- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Complete Guide to Risk Management in US Stock Trading
Image Source: pexels
In the US stock market, risk management determines the safety of your capital and the sustainability of your profits. The US stock market is highly volatile; for example, the collapse of Silicon Valley Bank once triggered significant fluctuations in the technology and pharmaceutical sectors. Liquidity risk is also noteworthy, as Silicon Valley Bank went bankrupt due to insufficient liquidity management. Although systemic risks are less likely, timely regulatory intervention can effectively control risk spillover, but you still need to be cautious of uncertainties caused by leverage and exchange rate fluctuations. Through stop-loss and diversification, you can better protect your assets and enhance trading stability.
Key Points
- Protecting capital is the top priority in US stock trading; setting stop-loss and controlling position sizes can effectively reduce losses.
- Diversifying investments across different assets and industries can reduce risks from a single stock or market fluctuations.
- Strictly adhere to trading discipline, pre-set stop-loss and take-profit points, and avoid emotional trading.
- Properly using tools like options and ETFs can help hedge risks and improve investment stability.
- Staying rational and patient, recognizing that market fluctuations are normal, is key to achieving long-term stable profits.
Risk Management Basics

Image Source: pexels
Capital Protection
In US stock trading, protecting your capital is the most important goal. Only with secure capital can you seize future investment opportunities. You can adopt several methods to reduce the risk of losses:
- Set stop-loss points. When the stock price falls below your set price, the system automatically sells to help you stop losses in time.
- Control position sizes. The capital for each trade should not exceed 5%-10% of your total funds, and for high-risk stocks, only 1%-2%. This way, even if a stock declines, your overall loss is limited.
- Diversify asset allocation. You can allocate funds to stocks, bonds, gold, and other asset classes to reduce the impact of a single market’s fluctuations.
- Use hedging tools. For example, use options or hedging ETFs (like SQQQ) to hedge market risks.
- Keep 10%-20% in cash or short-term treasuries (like US Treasury bonds) to buy low during market downturns.
- Periodically adjust your portfolio to ensure asset allocation aligns with your goals.
- Stay calm and avoid emotional trading due to market fluctuations.
These methods can help you better protect your capital in the US stock market and enhance investment stability.
Long-Term Profitability
To achieve long-term profitability in the US stock market, you need to adhere to scientific risk management. You can:
- Strictly manage positions, ensuring the risk per trade does not exceed 1% of your total account funds.
- Set stop-loss points to quantify the maximum loss per trade.
- Adjust position sizes based on market volatility: reduce positions during high volatility and increase them during low volatility.
- Maintain trading discipline, avoiding impulsive actions driven by fear or greed.
- Allocate funds reasonably, maintain account liquidity, and seize new investment opportunities.
These measures can help you maintain a stable mindset in volatile markets and achieve consistent profits.
Investment Mindset
A good investment mindset is the foundation of risk management. You need to recognize that market fluctuations are normal and avoid anxiety or impulsiveness due to short-term gains or losses. You need to:
- Understand your risk tolerance and choose an investment strategy that suits you.
- Develop and strictly follow a trading plan without making arbitrary changes.
- Learn to accept losses, treating each trade as a learning opportunity.
Investing is not a sprint but a marathon. Only by staying rational and patient can you go further in the US stock market.
Major Risks in US Stock Trading
Market Volatility
In the US stock market, you will encounter significant price fluctuations. The US stock market has no daily price limits and is influenced by global economic conditions, policies, and technological innovations. Historical data shows that from 1960-2020, US stock market volatility was driven by factors like inflation, earnings, and financial conditions.
- Inflation (e.g., CPI, oil prices) and monetary policy directly affect market sentiment.
- Changes in corporate earnings and technological innovations often cause fluctuations.
- Financial conditions (e.g., interest rates, credit spreads) lead to strong market reactions when they change.
- Unexpected events (e.g., 9/11, trade wars) cause short-term sharp volatility.
- Global major indices are highly correlated, with significant risk spillover effects. You need to manage risks to reduce losses from market volatility.
Leverage Risk
When you use leverage, risks are amplified. Many investors face margin calls during extreme market fluctuations due to leverage. For example, an internet entrepreneur once suffered heavy losses from 1.3x leverage in Chinese concept stocks, facing three margin calls during a market crash. During the three US stock market circuit breakers in March 2020, many heavily leveraged investors were forced to liquidate. Leverage can amplify gains but also accelerates losses. You should use leverage cautiously and strictly control position sizes.
Liquidity
Liquidity risk is also common in the US stock market.
- When the VIX fear index exceeds 30, market volatility is high, and liquidity tightens.
- Federal Reserve rate hikes, balance sheet reduction, and changes in fiscal accounts can drag down market liquidity.
- Rapid rises in long-term interest rates cause capital outflows from stocks, exacerbating liquidity risks.
- Although the tech sector has strong earnings, it can still face differentiation during liquidity crunches. You should watch for liquidity risks during high-volatility periods to avoid forced sales.
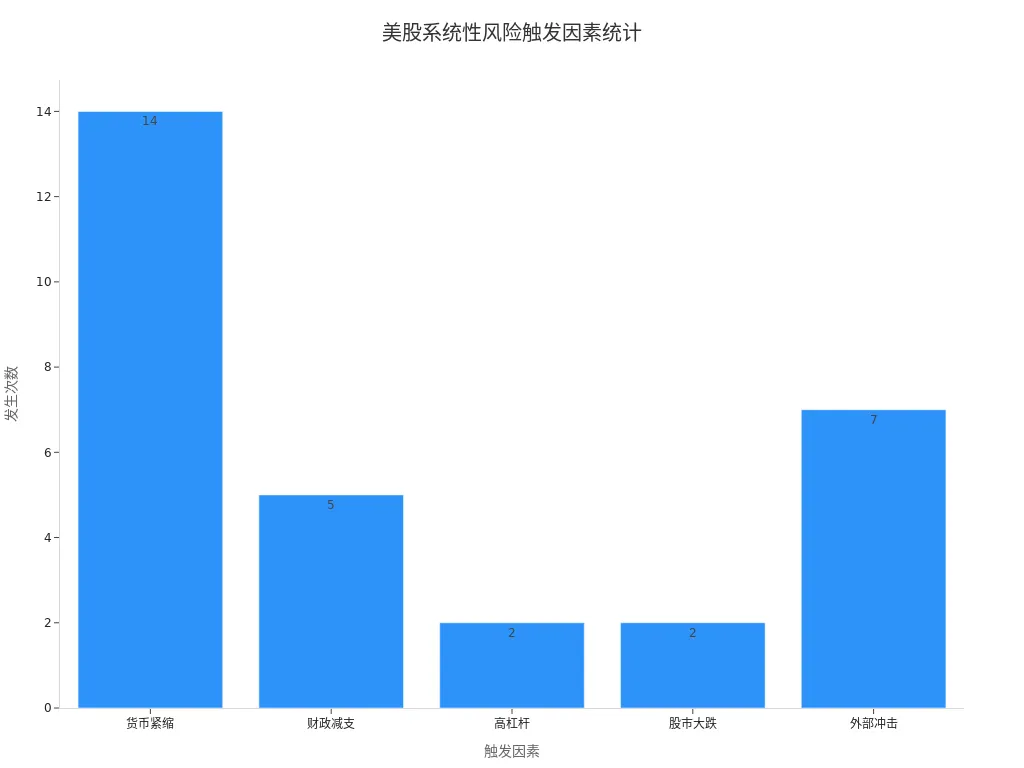
Systemic Risk
Systemic risks affect the entire market. Historical data shows that since the 1920s, the US has experienced 18 economic recessions, with the following main triggers:
| Trigger | Occurrences |
|---|---|
| Monetary Tightening | 14 |
| Fiscal Austerity | 5 |
| High Leverage | 2 |
| Stock Market Crashes | 2 |
| External Shocks | 7 |
During deep recessions, the US stock market’s maximum drawdown can reach 44%. You should monitor macroeconomic and policy changes and adjust your investment strategy in time.
Individual Stock Risk
When investing in a single stock, you are susceptible to company fundamentals, policies, and market sentiment. For example, in 2021, GameStop surged 1500% due to a retail-driven short squeeze, causing market panic. Historically, Trump’s tariff policies, weak economic data, and deteriorating market sentiment have led to sharp fluctuations in individual stocks and sectors. You should diversify investments to reduce individual stock risks.
Exchange Rate Risk
When you invest in US stocks using RMB, exchange rate fluctuations affect your actual returns. Changes in the USD-to-RMB exchange rate may reduce your gains even if the stock price rises. You should monitor exchange rate trends and use hedging tools when necessary.
Short Squeeze Risk
The US stock market occasionally experiences short squeeze events. Short-sellers using naked shorts or options may face forced liquidations when stock prices surge. For example, during the GameStop event, short-sellers suffered huge losses and even required external capital injections. Regulatory authorities have strengthened oversight of naked shorts and options markets. You should be cautious of stocks with high short interest to avoid getting caught in short squeezes.
Risk Management Strategies
Position Sizing
In US stock trading, position sizing is the most fundamental risk management method. Reasonably allocating funds for each trade can effectively prevent significant impacts from fluctuations in a single stock or sector. It’s generally recommended that a single stock’s position not exceed 10% of your total funds, and for high-volatility or high-risk assets, only 1%-2%. This way, even if a sudden event causes a stock to plummet, your total assets won’t suffer significant losses. You can flexibly adjust positions through phased entries or gradual increases. During heightened market volatility, reduce positions, keep more cash, and wait for better opportunities. Position sizing not only protects capital but also helps you stay calm during market corrections, avoiding emotional trading.
Stop-Loss Settings
Stop-loss settings are the most direct and effective risk management tool in US stock trading. You need to clearly set entry, stop-loss, and take-profit prices before each trade and strictly execute them. Common stop-loss methods include:
- Fixed percentage stop-loss: Sell automatically when the stock price drops 5%-10% to prevent further losses.
- Technical indicator stop-loss: Use moving averages, RSI, MACD, and other tools, combined with market trends and support/resistance levels, to determine stop-loss points.
- Trailing stop-loss: Adjust the stop-loss line based on market volatility to protect profits.
For short-term trading, stop-loss strategies must be strictly executed. You cannot hesitate and miss the optimal stop-loss timing. Although no clear success rate data exists, the effectiveness of stop-loss depends on your trading experience, strategy execution, and market conditions. You should stay calm and rational, avoid emotional influences on stop-loss decisions, and combine fundamental and market news for comprehensive judgments.
Tip: Before placing each order, consider the worst-case scenario, set stop-loss points in advance, and stay composed during market fluctuations.
Diversification
Diversification is a key way to reduce risk management pressure. You can allocate funds to different industries, asset classes, and regions to minimize the impact of fluctuations in a single market or sector. Bank of America’s large-client net buying data shows that institutional investors increasingly value industry diversification to mitigate risks from declines in popular sectors. The practical effects of diversification include:
- Low correlation between stocks, bonds, and gold effectively hedges market risks. For example, during the April 2025 tariff war, gold helped reduce portfolio volatility.
- Cross-regional allocation, such as US stocks with Chinese A-shares or European markets, has lower correlation, balancing returns and risks. From 2021-2023, when A-shares corrected, the S&P 500 maintained an annualized return above 8%.
- Diversified asset allocation addresses different economic cycles. In early 2020, during the pandemic, gold achieved nearly 25% excess returns, serving as a key diversification tool.
- Pure stock portfolios yield high returns in bull markets, but a balanced stock-bond-gold portfolio has lower volatility, demonstrating diversification’s effectiveness.
You can allocate stocks, bonds, and gold based on your risk tolerance to build a diversified portfolio.
Money Management
Money management is key to achieving long-term stable returns in US stock trading. The US stock market supports T+0 trading, allowing you to buy and sell on the same day and adjust funds flexibly. You can use various order types for money management:
- Limit orders: Ensure the transaction price meets your expectations, avoiding losses due to market price fluctuations.
- Stop-limit orders: Automatically control losses to prevent escalation.
- Conditional orders: Support automated trading strategies to improve execution efficiency.
Intelligent trading tools can also help you manage funds better. For example, technical analysis tools assist in trend identification, and split-order algorithms reduce the market impact of large orders. You can customize your portfolio to achieve asset allocation and risk diversification. In practice, reasonable fund allocation, diversification, and stop-loss/take-profit orders are key to money management. You should avoid overtrading, monitor market risks, and set stop-losses to effectively control overall risks.
Trading Discipline
Trading discipline is your final line of defense in risk management. You need to develop a detailed trading plan, including entry, stop-loss, take-profit, and fund allocation, and strictly execute it. You should:
- Avoid arbitrarily changing the trading plan or frequent trading due to market fluctuations.
- Stay calm, avoiding blind additions to losing positions or greed during profits.
- Regularly review trades, summarize experiences, and continuously optimize strategies.
Only by adhering to discipline can you survive long-term in the US stock market and achieve stable profits.
Practical Operational Methods

Image Source: pexels
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Points
In US stock trading, setting stop-loss and take-profit points is critical. Proper stop-loss settings help you control losses in time and protect capital. Common stop-loss methods include:
- Loss percentage stop-loss: You can set a 5% or 10% loss threshold based on your risk tolerance. When the stock price falls to this level, the system automatically sells to prevent further losses.
- Moving average stop-loss: Monitor 10-day or 20-day moving averages. If the stock price falls below these key averages, it often signals a trend reversal, making timely stop-loss critical.
- Support level stop-loss: When the stock price breaks below a key support level, you should decisively stop losses to avoid deeper entrapment.
- Technical indicator stop-loss: Use signals like MACD crossovers or SAR indicators as a basis for stop-loss.
- Unconditional stop-loss: If a company’s fundamentals change significantly, such as a financial crisis or major negative news, you should stop losses immediately and exit.
When setting stop-losses, you must predefine the stop-loss point and strictly execute it. Don’t delay due to hesitation or optimism, as this can lead to greater losses. For short-term strong stocks, they may sometimes break through technical indicators, so you need to adjust stop-loss points flexibly based on market conditions. Take-profit settings are also important; you can take profits when the stock price hits key resistance levels or shows technical sell signals to avoid profit retracement.
| Method Type | Description | Applicable Scenarios and Practicality |
|---|---|---|
| Fixed Amount Stop-Loss | Set a fixed loss percentage (e.g., 5%, 10%), stop loss when reached. | Simple and executable, suitable for volatile markets like US stocks, effectively controls risks. |
| Moving Average Stop-Loss | Use moving averages (e.g., MA10 for short-term, MA120 for long-term) as stop-loss points. | Dynamically adjusts stop-loss points, suitable for trend following. |
| Technical Indicator Stop-Loss | Use MACD crossovers, SAR, etc., as sell signals for stop-loss. | Provides objective signals, aids in determining sell timing. |
| Unconditional Stop-Loss | Stop loss immediately when fundamentals change significantly. | Addresses sudden risks, protects capital. |
| Take-Profit Settings | Take profits when the stock price hits resistance or technical sell signals. | Prevents profit retracement, secures gains. |
Tip: Before each trade, consider the worst-case scenario, set stop-loss and take-profit points in advance, and strictly adhere to discipline to survive long-term in the US stock market.
Portfolio Construction
To reduce risks from a single stock, you can achieve this by building a diversified portfolio. The core of portfolio construction is diversification, allocating funds to different assets and industries. You can refer to these classic approaches:
- You can learn from BlackRock’s “32Cap Global Hedge Fund Product”, using long-short equity strategies with futures hedging to enhance risk management.
- Multi-factor stock selection models are also common. You can select more stable stocks based on factors like P/E ratio, growth, and volatility to improve portfolio resilience.
- You can adopt John Neff’s small-cap investment strategy, carefully selecting small-cap stocks to balance risk and return.
- In a permanent portfolio, the bond portion includes long-term and short-term treasuries. Long-term treasuries are volatile but move differently from stocks and gold, providing a hedge. Short-term treasuries are stable, enhancing portfolio resilience.
- The 1987 Wall Street crash reminds you that single-strategy portfolios are risky in extreme markets, and diversified portfolios are safer.
You can allocate stocks, bonds, and gold based on your risk tolerance to build a diversified portfolio. This ensures that even if one asset class declines, others can help mitigate risks and maintain stable growth.
Regularly review and adjust your portfolio to ensure asset allocation aligns with your goals and market conditions.
Options and ETF Hedging
In the US stock market, you can use options and ETFs for risk hedging. Options are flexible financial tools that allow you to lock in profits or limit losses. For example, when holding a stock, you can buy a put option to gain compensation if the stock price falls.
ETFs (exchange-traded funds) are also common hedging tools. You can choose inverse ETFs (e.g., SQQQ, SPXU) to profit during market downturns. Volatility ETFs (e.g., VIXY) can hedge risks during market panic.
In practice, you can use these tools as follows:
- When you anticipate market downside risks, buy inverse ETFs or put options to reduce overall portfolio volatility.
- If you hold a large amount of tech stocks, use inverse tech ETFs for hedging.
- You can also use options strategies (e.g., protective puts, covered calls) to lock in profits or reduce losses.
Options and ETFs are flexible tools, but you should learn the relevant knowledge in advance to avoid increasing risks due to unfamiliarity with rules.
Day Trading Risk Control
If you prefer day trading, you need to pay special attention to risk control. The US stock market is highly volatile, offering many day trading opportunities but also high risks. You can take these measures:
- Set stop-loss and take-profit points before each trade, strictly execute them, and avoid arbitrary changes.
- Control the capital proportion per trade, avoiding heavy positions. Generally, a single trade should not exceed 5% of total funds.
- Use limit orders, stop-loss orders, and other tools to prevent losses from sharp price fluctuations.
- Monitor market liquidity and choose actively traded stocks to avoid liquidity risks.
- Stay calm, avoid frequent trading due to short-term fluctuations, and prevent emotional trading.
- Regularly review trades, analyze gains and losses, and continuously optimize strategies.
Day trading is high-risk; only strict risk control measures ensure long-term survival in the market.
Account Rules
When opening an account and trading in the US stock market, you need to understand the latest account rules. US regulators plan to lower the minimum net asset threshold for day traders from $25,000 to about $2,000 (approximately 14,400 RMB at the current exchange rate of 1 USD to 7.2 RMB) and remove the three-trade-in-five-days limit. This change allows more retail investors to participate in day trading but also introduces new risks.
Brokers like Robinhood and Fidelity have upgraded trading monitoring technologies, using automated systems for real-time risk management to help you avoid margin calls. After the popularization of zero-commission trading, your trading costs and financial risks have decreased.
However, relaxed rules may lead to impulsive trading and increased losses for some investors. A 2024 Stanford Business School study indicates that retail investor performance worsened after market entry barriers were lowered. Regulators need to balance accessibility and risk control to prevent uncontrolled risks.
Before opening an account and trading, carefully read the broker’s account rules, understand margin requirements, trading restrictions, and risk disclosures. Only by fully understanding the rules can you better protect your capital.
Account rule changes bring more opportunities but also greater risk management challenges. You should participate rationally in the US stock market based on your situation.
Investor Tiered Recommendations
Beginner Recommendations
When you start investing in US stocks, risk management is crucial. Common mistakes include not clearly defining risk and stop-loss points per trade, lacking control over daily maximum losses, and not planning initial capital allocation. You may also be influenced by emotions, leading to greed or fear, resulting in impulsive trading. You can follow these recommendations:
- Clearly define stop-loss points for each trade and set a maximum loss percentage in advance.
- Plan capital allocation and assess your risk tolerance.
- Don’t trust free stock recommendations or illegal promotions, and avoid the illusion of “high returns, low risk, instant redemption.”
- Diversify investments and allocate stocks, bonds, and other assets reasonably.
- Stay calm and avoid blindly adding to positions or cutting losses during fluctuations.
There’s no perfect asset in investing; you need to balance risk, return, and liquidity.
Advanced Recommendations
If you have some experience, you can try more systematic risk management strategies. Proper asset allocation is key, such as 70% in equities, with 30% in overseas markets, 20% in sector-themed ETFs, and 10% in cash. You can focus on 3-5 high-growth sectors, with no single sector exceeding 25%. Recommendations include:
- Learn and simulate using hedging tools like options, starting with 6 months of demo trading.
- Use dynamic take-profits, such as selling part of the position when it retraces 8% from its peak.
- Keep an investment journal to record decisions and avoid confirmation bias.
- Limit single stock positions to 15% and single sectors to 35%.
- Retain at least 10% cash to handle extreme market conditions.
- Set daily trading limits and pause trading for 72 hours after significant losses.
- Regularly review and optimize asset allocation and psychological resilience.
Continuously learn, build a healthy investment mindset and discipline, and avoid emotional trading.
Short-Term Trading Recommendations
If you prefer short-term trading, focus on settlement and liquidity risks. The US stock T+1 settlement system speeds up fund settlement but increases the risk of settlement failures. You can:
- Use broker T0 algorithms for intraday round-trip trading to reduce overnight risks.
- Strengthen understanding of T0 strategies to prevent model failures.
- Diversify funds across different strategies and markets to reduce single-strategy risks.
- Monitor brokers’ risk control measures to ensure sufficient fund and security reserves.
- Enhance technical risk prevention and standardize operations to avoid losses from errors.
Improve liquidity management, arrange margins reasonably, and prevent forced margin calls.
Long-Term Investment Recommendations
For long-term investing, systemic risk management is critical. You can reduce risks through:
- Control emotions and positions, avoid panic trading, and reduce leverage.
- Diversify investments with safe-haven assets like gold and yen to balance portfolio volatility.
- Use options insurance strategies, such as buying put options, for automatic stop-loss and limited losses.
- Monitor market reactions to policy changes, especially tariff impacts on supply chains.
- Regularly use options for hedging to reduce index futures risks.
- Stay patient and wait for market confidence recovery and institutional stabilization signals.
Persist with diversification and hedging, stay rational, and achieve long-term stable growth in the US stock market.
Common Misconceptions
Overconfidence
In US stock trading, overconfidence can easily lead you to overlook risks. Many investors, after consecutive profits, overestimate their judgment, frequently adding positions or trading heavily. You may think you can accurately predict market trends, but market changes often exceed expectations. Overconfidence can make you ignore fundamental changes and lead to chasing highs. You need to constantly remind yourself that there are no absolute winners in the market, and staying humble and cautious helps protect your capital.
Ignoring Stop-Loss
If you ignore stop-loss, small losses can turn into large ones. Some investors believe stock prices will rebound and hesitate to stop losses, resulting in deeper entrapment. You should understand that stop-loss is not admitting defeat but a critical means to protect capital. Before each trade, set a stop-loss point and strictly execute it. Only then can you remain resilient in volatile markets.
Concentrated Capital
Concentrating capital in a few stocks or sectors significantly increases risks. US stock market data shows:
- The top 10 S&P 500 constituents account for over 37.5% of market cap.
- The “Magnificent Seven” tech stocks contribute over half of the S&P 500’s returns.
- Market cap concentration is historically rare, posing potential risks.
- In 2025, US retail investors’ net inflows to stocks and ETFs reached $155 billion, with stock holdings accounting for about 49% of US household financial assets, nearing 60% with indirect holdings.
- Institutional cash ratios are below 3.9%, market breadth is only 66%, and global capital flows are near critical levels, with similar signals leading to an average S&P 500 drop of about 2%.
- Market drivers are overly concentrated in top tech giants, diverging from economic fundamentals.
If you only bet on popular tech stocks, a market shift could lead to significant losses. You should diversify to reduce risks from single industries or stocks.
Emotional Trading
During trading, emotional fluctuations affect decision-making. When the market rises, you may chase highs out of greed; when it falls, you may cut losses out of fear. Emotional trading can deviate from your original plan, increasing loss probability. You need clear trading rules, stick to them during fluctuations, and avoid being swayed by emotions. Only rational investing allows you to go further in the US stock market.
In US stock trading, only by prioritizing risk management can you protect capital and achieve long-term profits. Apply strategies like stop-loss and diversification to every trade. Continuously learn new knowledge and optimize your risk management system. Stay rational and disciplined, and you’ll go further in the market.
FAQ
How to quickly determine if a stop-loss is needed in US stock trading?
You can set a stop-loss point, such as selling automatically when losses reach 5%. You can also combine moving averages and technical indicators to stop losses when trends reverse.
What is the minimum deposit requirement for a US stock account?
Most US stock brokers have a minimum deposit of 0-500 USD, depending on the broker’s rules. You can use a Hong Kong bank for transfers, with exchange rates based on real-time USD-to-RMB rates.
Is there a time difference between US stock trading hours and China?
Yes, there’s a time difference. US stock regular trading hours are 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM ET. When trading from China, note the changes between daylight saving time and standard time.
How to use ETFs to reduce US stock investment risks?
You can choose diversified ETFs, like the S&P 500 ETF (SPY), to spread investments across multiple industries. You can also use inverse ETFs to hedge downside risks, reducing the impact of single stock fluctuations.
How to avoid emotional trading in US stocks?
Develop a trading plan in advance, set stop-loss and take-profit points. During fluctuations, strictly adhere to discipline and avoid impulsive buying or selling based on market sentiment.
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of risk management in U.S. stock trading, offering a detailed guide on topics ranging from capital protection and major risk types to specific strategies and methods. It emphasizes the importance of setting stop-losses, controlling position sizes, diversifying investments, and maintaining trading discipline. However, no matter how skilled you are at managing risk, you still face a core challenge: how to transfer funds across borders safely and efficiently. The high fees, cumbersome procedures, and long transfer times of traditional bank wire transfers can become a major obstacle to seizing fleeting investment opportunities in the U.S. stock market.
Now, you can choose a simpler and more efficient financial channel. BiyaPay is designed for global investors, offering a one-stop, seamless cross-border financial service. We support the convenient exchange between various fiat and digital currencies and provide a real-time exchange rate query, allowing you to catch the best conversion times. Our service, with remittance fees as low as 0.5% and same-day delivery, significantly reduces your transaction costs and time. What’s more, we enable you to invest in both the U.S. and Hong Kong stock markets from a single platform, all without the need for a complex overseas bank account. Say goodbye to complexity and embrace efficiency. Register with BiyaPay today to easily begin your global investment journey.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















