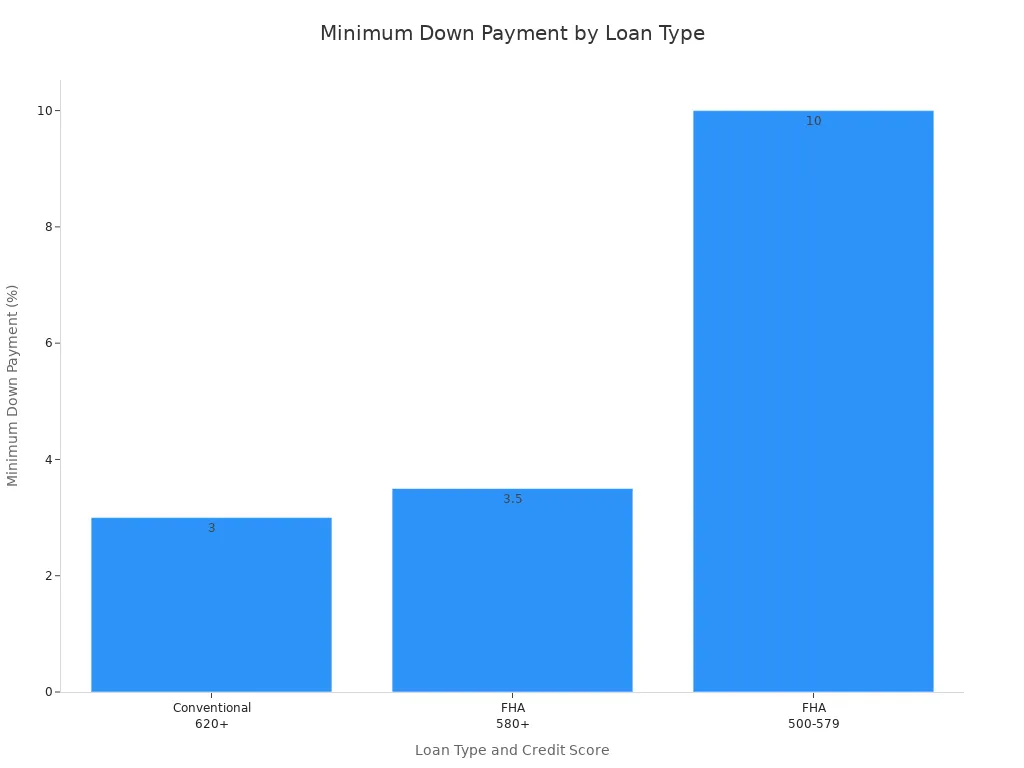
FHA home loans can help many types of buyers. You may benefit from an FHA loan if you are a first-time homebuyer or have a limited credit history. FHA loans often work well for people who do not have a large down payment saved. The minimum down payment is 3.5% if your credit score is at least 580. If your score is between 500 and 579, you may still qualify with a 10% down payment.
You should also consider FHA home loans if you have experienced financial setbacks. For example, you can become eligible two years after a Chapter 7 bankruptcy or three years after a foreclosure. FHA loans do not have income limits, but you must show steady employment and provide recent pay stubs. The debt-to-income ratio usually should not exceed 43%, but lenders may allow higher ratios if you have strong credit or extra savings.
- FHA home loans are especially helpful for:
- First-time buyers with low or no credit scores
- Borrowers with limited income documentation
- People who want to use alternative data, like rental payment history, to qualify
- Buyers from minority groups who may face challenges with conventional home loans
FHA home loans can open the door to homeownership for many people who might not qualify for other home loans. The benefits of the FHA program include flexible rules and the chance to use gift funds for your down payment.
FHA Loan Requirements
Understanding FHA loan requirements helps you prepare for a successful application. You need to meet specific guidelines for credit score, down payment, income, employment, and property type. FHA mortgage insurance also plays a key role in the process. Let’s break down each part of the loan requirements so you know what to expect.
Credit Score and Down Payment
FHA loan requirements for credit score and down payment are more flexible than many other loan programs. According to current FHA guidelines, you can qualify for the lower down payment advantage of 3.5% if your credit score is 580 or higher. If your score falls between 500 and 579, you may still qualify, but you must provide a 10% down payment. Some lenders may accept scores as low as 550, but the official FHA guidelines set 580 as the threshold for the lower down payment benefit.
| Loan Type | Minimum Down Payment | Credit Score Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| FHA Loan | 3.5% | 580 or higher |
| FHA Loan | 10% | Between 500 and 579 |
| Conventional | 3% | Typically 620 or higher |
You see that FHA loans allow you to buy a home with a lower down payment even if your credit is not perfect. This makes FHA loan requirements attractive for many first-time buyers. The down payment requirement can be met with your own savings or with gift funds from family, friends, or approved organizations. This flexibility helps you if you have trouble saving for a large down payment.
FHA mortgage insurance is required for all FHA loans. You pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) at closing, usually 1.75% of the loan amount. You also pay an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP), which is divided into monthly payments. FHA mortgage insurance protects the lender if you default, but it adds to your monthly costs. You must keep this insurance for at least 11 years, or for the life of the loan if your down payment is less than 10%.
Income and Employment
FHA loan requirements focus on your ability to repay the loan. You do not need a minimum income, but you must show steady income and employment history. FHA guidelines usually ask for at least two years of consistent employment. If you have gaps in your work history longer than six months, you must explain them and show at least two years of stable work before the gap and six months of re-employment after.
- You need to provide documents such as pay stubs, W-2s, and tax returns.
- Self-employed borrowers must submit business tax returns and profit and loss statements.
- FHA guidelines allow exceptions for military service, recent schooling, or medical leave.
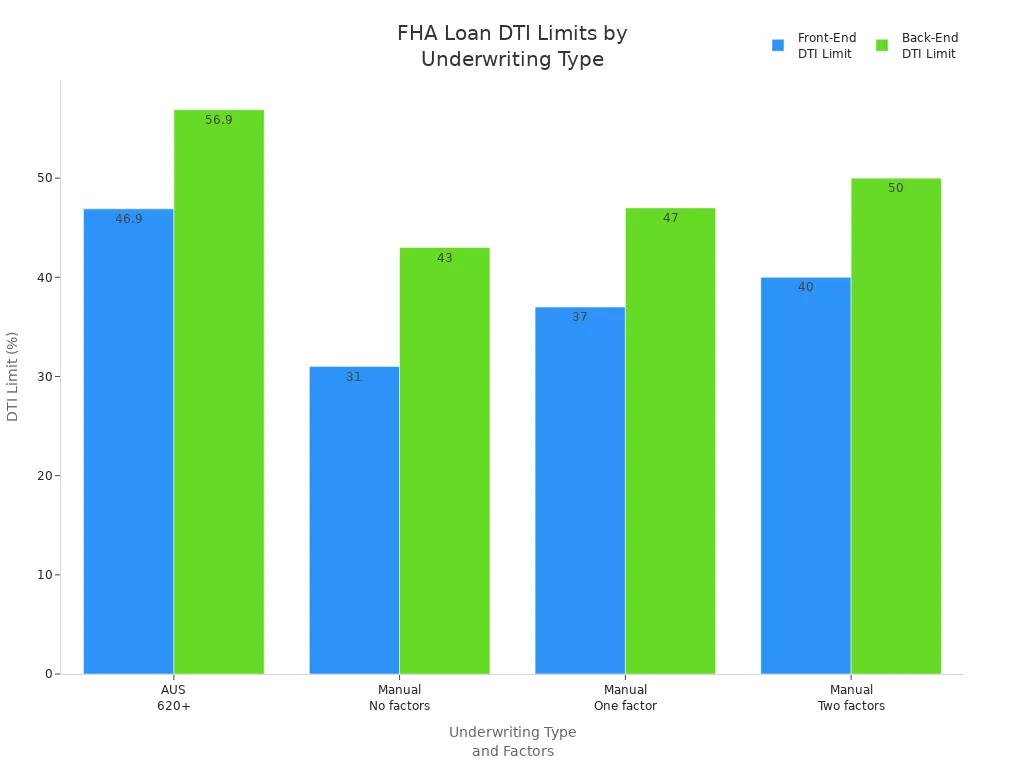
The FHA also looks at your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio. This ratio compares your monthly debt payments to your gross monthly income. FHA loan requirements allow a maximum back-end DTI of 56.9% and a front-end DTI of 46.9% if you have a credit score of 620 or higher and get approval through an automated underwriting system. Manual underwriting has stricter limits, but compensating factors can help you qualify for a higher DTI.
| Underwriting Type | Credit Score Condition | Front-End DTI Limit | Back-End DTI Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automated Underwriting System (AUS) | 620 or higher | Up to 46.9% | Up to 56.9% |
| Manual Underwriting | No compensating factors | 31% | 43% |
| Manual Underwriting | One compensating factor | 37% | 47% |
| Manual Underwriting | Two compensating factors | 40% | 50% |
| General (most lenders) | Credit score below 620 | N/A | Typically under 43% |
FHA mortgage insurance is required regardless of your income or DTI. This insurance helps lenders offer loans to more people, even if you have a higher DTI or lower credit score.
Property Eligibility
FHA loan requirements also cover the type of property you can buy. You must use the home as your primary residence. You need to move in within 60 days of closing and live there for at least one year. The FHA defines a primary residence as the place where you live most of the year. At least one borrower must occupy the property during this period.
‘At least one Borrower must occupy the Property within 60 Days of signing the security instrument and intend to continue occupancy for at least one year.’
Eligible properties for FHA financing include:
- Single-family homes
- Multifamily homes with up to four units
- Condos in approved condominium projects
- Manufactured homes that meet FHA guidelines (built after June 15, 1976, on a permanent foundation)
- Fixer-uppers using FHA 203(k) loans
- Mixed-use properties with at least 51% residential use
The property must meet FHA minimum property standards for safety, security, and soundness. Unique homes, such as log cabins or small homes, may qualify if they are structurally sound and marketable. Properties with shared lots or excessive land are not eligible. Nonresidential use cannot exceed 25% of the total floor area.
FHA mortgage insurance applies to all eligible property types. You cannot use an FHA loan for vacation homes or investment properties. After the first year, you may rent out the property, but you must follow FHA guidelines.
FHA loan requirements make homeownership possible for many people. You benefit from a lower down payment, flexible qualification, and the ability to use gift funds. FHA mortgage insurance helps lenders approve more borrowers, but you must meet all loan requirements to qualify.
FHA Loan Application Steps

Image Source: pexels
How to Get an FHA Loan
You can start your journey to homeownership by learning how to get an FHA loan. The first step is to find an FHA-approved lender. You can use the HUD lender directory to search for lenders who offer FHA loans. Review each lender’s eligibility criteria and compare their interest rates and fees. Gather your financial documents, such as income verification and proof of assets, before you apply for an FHA loan. You should apply to more than one lender to get preapproval letters. These letters show the loan type, amount, and interest rate you qualify for. Choose the lender that offers the best terms for your needs.
Tip: Shop around with at least three FHA lenders. Compare their offers, ask about down payment assistance, and check their reputation through online reviews.
FHA Loan Application Process
The FHA loan application process follows a series of clear steps. You can use this ordered list to guide you:
- Find an FHA-approved lender. Make sure the lender participates in FHA financing and matches your credit score and communication preferences.
- Fill out the FHA loan application. Many lenders let you apply online. Contact several lenders to compare offers.
- Submit your documentation. Provide personal and financial documents, such as tax returns, pay stubs, and bank statements.
- Compare Loan Estimates. Each lender will send you a Loan Estimate within three business days. Review these to compare interest rates, fees, and terms.
- Schedule an FHA appraisal. The lender will arrange for an FHA-approved appraiser to check the property’s value and condition.
- Wait for loan processing and underwriting. The lender verifies your information. An underwriter reviews your file and may ask for more documents.
- Close on your FHA loan. Review the closing disclosure, attend the closing meeting, sign documents, pay closing costs and down payment, and take ownership of your new home.
The average time to close an FHA loan is about 43 days, which is almost the same as a conventional loan.
| Loan Type | Average Closing Time |
|---|---|
| Conventional | 42 days |
| FHA | 43 days |
Required Documents
You need to prepare several documents for your FHA loan application. Lenders require these to verify your identity, income, and financial stability. Here is a checklist to help you stay organized:
- Residence addresses for the past two years
- Social Security numbers
- Employer names and locations for the past two years
- Gross monthly salary from current jobs
- Information on all checking and savings accounts
- Details on all open loans
- Information on other real estate owned
- Approximate value of personal property
- Certificate of Eligibility and DD-214 for veterans
- Current pay stubs and W-2 forms (past two years)
- Personal tax returns (past two years), income statements, and business balance sheets for self-employed
- Payment for credit report and property appraisal
- Bank statements (three months)
- Retirement and investment account statements
- Recent bills and statements
- Landlord contact or rent checks
- Utility bills
- Bankruptcy and discharge papers if applicable
- Cancelled checks for co-signed loans
- Driver’s license and Social Security card
- Divorce, alimony, or child support papers
- Green card or work permit if applicable
- Homeownership papers
Note: Missing or incomplete documents can delay your FHA loan approval. Double-check your paperwork before submitting it. Make sure gift letters for down payments include the donor’s relationship, amount, and signatures, and provide proof of transfer.
Appraisal and Underwriting
The FHA loan process includes a property appraisal and underwriting review. The lender will order an appraisal from an FHA-approved appraiser. This appraisal is more detailed than a conventional loan appraisal. The appraiser checks the home’s value and ensures it meets FHA minimum property standards for safety, security, and soundness.
| Feature | FHA Appraisal | Conventional Appraisal |
|---|---|---|
| Appraiser Certification | Must be FHA-approved appraiser | No FHA certification required |
| Inspection Thoroughness | More thorough inspection; includes additional reporting to verify home condition | Inspection focuses on items affecting safety, soundness, or structural integrity only |
| Repair Requirements | Appraisal often completed “subject to” repairs; repairs must be done before loan closing | Repairs noted but not always required before closing |
| Final Inspection | Required after repairs to clear conditions | Not typically required |
| Appraisal Purpose | Ensures compliance with FHA Minimum Property Standards for loan insurance | Primarily determines market value and notes major deficiencies |
The underwriter reviews your financial documents, credit score, and debt-to-income ratio. If you have a credit score of 580 or higher, you can qualify for a 3.5% down payment. If your score is between 500 and 579, you need a 10% down payment and manual underwriting. The underwriter may ask for more documents, especially if you have non-traditional income or recent financial setbacks. Compensating factors, such as cash reserves or a strong payment history, can help you qualify.
Tip: Stay in close contact with your lender during underwriting. Respond quickly to requests for more information to avoid delays.
Closing the Loan
The final step in the FHA loan application process is closing. You will attend a settlement meeting where you sign the loan documents. The property title transfers to you, and the seller receives the funds. You must pay closing costs at this meeting. These costs usually range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount and include:
- Lender fees: application, processing, underwriting, origination, credit report, discount points, rate lock, prepaid interest, and courier fees
- Property-related expenses: home insurance premium, property taxes, HOA dues, home warranty, and survey fees
- FHA-specific fees: upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) of 1.75% of the loan amount, paid at closing or rolled into the loan
- Prepaid property taxes and homeowners insurance
You can pay closing costs with a wire transfer or cashier’s check. You may reduce your out-of-pocket costs by negotiating seller contributions (up to 6% of the purchase price), using gift funds, or applying for closing cost assistance programs.
Note: Review your closing disclosure carefully. Make sure all fees and terms match your expectations before you sign.
The FHA loan application process may seem complex, but you can succeed by staying organized and working closely with your FHA-approved lender. Prepare your documents, compare offers, and respond quickly to requests. This approach helps you move smoothly from application to closing and into your new home.
FHA Loan vs Conventional Loan

Image Source: pexels
Key Differences
When you compare FHA loans and conventional home loans, you see some important differences. FHA loans help you qualify with a lower credit score and a smaller down payment. Conventional home loans usually need a higher credit score and a bigger down payment. You can use the table below to see how these two types of home loans compare:
| Aspect | FHA Loans | Conventional Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Qualification | Lower credit scores accepted (580+ with 3.5% down; 500-579 with 10% down) | Higher credit scores usually required (620+), down payments often 20%, some as low as 3% |
| Loan Limits | Lower loan limits, only for primary residences | Higher loan limits, can be used for primary, vacation, or investment properties |
| Mortgage Insurance Cost | Upfront mortgage insurance premium (1.75% of loan) + monthly MIP for all loans | No upfront premium; PMI only if down payment <20%, can be canceled at 20% equity |
| Mortgage Insurance Term | MIP usually lasts at least 11 years | PMI can be canceled once you reach 20% equity |
| Debt-to-Income Ratio | Allows higher DTI ratios (up to 50%) | Usually capped at 45%, often 36% or lower |
| Interest Rates | Often competitive or lower fha loan rates and fha mortgage rates | May have slightly higher rates but lower fees and closing costs |
| Property Use | Only for primary residences | Can be used for primary, vacation, or investment properties |
| Refinancing | Easier and faster with streamline refinance | Needs more documentation and appraisal |
You notice that FHA loans offer more flexible rules, especially if you have less savings or a lower credit score. FHA loan rates and fha mortgage rates are often lower for people with less-than-perfect credit.
Pros and Cons
You should look at the pros and cons before choosing between FHA loans and conventional home loans. Each option has strengths and weaknesses.
Pros of FHA Loans:
- You can qualify with a credit score as low as 580 for a 3.5% down payment.
- FHA loans allow down payments as low as 3.5%, making home loans more accessible.
- FHA loan rates and fha mortgage rates are often competitive, even for lower credit scores.
- You can get help with closing costs from sellers, builders, or lenders.
- FHA loans offer easier refinancing through streamline programs.
Cons of FHA Loans:
- You must pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium of 1.75% of the loan amount.
- FHA mortgage insurance stays for at least 11 years, sometimes for the life of the loan.
- FHA loans only work for primary residences, not for vacation or investment properties.
- The property must meet strict health and safety standards, which can limit your choices.
- FHA loan limits are lower, so you may not be able to buy higher-priced homes.
Note: FHA mortgage insurance costs can add up over time. Conventional home loans let you remove private mortgage insurance once you reach 20% equity, which can save you money in the long run.
When you compare fha loan rates and fha mortgage rates to conventional rates, you may find FHA loans cost less each month, but insurance lasts longer. Conventional home loans may have higher rates, but you can drop insurance sooner. Think about your credit score, savings, and long-term plans before you choose.
Tips and Common Pitfalls
Mistakes to Avoid
You can avoid many common mistakes during the FHA loan process by learning from other applicants. Many people do not check their credit reports from all three bureaus before applying. Errors on your credit report can lower your score and affect your eligibility for the best down payment options. Some applicants misunderstand the requirements for credit scores. You need a score of 580 or higher for a 3.5% down payment. If your score is below 580, you must put down 10%.
Other frequent mistakes include:
- Not correcting credit report errors before applying.
- Spending up to the maximum loan amount instead of choosing a comfortable payment.
- Making big financial changes, like changing jobs or taking on new debt, after pre-approval.
- Not maintaining stable employment or financial status during the process.
- Failing to shop around for the best loan terms and not locking in your interest rate.
- Confusing pre-qualification with pre-approval, which can lead to surprises later.
- Overlooking the total cost of the loan, including fha mortgage insurance and annual premiums.
Tip: Always review your credit reports, fix errors, and understand all requirements before you apply. This helps you avoid delays and extra costs.
Improve Approval Odds
You can improve your chances of FHA loan approval by following a few key steps. Start by maintaining a strong credit profile. Pay your bills on time and keep your credit card balances low. Avoid opening new credit accounts before you apply. Lower your debt-to-income ratio by paying down existing debts. This shows lenders you meet their requirements.
Here are some strategies to help you succeed:
- Organize all required documents, such as proof of income, assets, and identification, before you start the application.
- Increase your down payment if possible. A larger down payment can reduce your loan amount and may help you get better terms.
- Prepare for the appraisal by fixing any known property issues. This helps the home meet FHA requirements.
- Communicate with your lender. Respond quickly to requests and ask questions if you do not understand something.
- Shop around for lenders. Compare interest rates, fees, and fha mortgage insurance costs to find the best deal.
- Consult with a mortgage advisor if you need help understanding requirements or choosing the right loan.
Remember, fha mortgage insurance is required for all FHA loans. You pay an upfront premium and monthly payments. These costs protect the lender but add to your monthly expenses. Make sure you understand how fha mortgage insurance affects your total loan cost.
Note: Meeting all requirements and preparing early can help you avoid common pitfalls and make your FHA loan process smoother.
You now understand the FHA loan process and its main requirements. Start by checking your eligibility, then gather your documents. Compare offers from FHA-approved lenders to find the best fit. FHA loans make homeownership possible for many first-time buyers and those with lower credit scores. Take the next step and begin your journey toward owning a home.
Tip: Stay organized and ask questions during each stage. This helps you move smoothly from application to closing.
FAQ
What credit score do you need for an FHA loan?
You need a credit score of at least 580 for a 3.5% down payment. If your score is between 500 and 579, you must put down 10%. Some lenders may set higher minimums.
Can you use gift money for the FHA down payment?
Yes, you can use gift money for your down payment. The donor must provide a signed letter stating the amount and relationship. You must show proof of the transfer.
How much are FHA closing costs?
FHA closing costs usually range from 2% to 5% of the loan amount. These costs include lender fees, appraisal, insurance, and taxes. You can ask the seller to pay up to 6% of the price.
Do you need mortgage insurance with an FHA loan?
Yes, you must pay both an upfront mortgage insurance premium and a monthly premium. The upfront fee is 1.75% of the loan amount. The monthly cost depends on your loan size and down payment.
Can you get an FHA loan for a condo?
You can get an FHA loan for a condo if the project appears on the FHA-approved list. Check the HUD website for approved condos before you apply.
Buying a home with an FHA loan already takes careful planning — the last thing you need is losing money on high remittance fees or slow international transfers when moving funds for your down payment or closing costs. With BiyaPay, you can check real-time exchange rates, instantly convert between fiat and digital currencies, and send funds with a transparent 0.5% remittance fee. Better yet, BiyaPay supports transfers to most countries worldwide and guarantees same-day exchange and same-day arrival, helping you keep your focus on securing your new home.
Take control of your finances when buying property: register with BiyaPay today and experience fast, global, and cost-efficient transfers.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















