- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
What’s Driving the Surge in Nuclear Energy Stocks

Image Source: pexels
Nuclear energy stocks have captured investor attention with record-breaking gains in 2025. The Nuclear Energy Index climbed nearly 61% in the past year, far outpacing wind and solar energy sectors. Companies such as Oklo, NuScale, and Cameco have seen notable surges, driven by demand for clean energy and the need for reliable power in AI data centers. Investors now look to four main drivers: robust policy support, rapid technology advances, shifting market trends, and positive investor sentiment. This momentum highlights why nuclear energy stands out in today’s clean energy landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Strong government policies and funding worldwide boost nuclear energy growth and investor confidence.
- New reactor technologies like small modular reactors make nuclear power safer, cheaper, and more flexible.
- Rising energy demand from AI and data centers increases the need for reliable, clean nuclear power.
- Investor interest grows as nuclear energy aligns with climate goals and offers promising stock returns.
- Regulatory challenges and waste management costs remain risks but do not overshadow nuclear’s long-term potential.
Policy Shifts
Government Support
Governments worldwide have introduced a wave of incentives and funding to accelerate nuclear energy deployment. In the United States, the Department of Energy’s Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program supports partnerships to bring advanced reactors to market faster. The “Reinvigorating the Nuclear Industrial Base” Executive Order prioritizes funding for restarting closed plants, expanding uranium enrichment, and constructing advanced small modular reactors (SMRs). The DOE plans to allocate up to $900 million to support advanced reactor deployment. China has implemented a national strategy that includes state financing, low-interest loans from state-backed banks, feed-in tariffs, VAT rebates, and discounted land for nuclear projects. These policies reduce nuclear energy costs to about $70 per MWh, making it more competitive. China also backs next-generation technologies, such as SMRs and molten salt reactors.
Recent funding programs highlight the scale of government commitment:
| Funding Program / Act | Amount (USD) | Purpose / Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act (IIJA) + IRA | $85 billion | Boosts DOE innovation, including nuclear fission technologies |
| DOE Civil Nuclear Credit Program | ~$6.4 billion | Supports existing U.S. nuclear reactor plants |
| High Assay, Low Enriched Uranium (HALEU) program (IRA) | ~$700 million | Builds domestic supply chains for advanced reactors |
These measures have boosted investor confidence. For example, Uranium Energy Corp’s stock price more than doubled in the past year. Goldman Sachs issued a buy rating, citing government efforts to rebuild nuclear fuel supply chains. Policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act and bipartisan support encourage investment and long-term stability for nuclear energy stocks.
Climate Goals
International climate agreements have elevated nuclear energy as a key solution for decarbonization. The COP28 agreement officially recognized nuclear energy as essential for deep decarbonization and called for tripling global nuclear capacity by 2050. Over 20 countries pledged to expand nuclear energy, and leaders from France and Belgium announced new initiatives to support this goal. National climate commitments now increasingly reference nuclear energy as a critical tool for reducing emissions and supporting economic growth. The Biden Administration’s target of 100% clean electricity by 2035 and the Paris Agreement’s goals drive significant investment in nuclear infrastructure. Modeling shows that advanced reactors could supply up to 50% of U.S. electricity by 2050, requiring capital investments of up to $1.1 trillion.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory agencies have modernized approval processes to support new nuclear energy projects. The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) introduced a new licensing framework (10 C.F.R. Part 53) tailored for advanced reactors and SMRs. This framework streamlines approvals, reduces timelines, and accommodates new technologies. The NRC now allows multiple license application types, combined applications for identical designs, and updated technical requirements for advanced reactors. Recent changes also expedite environmental reviews and clarify waste management requirements. A presidential directive calls for further reforms to promote efficient licensing and deployment of innovative nuclear technologies. These regulatory updates lower barriers and accelerate the growth of nuclear energy.
Technology in Nuclear Energy

Image Source: pexels
Reactor Innovation
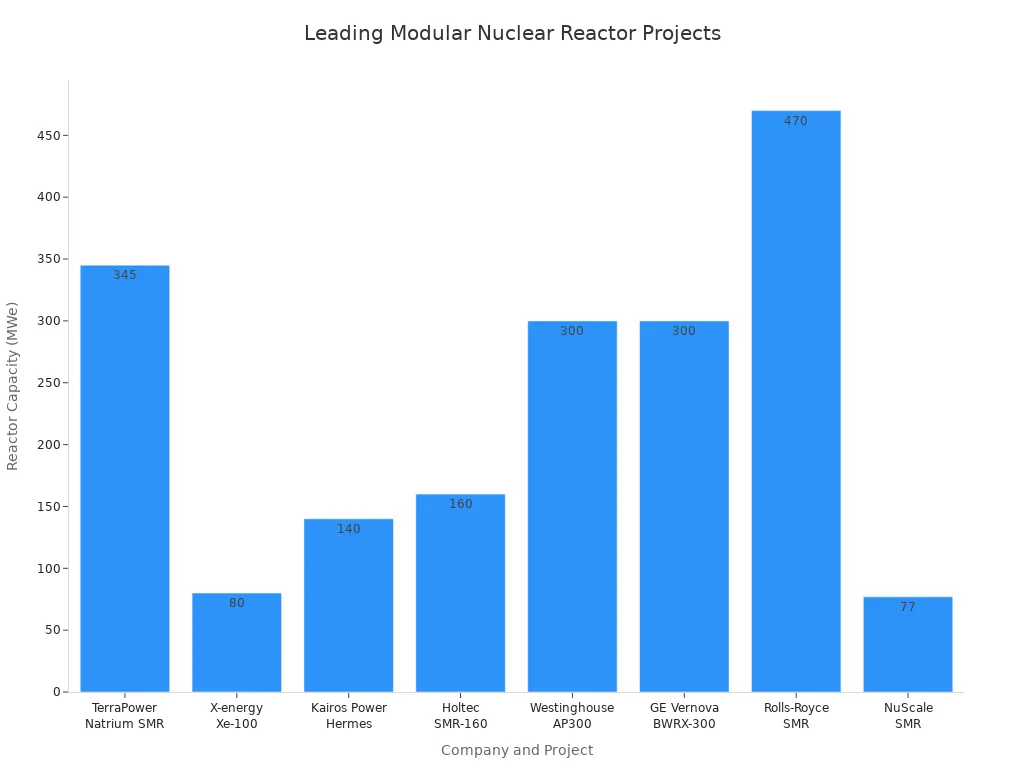
Recent advances in nuclear energy technology have transformed reactor design. Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) now offer compact, scalable solutions with passive safety systems and lower upfront costs. Companies such as NuScale, TerraPower, and Kairos Power lead the development of these reactors. TerraPower’s Natrium SMR, supported by the U.S. Department of Energy, aims for operation in Wyoming by 2030. X-energy’s Xe-100 and Holtec’s SMR-160 have secured major funding and partnerships, including Amazon and Dow. Westinghouse Electric unveiled the AP300 modular reactor, targeting certification by 2027. These projects highlight the global push for advanced nuclear energy solutions.
| Company | Headquarters | Reactor Type / Project | Latest Milestones / Developments |
|---|---|---|---|
| TerraPower | USA | Natrium SMR (345 MWe sodium-cooled) | DOE award for demo plant in Wyoming, aiming operation ~2030; molten salt energy storage system |
| X-energy | USA | Xe-100 (80 MWe high-temp gas reactor) | DOE award; 4-unit plant planned in Washington by late 2020s; Amazon investment; partnership with Dow |
| Kairos Power | USA | Hermes molten salt test reactor | NRC construction permit; demo startup by 2027; Google partnership; plans for ~140 MWe commercial SMR |
| Holtec International | USA | SMR-160 (160 MWe PWR) | DOE grant for final design; agreement to build up to 20 units in Ukraine, first unit targeted for 2029 |
| Westinghouse Electric | USA | AP300 (300 MWe modular PWR) | Unveiled AP300 in 2023; NRC certification targeted by 2027; microreactor eVinci in development |
| GE Vernova | USA | BWRX-300 (300 MWe SMR) | Ontario Power Generation building first grid-scale SMR in Canada, online by 2028 |
| Rolls-Royce Holdings | UK | 470 MW modular SMR | UK government funding; first units expected mid-2030s; leveraging submarine reactor experience |
| Fluor Corporation | USA | Majority owner of NuScale Power | Holds ~60% stake; supports NuScale SMR development; potential contractor for deployments |
Safety Advances
Safety remains a top priority in nuclear energy innovation. Next-generation reactors use passive safety systems that rely on gravity and natural coolant circulation. These systems can shut down and cool the reactor core without human intervention or external power. Advanced accident-tolerant fuels, such as Cr-coated Zircaloy and FeCrAl cladding, improve performance under extreme conditions. TRISO microparticles feature triple-layer coatings that act as containment barriers, preventing fuel melting and retaining fission products at very high temperatures. Regulatory agencies now use risk-informed frameworks to address unique safety challenges. Public engagement and transparency have become essential, especially as some reactors may be located closer to communities.
Recent safety advances have improved insurability and public acceptance:
- Small modular reactors and new technologies support growth and safety.
- Positive financing environments and tax credits encourage nuclear energy projects.
- The World Bank now considers small reactors transformative and safe.
- Executive orders reduce regulatory burdens and promote nuclear energy as reliable baseload power.
Cost Efficiency
Technological innovation has driven significant cost reductions in nuclear energy production. SMRs and advanced reactors benefit from learning rates and deployment scale effects. Multi-unit sites achieve lower capital and operational costs. The following table shows projected cost reductions for SMRs and large reactors compared to a 2030 baseline:
| Year | Projected Nuclear Capacity (GW) | SMR Cost Reduction vs 2030 (%) | Large Reactor Cost Reduction vs 2030 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | 1 | Reference | Reference |
| 2035 | 3 (Moderate) / 14 (Advanced) | 19 / 41 | 4 / 25 |
| 2040 | 8.5 (Moderate) / 58 (Advanced) | 34 / 55 | 18 / 43 |
| 2045 | 17 (Moderate) / 124 (Advanced) | 44 / 61 | 28 / 51 |
| 2050 | 34 (Moderate) / 200 (Advanced) | 50 / 64 | 37 / 55 |
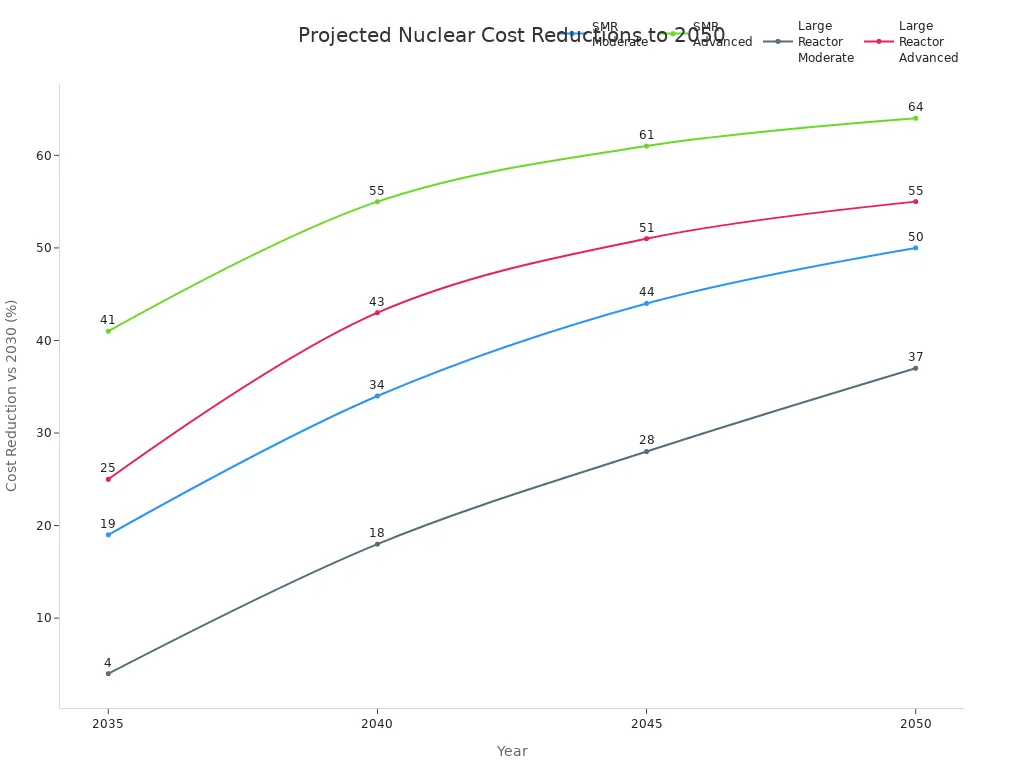
Operating costs for new nuclear energy technologies remain competitive with fossil fuels and renewables, especially when factoring in carbon mitigation. Multi-unit sites further reduce costs, with overnight capital cost reduction factors as low as 0.7 for ten units. These advances make nuclear energy a more attractive option for clean and reliable power.
Market Trends in Nuclear Energy Stocks
Image Source: pexels
Energy Demand
Global energy demand is rising at an unprecedented pace, driven by the rapid expansion of data centers, artificial intelligence, and technology infrastructure. In the United States, data center electricity demand is projected to increase five-fold by 2035, reaching 176 GW. Data centers, AI, and cryptocurrencies accounted for 2% of global electricity consumption in 2022, with expectations to double by 2026. Major technology companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Meta have more than doubled their electricity use since 2017. These companies require reliable, clean baseload power to support uninterrupted operations. Nuclear energy offers a solution with a capacity factor exceeding 92.5%, outperforming both natural gas and renewables. Its high energy density, low carbon emissions, and efficient land use make it attractive for meeting the surging needs of the technology sector.
The nuclear industry is responding by expanding its workforce and attracting record levels of private equity investment. Tech giants are signing power purchase agreements with nuclear utilities and investing in advanced nuclear technologies, including small modular reactors (SMRs). These reactors, expected to be commercially available around 2030, promise scalable and cost-effective solutions tailored to data center requirements. As a result, nuclear energy stocks have gained momentum, reflecting investor confidence in the sector’s ability to meet growing and decarbonizing energy demands.
Supply Chain
The nuclear energy sector faces significant supply chain challenges that affect project timelines and costs. Building nuclear power plants requires multi-billion dollar capital investments and involves lengthy licensing and regulatory approval processes. These factors often lead to construction delays and increased costs, which can deter both public and investor interest.
- High capital costs and regulatory delays extend project timelines.
- Limited supplier competition and reliance on custom components drive up procurement costs.
- The nuclear fuel supply chain faces critical gaps, especially in the production of high-assay low-enriched uranium (HALEU), with the United States producing almost none domestically.
- Geopolitical risks, such as reliance on foreign suppliers like Russia for nuclear fuel, add further uncertainty.
For example, Vogtle Units 3 and 4 in the United States received their operating license in 2008 but only began commercial operation in 2024 due to post-Fukushima safety requirements and design changes. Regulatory unpredictability and bespoke approvals also contribute to extended construction timelines. To address these issues, companies are pursuing vertical integration, standardizing components, and investing in domestic HALEU production. These efforts aim to improve procurement efficiency and reduce economic and geopolitical risks. However, current supply chain limitations continue to pose challenges for nuclear energy stocks, especially for junior miners and new entrants.
Uranium Prices
Uranium prices play a critical role in the performance of nuclear stocks. The spot price of uranium peaked at $107 per pound in early 2024, then stabilized around $65 per pound by early 2025. Term prices remain strong above $80 per pound. The market remains structurally bullish, with a deepening multi-year supply deficit, constrained production growth, and accelerating demand from global nuclear fleet expansion and policy support. Uranium prices have shown resilience and independence, holding steady even as broader financial markets experienced volatility.
Supply chain disruptions have caused volatility and mixed impacts on nuclear energy stocks. For instance, Cameco, a leading uranium producer, reduced its 2023 production guidance due to operational challenges. Despite this, Cameco’s stock price performed positively, benefiting from higher uranium spot prices and increased production readiness. In contrast, junior miners such as Global Atomic Corporation and GoviEx Uranium Inc. experienced sharp declines in stock prices due to geopolitical unrest in Niger, which raised concerns about mine delays.
| Company/ETF | 1-Year Return | Key Factors Driving Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Global X Uranium ETF (URA) | 47.98% | Exposure to uranium mining, regulatory reforms, global nuclear energy interest |
| Range Nuclear Renaissance ETF (NUKZ) | 45.89% | Focus on alternative energy equities, clean energy partnerships, favorable policy environment |
| Cameco Corp. (CCJ) | N/A | Benefited from higher uranium prices and production readiness |
| Oklo Inc. | N/A | Gained from innovation in microreactors and clean energy demand |
Nuclear energy ETFs such as Global X Uranium ETF and Range Nuclear Renaissance ETF delivered strong returns over the past year. Their performance reflects increased uranium mining activity, a global shift toward nuclear as a low-carbon energy source, and supportive regulatory developments. While uranium mining equities and junior miners declined in early 2025 due to investor sentiment and macroeconomic uncertainty, the underlying fundamentals remain strong. Utilities are expected to resume contracting as policy clarity improves, supporting future price strength and a positive outlook for nuclear energy stocks.
Investor Sentiment and Clean Energy
ESG Investing
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing has become a major force in shaping the direction of clean energy markets. Investors now seek companies that align with global sustainability goals. Clean energy mandates increasingly include nuclear energy as a core component. In May 2025, President Trump signed executive orders that expanded nuclear power production and excluded uranium from new tariffs. This policy shift led to a surge in nuclear energy stocks. Cameco shares rose nearly 100% over twelve months, while BWX Technologies climbed more than 50% in 2025. These gains reflect investor confidence in nuclear energy’s role in meeting clean energy targets and long-term demand growth. Companies that demonstrate strong ESG credentials attract more capital and enjoy higher valuations.
Institutional Interest
Large institutional investors have increased their exposure to nuclear energy companies. Their investments signal confidence in the sector’s growth prospects and stability. The following table highlights recent institutional moves:
| Institutional Investor | Nuclear Energy Company | Investment Amount (USD) | Additional Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional investors (undisclosed) | NANO Nuclear Energy | $99 million | Closed $105 million common stock offering; net proceeds approx. $99 million; investors not named. |
| Energy Impact Partners | Atomic Canyon | $7 million | Led seed round; VP Jenny Gao joined Atomic Canyon board. |
| Brookfield Asset Management | Westinghouse Electric | N/A | Holds controlling stake; planning entry into India nuclear market; amount not disclosed. |
Institutional participation provides stability and resources for innovation. These investments support the development of advanced reactors and new clean energy solutions. The presence of major asset managers and venture capital firms in nuclear energy signals a shift toward mainstream acceptance.
Public Perception
Public opinion about nuclear energy has shifted over time. Safety concerns and environmental priorities influence attitudes. Recent polls show a resurgence in support for nuclear energy in the United States. A 2024 Pew Research Center poll found that 56% of Americans favor expanding nuclear capacity, up from 43% in 2016. This increase reflects growing recognition of nuclear energy as a clean energy option. However, wind and solar remain more popular among the public. Support varies by region and age group, with older adults and those near nuclear plants showing higher approval.
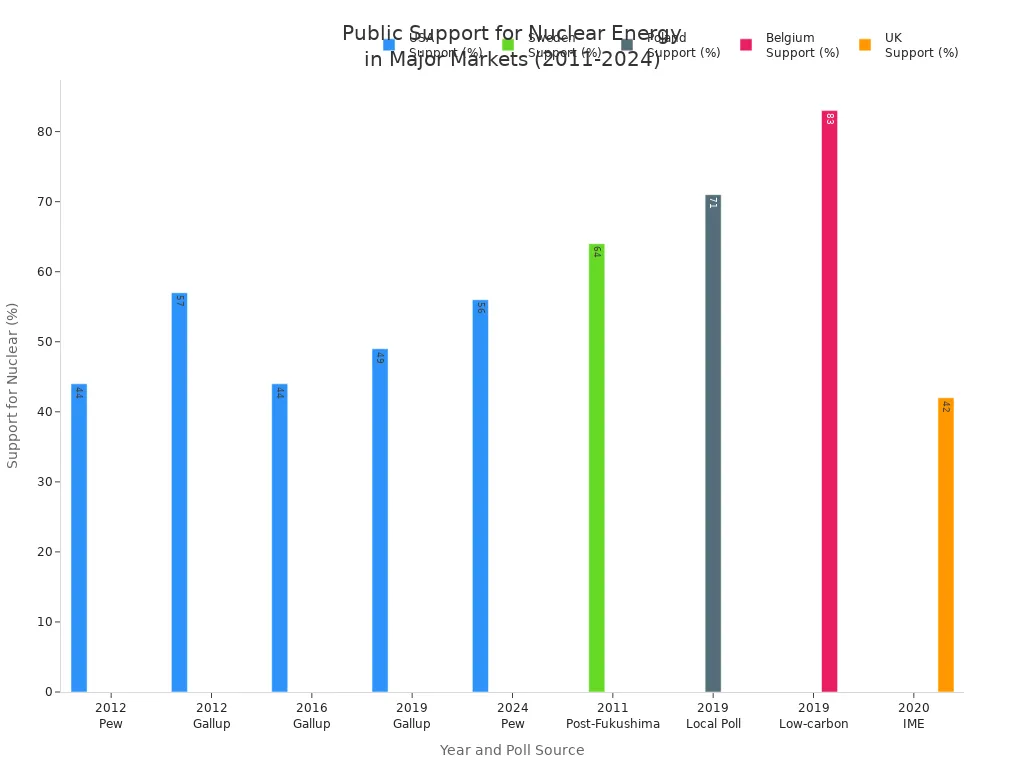
Note: Public perception can change quickly after major events. Environmental awareness and climate change concerns have helped nuclear energy regain some support as part of the clean energy mix.
Risks for Nuclear Stocks
Regulatory Hurdles
Nuclear energy companies face ongoing regulatory challenges that can impact both project timelines and stock performance. Regulatory delays and complex licensing processes remain significant risks. These hurdles often lead to unpredictable approval timelines for new reactors and technologies. Companies such as Oklo Inc. have experienced sharp stock fluctuations due to uncertainties in regulatory approvals. For example, Oklo Inc.'s stock volatility reached approximately 10.68%, reflecting how sensitive the market remains to regulatory developments. Political support and efforts to speed up permitting have provided some positive momentum, but overall uncertainty continues to influence investor sentiment and stock prices.
Key regulatory risks include:
- Lengthy and complex licensing processes
- Unpredictable approval timelines for new technologies
- Shifting political support and regulatory frameworks
Waste Management
Nuclear waste management presents both financial and operational challenges for companies in the sector. The costs associated with safe storage, transportation, and disposal of nuclear waste remain high. Companies must invest continuously in new technologies and compliance measures to meet evolving safety standards. The following table summarizes the latest statistics on nuclear waste management:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Market Value 2025 | USD 5.12 billion |
| Projected Market Value 2032 | USD 6.00 billion |
| CAGR (2025-2032) | 2.3% |
| Financial Challenges | High costs, strict regulatory guidelines for storage and transportation |
| Impact on Companies | Ongoing investment in technology and compliance affects financial performance |
| Key Players | Veolia, Orano Group, Bechtel Corporation, Holtec International |
Companies must also adapt to frequent upgrades and global harmonization efforts, which can further increase costs. These factors place pressure on financial results and require careful management.
Market Volatility
The energy sector has experienced significant volatility in recent years. Traditional energy stocks, such as oil and gas, often react sharply to changes in crude oil prices and geopolitical events. For example, the S&P 500 energy sector saw annual returns swing from -33.68% in 2020 to 65.72% in 2022, then to 5.7% in 2024. Nuclear energy stocks, however, benefit from strong government support in the United States, Europe, and Asia, which helps insulate them from some of this volatility. Nuclear power’s ability to provide continuous electricity also supports grid stability and energy security. While nuclear stocks remain less volatile than traditional energy stocks, regulatory and supply chain risks can still cause sharp price movements, especially for companies awaiting project approvals or facing operational delays.
Nuclear energy stocks continue to surge due to strong policy support, rapid technology innovation, and rising global energy demand. Investors see opportunity as companies like Constellation Energy and Vistra expand capacity to meet the needs of AI data centers and electrification.
- Global energy demand rises, driven by AI and urbanization.
- Climate change goals position nuclear as a key low-carbon solution.
- Over 60 reactors are under construction worldwide, with 20 countries planning to triple capacity by 2050.
| Aspect | Key Insight |
|---|---|
| Investment Outlook | IEA projects annual nuclear investment to exceed $150 billion by 2030. |
| Stock Opportunities | Both established firms and new entrants offer growth potential. |
Investors should balance opportunity with risks, but the outlook for nuclear energy remains strong in the clean energy transition.
FAQ
What makes nuclear energy stocks attractive to investors?
Nuclear energy stocks offer growth potential due to strong policy support, new technology, and rising clean energy demand. Investors see these companies as key players in the global shift toward low-carbon power.
How do uranium prices affect nuclear energy stocks?
Uranium prices directly impact the profitability of nuclear companies. Higher uranium prices often lead to increased stock values for producers and miners. Investors monitor price trends closely.
For current rates, see USD exchange rates.
Are there risks involved in investing in nuclear energy stocks?
Yes. Regulatory delays, waste management costs, and market volatility present risks. Investors should research each company’s exposure to these factors before making decisions.
Which companies lead in nuclear technology innovation?
Companies such as NuScale, TerraPower, and NANO Nuclear Energy lead in advanced reactor design and safety improvements. Their projects focus on small modular reactors and next-generation safety systems.
Can international investors participate in nuclear energy markets?
International investors can access nuclear energy stocks through global exchanges and ETFs. Many Hong Kong banks offer brokerage services for U.S.-listed nuclear companies.
Tip: Always check USD exchange rates before investing internationally.
The surge in nuclear energy stocks is more than a fleeting trend; it reflects a fundamental shift in global energy policy and technology. With strong government support, innovative SMRs, and rising demand from the tech sector, nuclear energy is positioned as a key player in the clean energy transition. While risks like regulatory hurdles and waste management remain, the long-term outlook appears robust. For international investors looking to capitalize on this trend, accessing US-listed nuclear energy companies and ETFs requires a reliable and efficient financial platform. BiyaPay provides a seamless solution. Our platform enables you to easily fund your account and trade US-listed stocks, with minimal friction. With our low fees for cross-border transactions and a transparent real-time exchange rate converter, you can preserve more of your investment gains. By simplifying the complexities of international finance, BiyaPay empowers you to build a portfolio that aligns with the future of clean energy. Take control of your financial future and begin your investment journey. Register with BiyaPay today.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.



















