- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
In-Depth Analysis of KYC and AML Compliance Key Points in International Remittances

Image Source: unsplash
In the field of international remittances, KYC and AML compliance requirements are critical measures for preventing financial crimes and ensuring fund security. Data shows:
- In 2022, 54.72% of virtual currency crimes were related to money laundering, with compliance measures helping authorities resolve cases involving up to $300 million in laundered funds.
- KYC effectively locks suspicious accounts, while AML requirements enhance risk identification through blockchain technology.
Businesses and individuals ignoring compliance face significant fines and legal risks.
| Case Entity | Violation | Penalty Outcome | Legal and Financial Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tether and Bitfinex | Fabricating trading volumes, misappropriating client funds | Fined $42.5 million, required audits | Heavy fines, reputational damage |
| BitMEX | Unregistered operations, failure to implement compliance measures | Fined $100 million, executives arrested | High litigation risks, required compliance overhaul |
| Binance | Violating KYC and AML obligations | Heavy fines, multiple regulatory lawsuits | Significant legal liabilities, high compliance pressure |
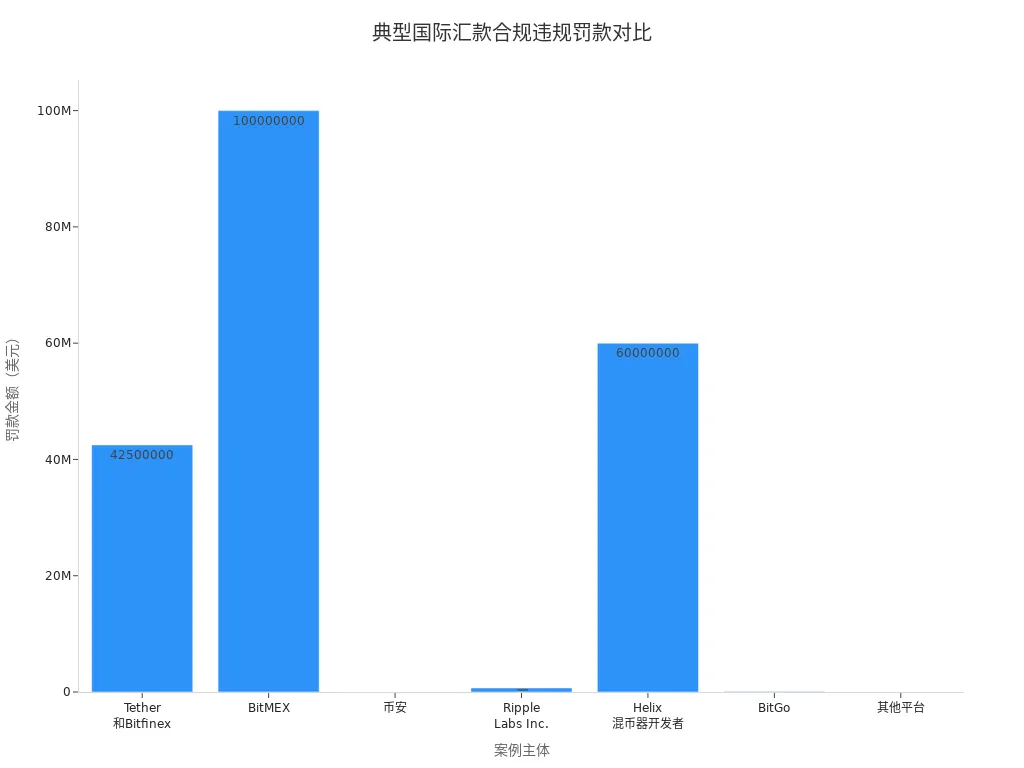
Businesses and individuals must focus on identity verification, risk assessment, and transaction monitoring, establishing efficient compliance processes to mitigate legal and financial risks.
Core Points
- KYC and AML are critical measures in international remittances to prevent money laundering and financial crimes, ensuring fund safety and legitimacy.
- Financial institutions verify customer information through identity checks, address proofs, and risk assessments to prevent fictitious accounts and illicit fund inflows.
- Transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting systems detect abnormal fund flows in time, preventing money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Ongoing due diligence and smart technology applications enhance risk identification, ensuring compliance and safety in international remittance operations.
- Businesses and individuals should establish efficient compliance processes, monitor local regulatory changes, and leverage technology to reduce legal and financial risks.
International Remittance Compliance Key Points
KYC Core Requirements
KYC (Know Your Customer) is an essential compliance component in international remittances. Financial institutions typically follow these KYC requirements:
- Customer Identification Program: Collect and verify customer identity information, such as passports or ID cards, and cross-check against international sanctions or terrorist lists.
- Customer Due Diligence: Verify customer information through multiple channels, assessing occupation, fund sources, and account purposes to screen high-risk customers.
- Enhanced Due Diligence: For high-risk customers, Hong Kong banks require more detailed proof of fund sources and business background materials.
- Simplified Due Diligence: For low-risk customers, the process is streamlined but still ensures identity and address authenticity.
- KYCC Mechanism: Some institutions also investigate customers’ customers to ensure the entire business chain’s compliance.
The KYC process not only ensures the safety of international remittances but also effectively prevents fictitious accounts and illicit fund inflows into the financial system.
AML Core Requirements
AML (Anti-Money Laundering) mechanisms require financial institutions to monitor the entire international remittance process. Key components include:
- Conducting penetrating reviews of non-resident accounts, focusing on verifying fund sources, beneficiary structures, and business logic.
- Requiring customers to provide proof of fund flows, such as related company statements or purchase/sale contracts, to ensure the reasonableness and legitimacy of fund movements.
- Requiring a tax residency declaration form (e.g., W-8BEN) during account opening to meet cross-border tax compliance requirements.
- Hong Kong banks cooperate to verify fund sources and transaction backgrounds, ensuring every international remittance undergoes strict scrutiny.
- Under the FATCA agreement, U.S. banks must report non-resident account information to the IRS, including account balances, interest income, and cross-border transaction records.
These measures collectively form a compliance barrier for international remittances, effectively preventing financial crimes like money laundering, tax evasion, and terrorist financing.
KYC Basics and Process

Image Source: pexels
The KYC (Know Your Customer) process is a core component of the international remittance compliance system. Financial institutions ensure customer information authenticity and fund legitimacy through identity verification, address proof, and risk assessment, effectively preventing financial crimes. Each step must strictly adhere to regulatory requirements, with document preparation and process execution being indispensable.
Identity Verification
Identity verification is the first step in the KYC process. Financial institutions require customers to submit various documents and materials to ensure identity authenticity. The required materials differ for corporate and individual clients. The table below summarizes common identity verification documents:
| Document Category | Specific Content |
|---|---|
| Corporate and Individual Documents | 1. Corporate business documents (color scans or photos issued by mainland China/Hong Kong/Taiwan) 2. Company articles of association 3. Company ownership structure chart (for complex ownership structures) 4. Individual identification documents (main contact, legal representative, or beneficiary) 5. Legal representative’s address information 6. Proof of bank account ownership (mainland China businesses) |
| Supplementary Documents | 1. Authorization letter 2. Notarized copies of related documents 3. Unified business license and code |
Customers must upload documents on designated platforms, ensuring authenticity, validity, and consistency. If key information changes or account receipts reach a certain threshold, institutions will re-verify and request additional materials. Hong Kong banks particularly emphasize verifying the identities of legal representatives and beneficiaries to ensure the compliance of each international remittance.
Identity verification is not only a compliance requirement but also the first line of defense against fictitious accounts and illicit fund inflows.
Address Proof
The address proof stage requires customers to submit official documents reflecting their actual residential or business address. Financial institutions typically request the following types of documents:
- Utility bills (water, electricity, gas)
- Telephone bills
- Tax receipts
- Credit card statements
- Bank statements
Compliance requirements include:
- The applicant’s name must appear on the document.
- The address must include the house number.
- Documents must be issued within the last three months to ensure timeliness.
- Documents must be issued by official institutions with seals or certification marks.
When preparing address proofs, customers should ensure document authenticity and completeness. Hong Kong banks strictly verify materials, and forged or altered documents will lead to rejected account openings or remittance applications. Diverse address proof documents help improve approval rates and reduce compliance risks.
Address proof is a critical basis for confirming customer identity and business location, directly impacting the progress of international remittance compliance reviews.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the most technically sophisticated stage of the KYC process. Financial institutions assess customer risk levels based on submitted identity and address information, combined with multi-dimensional data. Common risk assessment processes include:
- Collecting customer identification documents and checking against international sanctions lists.
- Conducting customer due diligence, integrating internal structured data and external unstructured data to clarify business relationships and beneficiary information.
- Scheduling reviews based on customer risk levels, with high-risk customers requiring more frequent screenings.
- Continuously monitoring customer risk status and dynamically updating risk information.
- Integrating and cleaning data to remove redundancies and ensure data quality for risk assessments.
- Aligning with policy and regulatory requirements to define risk factors and due diligence processes.
Some institutions have introduced machine learning models for risk scoring. For example, random forest models select features like age, income, and sanctions list inclusion, achieving an F1 score of up to 0.84, significantly improving risk identification accuracy. Logistic regression models, due to their interpretability and computational efficiency, are also commonly used for risk scoring cards.
A scientific risk assessment system helps institutions dynamically identify potential high-risk customers, ensuring the safety and compliance of international remittances.
AML Monitoring and Management

Image Source: pexels
Transaction Monitoring
Financial institutions must establish robust transaction monitoring systems in international remittance operations to identify and prevent money laundering and terrorist financing risks. Hong Kong banks typically use multi-dimensional monitoring rules and technologies to ensure real-time analysis and alerts for all transactions.
- Transaction monitoring focuses on the following suspicious transaction types:
- Transactions inconsistent with a customer’s usual activities
- Complex or unusually large transactions
- Unusual transaction or activity patterns without clear commercial or legal purposes
- Any suspicious activities linked to criminal behavior
- Transactions requiring reporting include:
- Single international wire transfers equivalent to $1,000 USD or more
- Cash transactions equivalent to $10,000 USD or more
- Multiple transactions below the reporting threshold are also considered suspicious and require focused monitoring and reporting.
- Banks identify and report these suspicious transactions through continuous monitoring to prevent money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Banks require customers to provide detailed identity and fund source information, and may refuse transactions or terminate services if customers fail to comply.
Hong Kong banks typically:
- Rely on monitoring rule engines, setting monitoring models based on transaction values, regions, industries, customer profiles, and behavioral habits
- Integrate blacklists and greylists, actively collecting or passively receiving user and transaction data
- Equip email and SMS alert functions to promptly notify compliance teams
- Daily workflows include alert handling, rule management, customer risk level adjustments, suspicious event processing, report submission, training drills, and regulatory assessment preparations
Transaction monitoring is not only a core component of AML systems but also the first line of defense against international remittance risks.
Suspicious Activity Reporting
In AML compliance for international remittances, financial institutions must strictly adhere to statutory requirements for suspicious activity reporting. The table below summarizes key compliance standards:
| Statutory Requirement Category | Specific Details |
|---|---|
| Account Type Restrictions | Prohibit anonymous accounts; corporate accounts require real-name verification and ultimate controller checks; multi-currency accounts require scrutiny of fund purposes |
| National Blacklist Mechanisms | Prohibit or restrict account openings and transactions from high-risk countries like North Korea, Iran, Syria, Cuba, and Sudan |
| Reporting Threshold (U.S.) | Single cross-border transactions exceeding $10,000 USD must be reported to FinCEN |
| Reporting Threshold (EU) | Cash transactions exceeding €10,000 require identity verification and suspicious activity reporting |
| Fund Source and Purpose Scrutiny | Monitor abnormal fund flows, frequent small-amount consolidations, or fund detours to ensure traceability |
| Regulatory Penalties | Failure to meet regulatory duties results in heavy fines, e.g., €27 million in the EU |
In practice, Hong Kong banks may freeze or permanently close accounts if customers fail to register accurate information or engage in fictitious transactions. For example, a Southeast Asian e-commerce merchant had their account frozen for 12 months due to unregistered authentic merchant information. Sellers receiving fictitious order payments through overseas related accounts may also have their accounts closed as suspicious transactions.
Compliance recommendations include:
- Improving real-name authentication and KYC documentation
- Planning fund flows reasonably to avoid abnormal reflux
- Ensuring transparent transaction notes with clear transaction nature and order numbers
- Choosing licensed, legitimate cross-border payment platforms
- Regularly reviewing account transaction records to prevent high-risk activities
The suspicious activity reporting system provides legal assurance for international remittance compliance, helping institutions promptly detect and block illicit fund flows.
Ongoing Due Diligence
Ongoing Due Diligence is a dynamic management component of AML compliance systems. Financial institutions must not only conduct due diligence during account opening but also continuously track and assess risks throughout the customer’s business lifecycle.
- Ongoing due diligence covers customer identity, business status, related companies, transaction counterparties, credit records, financial metrics, international operations, and cross-border payment behaviors.
- Risk identification follows “know your business,” “logical reasonableness,” and “commercial reasonableness” principles, focusing on reviewing transaction backgrounds, nature, processes, and purposes, with particular attention to material relevance and consistency.
- Institutions monitor abnormal account transactions, intensifying due diligence upon detecting risks, submitting suspicious activity reports if necessary, and imposing restrictions on transaction methods, scales, or frequencies, or refusing transactions or terminating business relationships in severe cases.
- Enhanced due diligence is applied to politically exposed persons (PEPs) and their associates to mitigate high risks.
- Institutions have periodic review obligations, regularly reassessing customer risk levels, dynamically adjusting based on time and behavior changes, and re-conducting due diligence when necessary.
- Multi-institutional collaborations may adopt stricter AML measures.
Hong Kong banks typically integrate industry-leading databases and identity verification technologies, continuously screening high-risk customers and PEPs, identifying ultimate beneficial owners (UBOs), and using automated data extraction combined with intelligence and expertise for risk trend analysis.
Per FATF guidelines, risk assessment involves identification, analysis, and evaluation, requiring institutions to combine quantitative and qualitative data to dynamically adjust AML monitoring strategies and resource allocation.
Ongoing due diligence helps institutions dynamically identify potential high-risk customers, ensuring the compliance and safety of international remittance operations.
Compliance Standards and Regulation
International Standards
The FATF (Financial Action Task Force) sets global standards for anti-money laundering and counter-terrorist financing. Most countries have conducted risk assessments on the virtual asset industry, implementing regulatory or prohibitive measures. FATF promotes compliance improvements through periodic assessments and international cooperation. Some countries achieve substantial compliance, but none are fully compliant. FATF maintains grey and black lists, imposing mandatory measures on non-compliant countries.
FATF continuously revises recommendations to address financial innovations and risk changes. For example, October 2023 revisions to Recommendation 8 emphasized risk-based principles, requiring risk controls for non-profits with terrorist financing risks. February 2023 initiated revisions to Recommendation 16 to enhance payment transparency. From 2024-2026, FATF will strengthen global network effectiveness, promote standard enforcement, focus on financial innovation risks, and enhance public-private cooperation.
International standards provide a unified framework for national regulations, but implementation varies.
Major Country Regulations
Countries tailor regulations to their financial environments. The U.S. implements strict AML and counter-terrorist financing regulations through FinCEN (Financial Crimes Enforcement Network), requiring institutions to report large and suspicious transactions. Canada’s FINTRAC (Financial Transactions and Reports Analysis Centre) emphasizes customer identity verification and continuous monitoring. Australia’s AUSTRAC (Australian Transaction Reports and Analysis Centre) requires timely reporting of international large transactions and suspicious activities.
China’s foreign exchange authorities require institutions to open foreign exchange accounts for customers and report foreign exchange receipts, payments, and account changes. Regulations differ in reporting thresholds, customer due diligence, and penalties, requiring businesses to address local compliance in cross-border operations.
Regulatory Authorities
Key regulators include FATF, FinCEN, FINTRAC, and AUSTRAC. China’s foreign exchange authorities enforce foreign exchange regulations, oversee institutional forex operations, manage national forex reserves, compile international balance of payments, supervise forex activities, and address violations legally.
These authorities ensure financial system safety through regulation development, market oversight, investigations, and asset freezing. They also regularly publish balance of payments data, accept and protect whistleblower reports, and penalize non-compliant entities and individuals.
Regulatory authorities balance compliance and business development in implementing international standards, posing localized compliance challenges for businesses.
Technology and Compliance Innovation
AI and Smart Monitoring
Technological innovation drives compliance management into the intelligent era. Hong Kong banks continuously iterate API interfaces, integrating blockchain and big data to build comprehensive risk control systems. Smart risk control models analyze transaction data in real-time, identifying potential risks and enhancing system resilience. Banks use machine learning algorithms to automatically detect abnormal transaction patterns, issuing timely alerts for money laundering and terrorist financing. Real-time tracking enhances compliance execution accuracy, ensuring effective monitoring of every cross-border payment. Technological innovation also supports banks in developing hybrid products, meeting diverse customer needs and improving service experiences. Expert Zeng Gang noted that banks’ technical capabilities and system integration stability are core competencies in cross-border payment operations. Technology not only boosts compliance efficiency but also creates a virtuous cycle for business expansion.
System Support
System support is critical in automating compliance processes:
- Helps organizations achieve ongoing regulatory compliance, proactively identifying potential risks.
- Automatically checks non-compliant areas, responding quickly to regulatory changes.
- Standardizes and customizes compliance efforts to meet regional and industry requirements.
- Clearly assigns tasks, tracks requests, and corrective actions, improving execution efficiency.
- Supports real-time risk monitoring, enabling timely corrective measures to prevent risk recurrence.
- Facilitates automated compliance audits and complaint handling, enhancing management comprehensiveness.
- Achieves seamless integration of compliance goals with business processes through system customization.
Highly automated system support enables banks to address compliance issues in real-time, reducing manual operation risks and enhancing the transparency and security of international remittances.
Practical Recommendations and Challenges
Efficient Compliance Processes
Efficient compliance processes help businesses and institutions reduce risks and improve management. Industry best practices typically include:
- Resource and IT Support: Businesses should allocate sufficient human, material, and IT resources to ensure smooth compliance operations.
- Compliance Performance and Monitoring: Regularly assess compliance goal achievement and promptly address identified issues.
- Communication and Reporting Mechanisms: Establish efficient internal communication and reporting channels to promote departmental collaboration.
- Independence and Accountability: Compliance teams must remain independent, ensuring effective accountability mechanisms.
- Diverse Evaluation Methods: Use interviews, surveys, sampling analysis, and system testing to comprehensively assess compliance effectiveness.
- Closed-Loop Management: Compliance processes should cover planning, preparation, implementation, analysis, reporting, and improvement for continuous optimization.
- Integration of International Standards and Chinese Policies: Reference ISO 37301, ISO 37302, and align with Chinese policies to form a systematic compliance framework.
- Clear Evaluation Entities: Compliance management departments or senior executives should oversee, ensuring professionalism.
- Key Area Controls: Set compliance control points for high-risk areas and critical business processes.
- Periodic Evaluation and Continuous Improvement: Conduct regular compliance system effectiveness evaluations to drive ongoing improvements.
For example, Ant Financial’s acquisition of MoneyGram failed due to inadequate assessment of CFIUS (Committee on Foreign Investment in the United States) review risks, resulting in a high breakup fee. Businesses must identify key risk points in advance and develop contingency plans when designing compliance processes.
Addressing Common Issues
Compliance failures occur frequently in practice, including inadequate AML regulation adherence, sanctions list screening deficiencies, weak exchange rate fluctuation risk management, and insufficient data security protection. For instance, Company G, due to ineffective screening of agent address information, conducted transactions with a sanctioned commercial center, amassing over $1 million USD and incurring an OFAC fine of over $400,000 USD. This case highlights sanctions list screening and address verification as compliance management challenges.
Businesses can adopt these measures:
- Establish integrated financial and tax systems for real-time cross-border transaction monitoring.
- Use automation tools to streamline compliance, such as smart contracts for transaction compliance verification.
- Conduct regular compliance training to enhance employee risk awareness.
- Collaborate with professional financial and legal advisors to identify potential risks.
- Improve sanctions screening logic with regular testing to ensure recognition of diverse place names and spellings.
- Promptly address violations, proactively report to regulators, and seek penalty reductions.
An e-commerce platform’s sanctions screening system failed to recognize multiple spellings of sanctioned regions, leading to compliance gaps. Regulators recommend maintaining strict automated screening rules, implementing remedial measures immediately upon detecting issues, and applying alternative controls until root causes are resolved.
KYC and AML compliance have become foundational standards in the international remittance industry. The industry widely recognizes that every stage of cross-border payments requires rigorous scrutiny to enhance transparency and security. The CPMI report notes that identity information sharing and consistent regulation are key to improving efficiency. In the future, AI and other technologies will drive intelligent compliance management, helping businesses and individuals navigate evolving policy environments for secure and efficient international remittances.
FAQ
What are the main documents required for the KYC process?
Customers need to prepare passports or ID cards, address proofs (e.g., utility bills), company articles of association, and ownership structure charts. Hong Kong banks require authentic, valid, and consistent documents.
Which behaviors in international remittances are likely to be deemed suspicious?
Frequent small-amount split remittances, funds directed to high-risk countries, unusually large transactions, or fund flows unrelated to business activities may be deemed suspicious by Hong Kong banks.
How do AML monitoring systems identify risky transactions?
Systems analyze transaction amounts, frequencies, customer historical behaviors, and sanctions list screenings to automatically detect abnormal patterns. Hong Kong banks combine manual reviews to ensure robust risk control.
How do compliance requirements differ across countries?
The U.S., Canada, and Australia differ in reporting thresholds, customer due diligence, and penalty standards. Businesses must monitor local regulations and adjust compliance strategies accordingly.
What are the applications of AI in compliance management?
AI automatically identifies abnormal transactions, optimizes risk assessment models, and enhances data processing efficiency. Hong Kong banks widely use AI to improve compliance monitoring accuracy and response speed.
After a deep dive into the KYC and AML compliance essentials of international remittance, it’s clear that while traditional financial institutions have strict compliance procedures, their complex material requirements and lengthy review cycles often overwhelm individuals and businesses. These cumbersome steps not only reduce the efficiency of fund circulation but can also introduce potential compliance risks due to information opacity. BiyaPay was created to solve these pain points, offering you a safer and more efficient cross-border financial solution. We have significantly simplified the traditional KYC process with one-stop digital identity verification, allowing you to remit with a fee as low as 0.5% and achieve same-day delivery, completely eliminating opaque exchange spreads and long waits. Moreover, our platform supports the conversion between various fiat and digital currencies, so you don’t need a complex overseas account to invest in both U.S. and Hong Kong stocks on one platform, easily diversifying your assets. Say goodbye to compliance hassles and register with BiyaPay today to start your smart remittance journey.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















