- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Understanding TT Payment Rates for International Transfers

Image Source: unsplash
When you send money overseas, tt payment rates play a crucial role in determining the actual cost of your international transactions. TT, short for telegraphic transfer, is a widely used payment method for international money transfer, especially for businesses and individuals handling large sums. TT payment rates and fees can affect the total amount your recipient receives, whether you use a wire transfer through a Hong Kong bank or another provider. The global value of international transactions using tt payments is enormous:
| Statistic Description | Value/Estimate |
|---|---|
| Annual volume of cross-border transactions | Nearly $23.5 trillion |
| Annual transaction costs (excluding FX costs) | Over $120 billion |
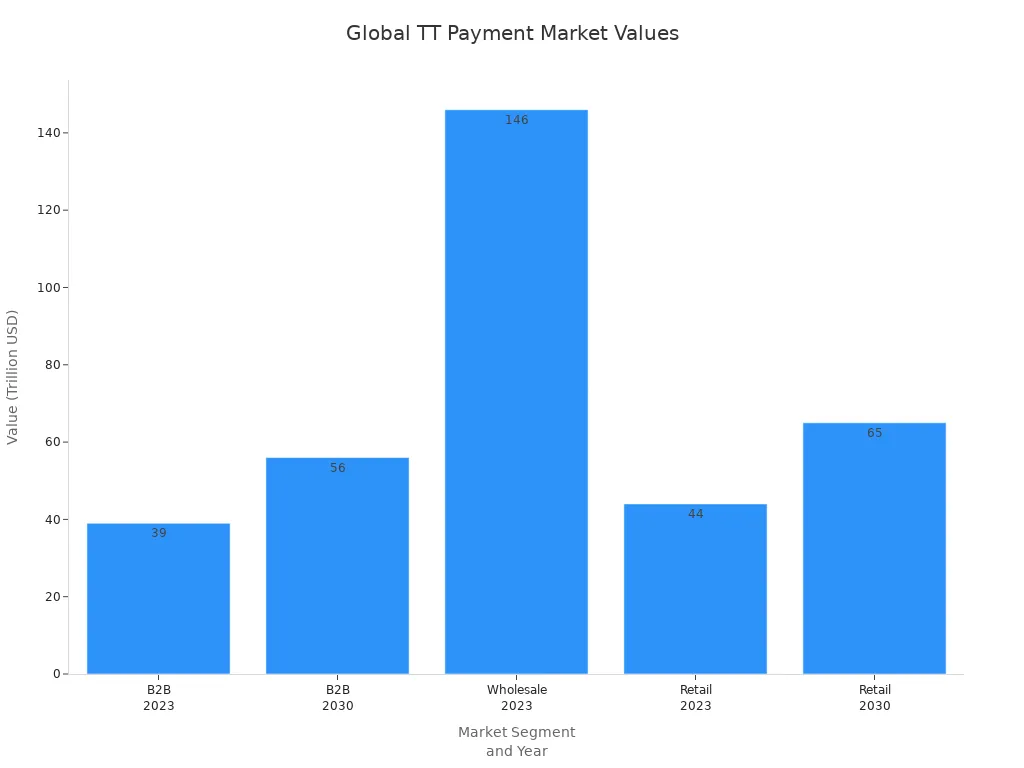
| B2B cross-border payments value (2023) | $39 trillion |
| Retail market value (2023) | Approximately $44 trillion |
TT payment rates can shift based on the provider, the wire transfer process, and the telegraphic transfer system used. You need to understand how tt, international money transfer, and wire transfer fees can add up so you can make informed choices for your international transactions.
Key Takeaways
- TT payments are electronic transfers used to send money internationally, usually taking 2 to 4 business days to complete.
- Banks set TT buying and selling rates with a margin that affects how much money you send or receive; small rate differences can change the final amount significantly.
- Various fees apply to TT transfers, including sending fees, intermediary bank fees, exchange rate markups, and receiving fees, which can add up and reduce the amount your recipient gets.
- Comparing providers, checking exchange rates and fees, and using digital platforms can help you save money and avoid hidden costs in international transfers.
- Timing your transfer and consolidating smaller transfers into one can improve rates and lower fees, making your international payments more cost-effective.
TT Payment Rates Explained

Image Source: unsplash
What Is TT Payment?
You often hear the term telegraphic transfer when you send money across borders. A telegraphic transfer, also called TT or T/T, is an electronic method for moving funds from your bank account to another bank account in a different country. Banks use the SWIFT network to process these transfers. In the past, banks sent instructions by telegraph, but now the process is digital and much faster. When you request a tt payment, you instruct your bank to send money overseas. The bank handles the transfer, making sure the funds reach the recipient’s account securely.
A telegraphic transfer is the standard for international wire transfers. You use tt payments for many reasons, such as paying for goods from another country, sending money to family, or investing abroad. The process usually takes two to four business days. You need to provide your bank with the recipient’s banking details, including their account number and SWIFT code.
Here are some common ways you might use a tt payment:
- You buy products from an online store in another country and pay in your local currency. The seller receives the payment in their own currency.
- Your company pays employees or contractors who live in other countries.
- You run a business and pay suppliers in China or other regions to support your supply chain.
- You transfer funds to invest in foreign stock markets or other assets.
- You send money to family members living abroad.
TT Buying Rate
When you send money overseas, you need to understand the tt buying rate. The tt buying rate is the exchange rate at which your bank buys foreign currency from you during a telegraphic transfer. Banks set this rate lower than the tt selling rate. This difference helps banks cover their costs and make a profit. The tt buying rate applies when you want to convert your local currency into a foreign currency for a transfer.
Banks use several types of operational exchange rates for buying foreign currency. For example, they may use a cash buying rate for immediate cash transactions, a tt clean rate for telegraphic transfers where funds are already covered, or a tt documentary rate for transfers involving documents like invoices. The tt buying rate specifically applies to telegraphic transfers or clean instruments.
Banks determine the tt buying rate by starting with a base exchange rate. They then subtract a margin or spread to cover their costs and ensure profit. For example, a bank in Hong Kong may calculate the tt buying rate by reducing the base rate by a margin of 0.025% to 0.080%. The final rate is rounded for simplicity. This margin reflects the bank’s operational costs and profit buffer.
Suppose you want to send $10,000 USD to a supplier in China. Your bank’s tt buying rate for USD to CNY is 7.20. The bank will use this rate to convert your USD into CNY before sending the funds. If the base market rate is 7.22, the bank’s margin creates a small difference, which is their profit.
You should always check the tt buying rate before making a transfer. Even a small change in the rate can affect the total amount your recipient gets. For example, if the tt buying rate is 7.20 instead of 7.22, your recipient will receive less CNY for the same amount of USD.
TT Selling Rate
The tt selling rate is the exchange rate at which your bank sells foreign currency to you during a telegraphic transfer. Banks set the tt selling rate higher than the tt buying rate. This difference, called the spread, allows banks to manage costs, market risks, and earn returns. The tt selling rate applies when you want to receive foreign currency or when your bank converts foreign currency into your local currency.
Banks like Wells Fargo set the tt selling rate at their discretion. They include a markup to cover costs, risks, and desired profit. The tt selling rate can change based on the currency pair, the size of your transaction, the payment channel, and the type of product you use. For example, the rate for a wire transfer may differ from the rate for a foreign currency check.
The tt selling rate is not fixed. It can vary between banks and even between customers making similar transfers. Foreign exchange markets change constantly, so tt selling rates also fluctuate. Banks act as independent parties and may refuse to process a transfer if the risks are too high.
Let’s look at a practical example. You receive $5,000 USD from a business partner in Europe. Your bank’s tt selling rate for EUR to USD is 1.10. The bank uses this rate to convert the euros into dollars before crediting your account. If the base market rate is 1.12, the bank’s markup means you receive slightly fewer dollars.
You should compare tt selling rates from different banks before accepting a transfer. A better tt selling rate means you get more value for your money. Even a small difference in the rate can have a big impact, especially for large transfers.
Tip: Always ask your bank for both the tt buying rate and the tt selling rate before making a telegraphic transfer. Comparing these rates helps you understand the true cost of your transfer and avoid surprises.
| Term | Definition | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| TT Buying Rate | Rate at which the bank buys foreign currency from you for a transfer | Sending USD to China, bank converts USD to CNY at this rate |
| TT Selling Rate | Rate at which the bank sells foreign currency to you for a transfer | Receiving EUR in USD, bank converts EUR to USD at this rate |
| TT Payment Rates | General term for both buying and selling rates used in telegraphic transfers | Any international transfer involving currency conversion |
You need to understand tt payment rates, including both the tt buying rate and the tt selling rate, to make informed decisions. These tt rates directly affect how much money your recipient gets or how much you receive from abroad. Always review the telegraphic transfer buying rates and selling rates before you complete a transfer. This knowledge helps you save money and avoid hidden costs in electronic funds transfer transactions.
TT Payment Fees
Types of Fees
When you make tt transactions, you face several types of fees. Banks and providers charge these fees to cover the cost of processing international transactions. The most common fees include sending bank fees, intermediary bank fees, exchange rate markups, and recipient bank fees. You may also see initiation or tracer fees for certain wire transfer services.
Here is a table showing typical fee ranges for tt transactions:
| Fee Type | Description | Example Fee Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Sending Bank Fee | Charged by your bank for sending funds; can be flat or percentage-based | $25 to $50 per transaction |
| Intermediary Bank Fees | Charged by banks in the SWIFT network between sender and recipient | $10 to $30 per intermediary bank |
| Exchange Rate Markup | Extra margin added to the exchange rate, increasing the cost | Variable, not always disclosed |
| Recipient Bank Fee | Charged by the recipient’s bank for receiving funds | $0 to $15 per transaction |
Some banks, especially in the U.S., charge $40 to $65 for each international wire transfer. Online tt transactions often cost less than those done in person or by phone. Providers like Wise offer lower, transparent fees and avoid intermediary charges.
You should know that fees can be flat, such as $30 per transaction, or percentage-based, like 0.33% of the transfer amount. Sometimes, banks deduct fees from the amount you send, so your recipient gets less money.
Intermediary Bank Charges
Intermediary banks play a key role in tt transactions. When your wire transfer moves through the SWIFT network, it may pass through one or more intermediary banks before reaching the recipient. Each intermediary bank can charge $15 to $50 per transaction. If your tt passes through several banks, these fees add up quickly.
You may not know the exact intermediary fees before you send your tt. These charges can be deducted from the transfer amount, reducing what your recipient receives. Some banks let you choose who pays these fees: you (OUR), the recipient (BEN), or both (SHA). If you pay all fees, your recipient gets the full amount, but your total cost increases. If the recipient pays, they receive less money.
Note: Intermediary bank charges are often hidden and can make tt transactions more expensive than you expect.
Processing Times
Processing times for tt transactions depend on several factors. Most international wire transfer transactions take 1 to 5 working days to complete. If you send money in major currencies like USD, your tt may arrive faster. Delays can happen because of fraud checks, incorrect details, holidays, or time zone differences.
Your tt may pass through up to three intermediary banks, which can slow down the process. Some fintech providers offer faster transfers, but traditional tt transactions usually take longer. Sending your wire transfer during business hours in the recipient’s country can help speed up the process.
Tip: Always check with your bank or provider for estimated processing times before starting your tt transactions.
Why Rates and Fees Differ
Spread and Margins
When you make a telegraphic transfer, you notice that banks do not use the same exchange rates you see online. Banks set their own tt buying rate and tt selling rate for every telegraphic transfer. The difference between these two rates is called the spread or margin. This spread is how banks earn money from currency exchange during your transactions.
Banks set the spread by looking at the bid-ask prices in the interbank market. The bid price is what banks pay to buy a currency, and the ask price is what they charge to sell it. The margin between these prices forms the basis for the tt buying rate and tt selling rate you receive. Banks also consider real-time quotes from other banks, counterparty risk, and how quickly they can settle the transfer.
Several factors influence the spread and margin for a telegraphic transfer:
- Market supply and demand for each currency.
- Economic indicators like inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth.
- Geopolitical events that may cause uncertainty.
- Central bank actions, such as interventions to stabilize a currency.
- Global trade patterns, including import and export needs.
You usually pay a markup over the interbank rate. For example, if the interbank rate for USD to INR is 85.71, your tt buying rate might be 85.20, and your tt selling rate could be 86.20. This markup can range from 0.3% to 4% or more, depending on the bank and market conditions.
Note: Banks balance competitive pricing with risk management and liquidity needs when setting spreads for telegraphic transfer transactions.
Bank and Country Differences
You will find that telegraphic transfer rates and fees change from one bank to another and from country to country. Each bank has its own fee structure and policy for telegraphic transfer transactions. For example, Hong Kong banks may charge different fees compared to banks in China or the United States.
Here are some reasons why rates and fees differ:
- Banks set their own tt buying rate and tt selling rate based on their costs and risk.
- The size of your transfer affects the fee. Some banks charge a flat fee, while others use a percentage. Larger transactions may get better rates.
- The destination country and currency pair can change the cost. Some countries have higher banking costs or less advanced technology.
- If you need a fast telegraphic transfer, you may pay extra for urgent processing.
- Additional charges, such as intermediary bank fees, can increase the total cost.
You can see the differences in the table below:
| Bank | Fee Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| HDFC Bank | $6 - $24 | Fee changes by amount and destination |
| State Bank of India | $5 - $22 | Charges depend on account type |
| ICICI Bank | $7 - $30 | Higher fees for urgent or large transactions |
| Axis Bank | $5.5 - $25 | Extra currency conversion fees possible |
| Kotak Mahindra Bank | $6 - $27 | Fees may change based on bank policy |
You should always compare the tt buying rate, tt selling rate, and all fees before making a telegraphic transfer. This helps you get the best value for your transactions and avoid hidden costs.
Impact on Transfers
For Individuals
When you send money abroad using a telegraphic transfer, you face several costs that can add up quickly. You need to look beyond the visible sending fee. The total cost of international transactions includes:
- Sending fees, which usually range from $10 to $50 per transfer.
- Intermediary bank fees, often $15 to $30 for each bank involved in the process.
- Receiving bank fees, which can reduce the final amount your recipient gets.
- Exchange rate markups, which are often 1% to 5% above the mid-market rate.
Suppose you want to send $2,000 to a family member in Europe. Your bank charges a $30 sending fee. The transfer passes through two intermediary banks, each taking $20. The recipient’s bank deducts another $10. If the bank uses a telegraphic transfer exchange rate that is 2% worse than the market rate, your recipient receives even less. These hidden costs can make a big difference, especially for smaller transfers.
You can lower your costs by comparing tt payment providers, choosing direct bank-to-bank transfers, or using fintech solutions in advanced markets. For large transfers, such as sending over $100,000, tt payments with flat fees may be more cost-effective than percentage-based fees from other platforms. You should also consider currency risk management, such as using multi-currency accounts.
For Businesses
Businesses rely on telegraphic transfer for international transactions, especially when paying suppliers or partners in other countries. The impact of tt rates and fees becomes more significant as the transfer amount increases.
| Scenario | Transfer Amount | Sending Fee | Intermediary Fees | Exchange Rate Markup | Total Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paying a supplier in China | $50,000 | $40 | $30 | 1.5% | $790 in total costs |
| Sending payroll to overseas staff | $10,000 | $25 | $20 | 2% | $245 in total costs |
| Importing goods from Europe | $200,000 | $50 | $60 | 1% | $2,110 in total costs |
If you use tt payments for large international money transfer needs, you must review both the tt buying rate and tt selling rate. Even a small change in the telegraphic transfer exchange rate can mean thousands of dollars lost or saved. Businesses can reduce costs by negotiating better rates, using SWIFT GPI for faster processing, or adopting local transfer systems where available.
Note: Always check the full fee structure and exchange rates before you complete a telegraphic transfer. Small differences in rates or fees can have a big impact on your bottom line.
Getting the Best Rates

Image Source: pexels
Comparing Providers
You can save money on every telegraphic transfer by carefully comparing providers. Start by researching the foreign exchange rates and processing times offered by each bank or transfer service. Contact Hong Kong banks and international providers to ask about their telegraphic transfer rates, minimum amounts, and whether they offer rate locks. Always compare the exchange rates you receive with the mid-market rate using online tools like Google’s currency converter. This helps you spot hidden markups.
Online comparison tools make it easy to see the differences between providers. These tools show you the exchange rate, transfer fee, and the final amount your recipient receives. For example:
| Provider | Exchange Rate (USD to PHP) | Transfer Fee (USD) | Amount Received (PHP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bank A | 56.2 | 30 | 56,200 |
| Bank B | 55.8 | 15 | 55,800 |
| Wise | 57.1 | 5 | 57,100 |
You should also check who pays the fees—whether you, the recipient, or both. Providers like Wise often offer transparent fees and use the real mid-market rate for telegraphic transfer, which can save you money.
Reducing Fees
You can reduce telegraphic transfer fees by taking a few smart steps:
- Ask your bank if they can waive the wire transfer fee, especially if you have a premium account or make frequent transfers.
- Use multi-currency accounts to hold and send funds in different currencies, which can help you avoid extra telegraphic transfer charges.
- Try digital wallets or fintech services that offer lower fees and real-time telegraphic transfer rates.
- Choose banks that offer fee waivers for certain account types, such as student or premium accounts.
Tip: Some Hong Kong banks waive telegraphic transfer fees for online transfers or for customers with high-tier accounts. Always ask about available discounts.
Timing Transfers
The timing of your telegraphic transfer can affect both the exchange rate and the total cost. Exchange rates change constantly because of economic news, supply and demand, and global events. You can monitor rates and set up alerts to catch the best time for your transfer. Sending your telegraphic transfer during off-peak periods, such as mid-month or on Mondays, can sometimes get you better rates and lower fees. Avoid sending money during holidays or at the end of the month, as banks may charge higher fees and offer less favorable rates.
Note: Consolidating several small telegraphic transfers into one larger transfer can help you get better rates and reduce total fees.
Understanding TT payment rates and fees helps you make smarter choices when sending money internationally. You now know how banks set rates, why fees differ, and how these costs impact your transfers. To save money, follow these expert tips:
- Compare providers by checking transaction fees, exchange rates, and processing times.
- Choose services with clear, transparent fee structures.
- Use digital platforms for lower costs and real-time rates.
Stay alert for hidden charges and always review the total cost before you transfer funds.
FAQ
What is the difference between TT buying rate and TT selling rate?
You use the TT buying rate when you send your local currency abroad. You use the TT selling rate when you receive foreign currency. Banks set the buying rate lower and the selling rate higher to cover costs and earn profit.
How can you avoid high intermediary bank fees in TT transfers?
You can ask your bank to use a direct correspondent relationship with the recipient’s bank. Some Hong Kong banks offer fee waivers for online transfers. Always confirm the fee structure before you send money.
How long does a TT transfer usually take?
Most TT transfers take 1 to 5 business days. Processing times depend on the currencies, banks involved, and accuracy of recipient details. Delays may occur during holidays or if banks require extra verification.
Can you track your TT payment after sending?
Yes, you can request a SWIFT tracking number from your bank. This code lets you monitor your transfer’s progress. Many Hong Kong banks provide online tracking tools for TT payments.
While TT payments remain a standard for international transfers, they come with high fees, hidden intermediary charges, and delays of 2–4 business days. For individuals and businesses that need faster, more transparent cross-border payments, TT is no longer the most efficient option.
That’s where BiyaPay makes a difference. With real-time FX rates, transfer fees as low as 0.5%, and same-day delivery to most countries, BiyaPay eliminates the hidden spreads and long waiting times of traditional wire transfers.
Stop losing money to TT spreads and slow processes. Switch to BiyaPay today and experience smarter, faster, and cheaper international transfers.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















