- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
2025 SME International Remittance Cost Trends and Optimization Suggestions

Image Source: unsplash
In 2025, the global average cost of cross-border remittances remains above 6%. According to World Bank data, inefficiencies and high fees are key concerns for SMEs. Many businesses face not only exchange rate differences but also high transaction fees during international payments. For example, some Hong Kong banks take 3-5 business days for international remittances to arrive. When selecting channels, how to reduce costs and improve efficiency becomes a critical direction for optimizing international remittances.
Key Points
- In 2025, international remittance costs have decreased but remain high. SMEs should focus on fees and exchange rate losses, selecting appropriate channels to reduce costs.
- Digital payments and blockchain technology accelerate transfer times, lower fees, and enhance security, serving as effective tools for SMEs to optimize remittances.
- Strengthened regulatory and compliance requirements mean businesses should prioritize compliance management, choosing licensed payment platforms to ensure fund safety and legality.
- Exchange rate fluctuations affect received amounts. SMEs should use multi-currency settlement and rate-locking tools to mitigate rate risks and protect profits.
- SMEs should flexibly choose bank wire transfers, third-party payment platforms, or digital platforms based on business needs to achieve low-cost, high-efficiency international remittances.
Cost Trends

Image Source: unsplash
Fee Changes
In recent years, global international remittance costs have been declining but remain relatively high. In Q2 2023, the global average remittance cost was 6.20%, still about 3.2 percentage points away from the UN’s 2030 goal of reducing costs to 3%. Remittance costs in some less-developed countries exceed 10%. The average costs for G8 and G20 countries are 5.83% and 6.43%, respectively, indicating cost reduction pressures for major economies.
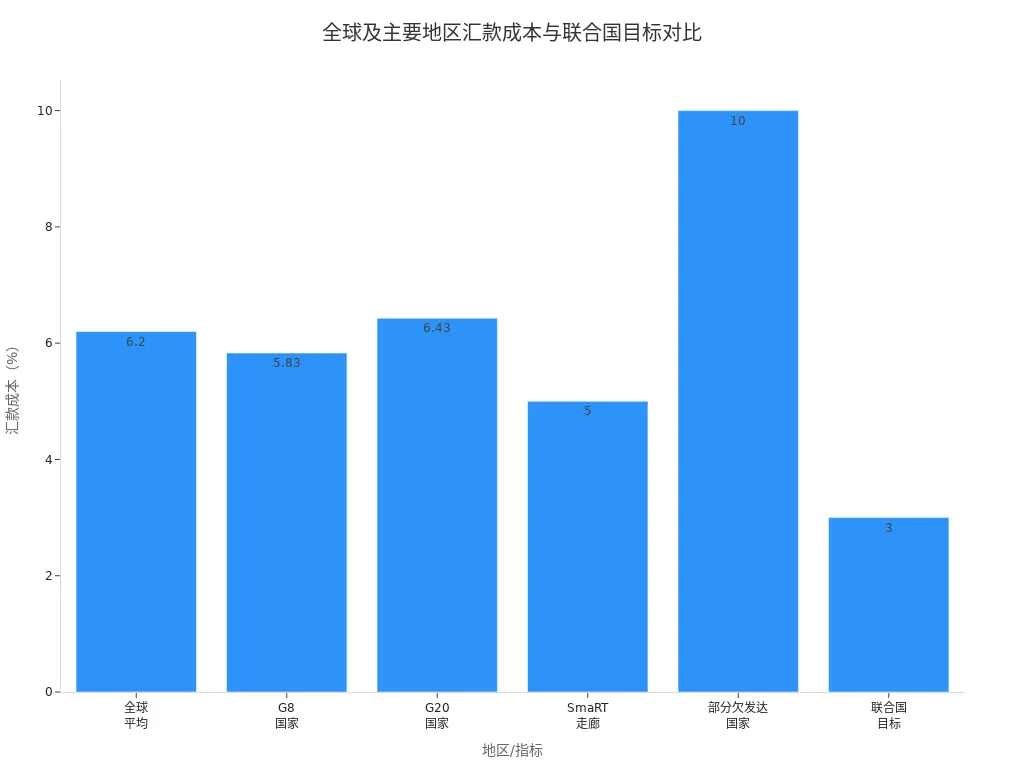
In China, international remittance fees and total cost ratios have been declining since 2015. Before 2015, foreign companies dominated the cross-border payment market with high fees and slow transfers. From 2015-2016, domestic payment institutions emerged, breaking the high-fee structure and significantly reducing costs for micro and small enterprises. After 2017, payment institutions improved services and risk controls, enhancing payment efficiency and security. Currently, innovative products and “payment+” services continue to drive cost reductions, improving overall service quality.
Fee differences across remittance methods are significant. The table below summarizes fees, rate markups, and trends for major channels:
| Remittance Method | Fee Range and Characteristics | Fee Example and Case | Trends and Policy Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Bank Wire | Fees 0.1%-1%, minimum $20, maximum $300; rate markup 1%-3% | A student remitting $100,000 incurs $200 in fees and ~$2,000 in rate losses | High fees with hidden costs; policies require proof of fund sources |
| Third-Party Payment Platforms | Rate markup 2%-4%; withdrawal fees, e.g., PayPal $35/transfer | Cross-border e-commerce seller receiving $10,000 loses $35 on withdrawal and ~$300 on rates | Convenient but with withdrawal fees and rate markups; strict regulatory limits |
| Blockchain Payment Technology | Fees ~1/10 of traditional banks; fast transfers | A company using Ripple for $1M remittance pays $100, saving 90% | Technology and regulation immature; central bank digital currency pilots may lower fees |
| Policy Environment | SAFE strengthens anti-money laundering checks; annual forex purchase limits | Individual annual forex limit of $50,000; excess requires proof | Free trade zones and digital currency pilots drive fee reductions; future digital currency and AI risk controls improve efficiency |
Hong Kong banks’ international remittance fees are generally 0.1%, with a minimum of $20 and a maximum of up to $300, and some banks charge additional telegraph fees and exchange rate spreads. Businesses should consult banks for the latest policies before proceeding to avoid increased costs due to hidden fees.
Technology Impact
The rapid development of digital payment technologies has significantly driven down international remittance costs. The application of digital RMB and blockchain technology reduces intermediaries in traditional cross-border payments, shortening transaction chains and enabling real-time transfers. A $1M remittance via blockchain platforms costs just $100 in fees, saving 90% compared to traditional banks. Cross-border digital RMB payments achieve second-level transfers, operate 24/7, and eliminate delays due to time zones or settlement cycles.
Digital technologies also enhance payment security. Encryption and distributed ledgers ensure transaction data authenticity and safety, reducing fraud risks. The use of digital identity and KYC sharing platforms further lowers compliance costs, reducing expenses related to anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing regulations.
Online remittance services are highly prevalent among Chinese businesses. In 2019, 84% of small and micro-enterprises used online banking, 38% used mobile banking, with 93% using mobile banking weekly. Mobile payment and transfer usage was 57%, and online collection services reached 56%. These data indicate businesses’ growing reliance on low-cost RMB funds and online remittance services, making digital tools a key means of cost reduction and efficiency improvement.
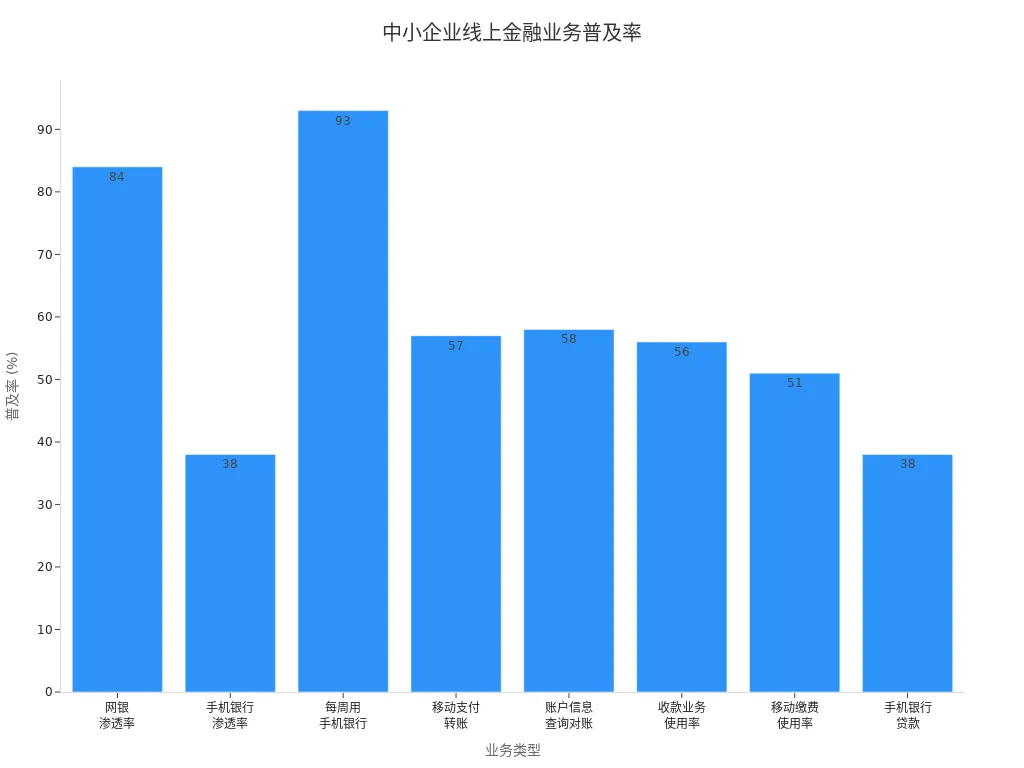
Digital payments not only reduce transaction costs but also improve payment efficiency and transparency, meeting businesses’ needs for efficient, low-risk cross-border fund flows.
Policy Trends
In 2025, major global economies continue to promote high-level openness in the payment sector, strengthening regulation and risk prevention to improve the quality and efficiency of payment services for the real economy. China’s payment and settlement conference emphasized risk prevention, strong regulation, and development, focusing on robust payment infrastructure and skilled payment talent.
National policies directly impact international remittance costs. In 2025, individual annual forex purchase and settlement limits remain at $50,000, with excess amounts requiring proof of legitimacy. Anti-money laundering checks have intensified, requiring declarations for single transactions exceeding $10,000, along with contracts, invoices, or other proof. Central bank digital currency (CBDC) cross-border payment pilots in the Greater Bay Area, Hainan Free Trade Port, and other zones are expected to further reduce costs in the future.
As the policy environment optimizes and digital currencies and AI risk controls become widespread, international remittance costs are expected to continue declining, making cross-border fund flows more efficient and secure.
Influencing Factors
Exchange Rate Fluctuations
Exchange rate fluctuations directly affect the actual amount received in international remittances. In 2024, the RMB-USD exchange rate fluctuated between 7.0-7.3, and in 2025, fluctuations are expected to widen. Rate instability leads banks to frequently adjust remittance fees to offset potential risks. During unfavorable rate changes, the actual amount received may fall below expectations, increasing financial costs and risks. SMEs should closely monitor rate trends and time remittances strategically to minimize losses from fluctuations.
- Exchange rate fluctuations cause changes in conversion rates, affecting received amounts.
- Banks may raise fees to mitigate risks.
- Fee policies vary across banks, requiring businesses to compare options.
- Optimizing rate management aids overall cost control.
Transaction Fees
Transaction fees are a significant component of international remittance costs. Fee structures vary widely across channels. For Hong Kong banks,with some also incurring intermediary bank fees of $10-50. Third-party platforms like PayPal charge 2.9%-4.4% plus currency conversion fees, while TransferWise charges 0.5%-1% with a $25 cap and better rates. Businesses should select channels based on remittance amount and frequency.
| Institution Type | Institution Name | Fee Rate | Minimum Fee (USD) | Maximum Fee (USD) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Third-Party Payment | PayPal | 2.9%-4.4% | N/A | N/A | Additional currency conversion fee |
| Third-Party Payment | TransferWise | 0.5%-1%, capped at $25 | N/A | 25 | Competitive exchange rates |
Compliance Costs
Compliance Costs
Compliance requirements significantly impact international remittance costs. Anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism financing policies mandate strict scrutiny of each transaction, potentially causing delays or freezes. Forex controls and tax declarations also increase compliance costs. SMEs, with limited resources, face greater compliance pressures. Businesses should establish compliance systems and select licensed payment providers to navigate complex regulatory environments.
Compliance complexity is a significant component of cross-border payment costs, and businesses should prioritize compliance investments to mitigate risks.
Channel Selection
Different channels have distinct cost structures and use cases. Bank wire transfers have higher fees and rate markups but suit large, high-security remittances. Third-party platforms have lower fees, ideal for small, frequent cross-border payments. Professional remittance companies charge higher service fees but offer fast transfers, suitable for urgent fund needs. Clearing network choices also affect costs; traditional networks like SWIFT are complex, with long cycles and high fees. Digital currencies and CBDCs offer low-cost, high-efficiency alternatives for businesses with varying efficiency and compliance needs.
| Channel Type | Cost Characteristics | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Wire Transfer | High fees and rate markups | Large, high-security remittances |
| Third-Party Payment Platforms | Lower fees, potential rate fluctuations | Small, frequent cross-border payments |
| Remittance Companies | High fees and service charges | Urgent, fast-transfer needs |
Selecting appropriate currencies and payment paths can optimize costs. For instance, using stablecoins or CBDCs reduces intermediaries, improving settlement efficiency and lowering time and cost expenses. Businesses must address compliance risks and adhere to declaration procedures to ensure legality.
SME Pain Points

Image Source: pexels
High Costs
SMEs face high explicit and implicit costs in international remittances. Some Hong Kong banks charge international wire fees up to $45-80 per transfer, with total cross-border costs often exceeding 4%. Beyond fees, exchange rate losses and intermediary bank charges further increase financial pressures. Smaller businesses, with limited bargaining power, struggle to secure lower rates. Small, frequent, fragmented orders require banks to process each transaction individually, increasing operational and time costs.
Many SMEs face lower-than-expected received amounts due to high fees and opaque cost structures, impacting profit margins.
Complex Processes
Complex international remittance processes are another major pain point for SMEs. Businesses must navigate forex conversions, tax declarations, account verifications, and KYC reviews. Adding withdrawal accounts and document verification requires submitting business licenses, legal representative IDs, supply chain contracts, and more. Cross-border e-commerce businesses also handle virtual account setups, payments, disbursements, and fund splits. Complex processes increase operational difficulty and extend transfer times.
- Complex settlement processes require multi-department coordination.
- Strict document reviews and high compliance requirements.
- Received amounts vary due to intermediary bank fees.
Risk Management
International remittances involve multiple risks. Exchange rate fluctuations directly affect costs and revenues, especially in multi-currency settlements, increasing fund management complexity. Wire transfers (T/T) carry risks like buyer default, fake accounts, or tampered payment details. Letters of credit (L/C) face soft clause and document discrepancy risks. SMEs, constrained by funds and credit, face higher fund security risks and need flexible payment adjustments to ensure safety.
| Payment Method | Main Risk Types | Risk Manifestations |
|---|---|---|
| Wire Transfer (T/T) | Pre-T/T, Post-T/T Risks | Buyer default, fake accounts, tampered information |
| Letter of Credit (L/C) | Soft Clauses, Document Discrepancies | Bank refusal, document errors |
| Documents Against Payment (D/P) | Refusal, Release Risks | Goods detention, port charges |
Transfer Timeliness
Transfer timeliness directly impacts SME cash flow efficiency. Traditional SWIFT systems require 3-5 business days, with delays during weekends or holidays. Some third-party platforms like Airwallex achieve transfers within one business day or even instantly, but coverage and currency options are limited. Slow transfers affect contract fulfillment and may lead to goods detention at ports, increasing inventory and storage costs.
- Traditional bank transfers take 3-5 business days.
- Third-party platforms can achieve instant transfers.
- Fund delays impact operations and cash flow.
Optimization Suggestions
Channel Optimization
SMEs should prioritize platforms with low fees, fast transfers, and transparent cost structures. Hong Kong bank wire transfers, while secure, have high fees and rate markups, suitable for large remittances. Third-party platforms like TransferWise and Airwallex charge 0.5%-1% with near-market rates, ideal for small, frequent cross-border payments. Some platforms support multi-currency accounts, allowing businesses to switch currencies flexibly and reduce conversion losses.
SMEs should compare channel fees and services based on remittance amount, transfer speed, and recipient location. For large, critical transactions, choose Hong Kong bank wires for security. For daily small settlements, prioritize third-party platforms to improve cash flow efficiency.
| Channel Type | Main Advantages | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Hong Kong Bank Wire | High security, global coverage | Large, critical transactions |
| Third-Party Payment Platforms | Low fees, fast transfers, user-friendly | Small, frequent settlements |
| Digital Remittance Platforms | Multi-currency accounts, instant transfers | Multi-currency operations, flexible settlements |
Digital Tools
Digital tools are critical for SMEs to reduce international remittance costs. Online platforms like HSBC Pulse and Airwallex offer one-stop cross-border payments, automated reconciliation, and multi-currency management. These platforms provide real-time exchange rate queries, transparent fee displays, and batch payment functions, significantly improving operational efficiency.
- Digital platforms support automated payment instructions, reducing manual errors.
- Multi-currency accounts help manage funds in different currencies, minimizing conversion losses.
- Real-time transfers and automated reconciliation enhance liquidity and financial management.
Digital tools enable SMEs to achieve low fees, transparent cost structures, and efficient fund flows, boosting international competitiveness.
Exchange Rate Management
Exchange rate fluctuations are a key factor affecting remittance costs. SMEs can use multi-currency settlements and rate-locking tools to effectively reduce rate risks and protect profit margins.
- Multi-currency settlements allow businesses to choose stable or appreciating currencies (e.g., USD, RMB) for settlements, reducing losses from fluctuations.
- Financial derivatives like forward contracts, forex swaps, and options enable businesses to lock rates in advance, minimizing rate risk exposure and securing profit margins.
- Flexible settlement timing and tools like letters of credit or collections further mitigate rate risks.
- Training professional forex staff and establishing risk management mechanisms enhance rate risk management capabilities.
With RMB exchange rate fluctuations becoming normalized, banks offer tailored rate hedging solutions for SMEs, promoting rate risk neutrality. Common hedging tools include RMB forex forwards, swaps, and options, helping businesses avoid fluctuations scientifically. One company used forward forex swaps to lock over 70% of its USD purchase price, reducing forex risk exposure to under 30%, significantly protecting profit margins in soybean import processing. This case demonstrates that rate-locking tools effectively reduce risks and enhance profitability.
Compliance Measures
Compliance management is a critical aspect of international remittances. SMEs should proactively understand and adhere to forex, anti-money laundering, and tax policies in China and recipient countries. Choosing licensed payment providers ensures complete documentation and compliant processes. Digital platforms can generate compliance reports automatically, simplifying declarations and reducing labor costs.
- Regularly train finance and trade staff to enhance compliance awareness.
- Establish internal compliance review mechanisms to prevent violations.
- Monitor policy changes and adjust remittance strategies to ensure fund safety.
Compliance measures not only reduce legal risks but also enhance business credibility, laying a foundation for future international expansion.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Platform Applications
Many SMEs use digital remittance platforms to improve fund flow efficiency. WorldFirst offers one-stop global collection and payment solutions, supporting multi-currency local collections and global payments. The platform provides API integration for automated system docking and fund management. With global payment licenses, WorldFirst ensures fund safety and compliance. Businesses can use batch payments and minute-level transfers to complete remittances quickly. The World Card supports multi-currency payments with no fees, ideal for daily cross-border payments and expense management. The platform covers 210+ countries and regions, serving tens of thousands of businesses with 24/7 customer support.
- WorldFirst: Multi-currency collections/payments, API integration, global licenses.
- World Card: Multi-currency payments, no fees, convenient management.
- Broad global coverage, fast transfers, low fees, ideal for efficient SME operations.
Cost Comparison
Banks and third-party platforms differ significantly in remittance costs and transfer speeds. The table below compares Wise and Hong Kong banks:
| Metric | Wise (Third-Party Platform) | Hong Kong Banks (Traditional Banks) |
|---|---|---|
| Exchange Rate | Real market mid-rate, no hidden markups | Rates include markups, hidden fees |
| Fees | Transparent fees, percentage-based | Multiple wire fees, higher costs |
| Transfer Speed | Instant or within 24 hours for most transfers | Typically 1-5 business days, uncertain timing |
| Fund Security | Regulated by e-money authorities, full amount guaranteed | Licensed bank regulation, intermediary bank deduction risks |
| Usability | Online signup, multi-currency accounts, Chinese interface | In-person signup, apps often lack Chinese support |
Wise uses its own network for local transfers, avoiding intermediary fees. For USD to RMB, Wise can achieve instant transfers, while Hong Kong banks typically take 2 business days. Third-party platforms are ~3 times cheaper than U.S. banks, significantly lowering SME remittance costs.
Risk Prevention
Businesses must focus on fund safety and compliance risks when selecting remittance channels. Platforms like WorldFirst hold global payment licenses and comply with regulatory requirements. They support automated compliance checks, reducing manual errors. Multi-factor authentication and real-time transaction monitoring prevent fraud and money laundering risks. Choosing platforms with guaranteed full-amount transfers minimizes losses from intermediary deductions.
Professional platforms’ compliance and risk control systems provide robust support for SME cross-border fund flows.
Case Study
A Chinese cross-border e-commerce business previously used Hong Kong bank wires to pay U.S. suppliers, incurring ~$60 per transfer with 3-5 business day delays. After switching to WorldFirst, fees dropped to $15, with transfers completed within 1 hour. The business, making 20 monthly transfers, saved over $10,000 annually. Automated reconciliation and batch payments reduced finance staff workload, improving fund management efficiency. The business noted that digital platforms not only cut costs but also enhanced international business responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
In 2025, international remittance costs continue to decline. SMEs can significantly boost competitiveness by optimizing channels and accelerating digital transformation.
- Jincheng Bank’s “Jincheng Quick Transfer” achieves full-amount, second-level transfers, reducing payment costs.
- Blockchain and digital RMB applications shorten transfer times, enhancing risk management.
- Big data risk control systems enable banks to serve SMEs more precisely, improving service quality.
FAQ
1. How should SMEs choose international remittance channels?
Businesses should compare channels based on remittance amount, transfer speed, and fees. Hong Kong banks suit large transactions, while platforms like Wise are ideal for small, frequent payments. Compare multiple channels to select the best option.
2. How can businesses reduce exchange rate losses during remittances?
Monitor real-time rates and choose favorable transfer times. Some platforms offer rate-locking to secure USD to RMB or other major currency rates, reducing risks.
3. What compliance documents are needed for international remittances?
Businesses typically need business licenses, contracts, invoices, and other proof. Hong Kong banks and third-party platforms require KYC verification to ensure fund source and purpose compliance.
4. Are digital remittance platforms secure?
Mainstream platforms like WorldFirst and Wise hold global payment licenses and use multi-layer encryption and risk controls. Automated compliance checks ensure fund safety.
5. How long do international remittances typically take?
Hong Kong bank wires take 3-5 business days. Platforms like Airwallex can achieve transfers within 1 hour. Speed depends on amount, currency, and destination.
This article provides an in-depth analysis of international remittance cost trends and optimization strategies for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in 2025. The article notes that despite the continuous decrease in global remittance costs, high fees, opaque exchange rate spreads, and cumbersome processes remain major pain points for SMEs. It thoroughly examines how technological innovation, policy changes, and exchange rate fluctuations affect remittance costs, and offers concrete optimization suggestions, including: choosing low-fee third-party payment platforms, using digital tools to boost efficiency, leveraging exchange rate hedging tools to manage risks, and strengthening compliance management.
However, despite the detailed content of the article, a core challenge for many Chinese investors remains: the flow of cross-border funds. Traditional funding methods, such as international bank wire transfers, are not only complex and time-consuming but also come with high fees and opaque exchange rate spreads. These issues can directly impact investment returns and increase transaction costs.
BiyaPay was created to solve these cross-border financial pain points. We offer a smoother, more cost-effective channel for your investments. We support the conversion between various fiat and digital currencies, allowing you to easily manage global assets, and provide a real-time exchange rate query feature to ensure you always get the best rates. What’s more, our remittance fees are as low as 0.5% with same-day delivery, significantly cutting down your transaction costs and time. Now, you don’t need a complex overseas account to invest in both U.S. and Hong Kong stocks on one platform. Say goodbye to the hassle of cross-border payments and start your efficient financial journey. Register with BiyaPay today to make fund management as smooth as trading.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















