- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Comprehensive Guide to Working in Thailand: Job Search Channels, Salary Standards, Tax Regulations, and Key Considerations

Image Source: pexels
When considering working in Thailand, you need to pay close attention to selecting job search channels. The Thai labor market is undergoing changes. According to the latest economic and government reports, more companies are leaning toward contract and part-time positions. Refer to the table below to understand current trends:
| Evidence Type | Content |
|---|---|
| Economic Report | Thailand’s labor market is experiencing a significant shift toward temporary and part-time employment due to economic uncertainty and the rise of artificial intelligence. |
| Statistical Data | According to a 2024 JobsDB survey, over 25% of organizations plan to reduce staff and restructure, favoring contract and part-time employment. |
| Government Report | The National Economic and Social Development Committee (NESDC) noted in its Q2 2025 report that economic uncertainty is prompting organizations to shift from full-time permanent positions to contract and part-time roles. |
You can combine your actual needs, stay updated on the latest policies, and flexibly plan your career development.
Key Points
- Choose appropriate job search channels, align with your background and industry trends, and enhance your skills and professional network.
- Understand salary standards across industries and regions, setting clear career goals to achieve higher income.
- Familiarize yourself with Thailand’s tax regulations and labor laws to ensure legal employment and social security.
- Respect Thai workplace culture and build good interpersonal relationships to adapt quickly to the work environment.
- Plan living costs reasonably, choosing a city and lifestyle that suits you to keep financial pressure manageable.
Job Search Channels

Image Source: pexels
When looking for a job in Thailand, you can choose from various job search channels. Different channels suit different types of job seekers. You need to flexibly select the appropriate method based on your career goals and actual circumstances. Below, we detail several mainstream job search channels and analyze their pros and cons.
Online Job Platforms
Online job platforms are among the most popular job search channels in Thailand. You can quickly browse a large number of job listings and filter for suitable positions. The widespread use of the internet and smartphones has led more people to choose online methods for job hunting. Data shows that 52% of job seekers prioritize online channels. These platforms are highly efficient for monitoring labor market trends and applying for jobs.
| Platform Name | Features |
|---|---|
| JobThai | Attracts millions of job seekers, offering various job categories suitable for all industries. |
| JobsDB | A leading recruitment portal in Asia, covering multiple industries with advanced search filters. |
| ThaiJob | Focused on the Thai market with a user-friendly interface, covering various industries. |
| A powerful professional networking tool, ideal for mid-to-senior-level professional recruitment. | |
| Glassdoor | Provides company reviews, suitable for building employer branding and attracting qualified candidates. |
| JobBKK | A local recruitment platform offering multi-industry job postings and career advice. |
| StartThailand | Focused on entry-level and technical positions, supporting job postings in Thai and English. |
| CareerJet | A global job search engine aggregating listings from multiple websites. |
| Adecco Thailand | Part of a global recruitment group, connecting employers and candidates across industries. |
| WorkVenture | Targets young professionals and startups, emphasizing company culture and work-life balance. |
| ThailandJobs77 | Focused on blue-collar and entry-level jobs, suitable for employers seeking temporary workers. |
| FreelanceBay | Thailand’s leading freelance recruitment platform, ideal for short-term projects and specialized skills. |
When using these platforms, you can filter by job category, location, salary, and other criteria. The advantages include a large volume of information, frequent updates, and ease of use. The disadvantages are intense competition and the potential for fraudulent job listings. You need to carefully verify information to avoid scams.
Social Media
Social media has become a significant part of job search channels in Thailand. You can access the latest job information through platforms like Facebook, Line, TikTok, and LinkedIn. Many companies post job vacancies in dedicated Facebook recruitment groups. Line allows you to communicate directly with companies for firsthand information. While TikTok is primarily for short videos, some companies use it to promote job openings. LinkedIn is ideal for professionals to build networks and find mid-to-high-level positions.
- Facebook: Wide coverage, fast updates, suitable for all job seekers.
- Line: Direct communication, ideal for quickly obtaining job details.
- TikTok: Suitable for exploring company culture and innovative positions.
- LinkedIn: Ideal for those with work experience looking to expand their professional network.
The advantages of social media include strong interactivity and fast information dissemination. You can directly communicate with recruiters and learn about company culture. The disadvantages are fragmented information and less detailed job postings. You need to actively filter to avoid missing important opportunities.
Job Fairs
Job fairs provide opportunities to interact face-to-face with employers. You can learn about company needs, submit resumes, and even participate in on-site interviews. Many universities and industry associations regularly host job fairs, attracting numerous companies and job seekers. You can collect company materials and gain insights into industry trends at these events.
Job fairs are suitable for recent graduates, career switchers, and those wanting to understand industry dynamics. The advantages include direct communication and diverse opportunities. You can showcase your abilities on-site, increasing your chances of being hired. The disadvantages are limited timing and locations, requiring you to stay updated on event information and plan your time accordingly.
Headhunters and Local Resources
Headhunters and local resources are also common job search channels in Thailand. Headhunting firms specialize in mid-to-high-level positions, helping you find roles that better match your qualifications. In industries with talent shortages, headhunters can effectively match companies with job seekers. Local resources, such as employment agencies and industry associations, can help you understand Thai culture and labor laws, aiding your adaptation to the local work environment.
- Advantages:
- Headhunters are highly effective in sourcing professional talent, especially for experienced job seekers.
- Local resources help you understand Thai work culture and legal regulations.
- Headhunters can attract passive candidates who aren’t actively job hunting, offering you more options.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex labor laws may make the recruitment process more challenging.
- You need competitive compensation and conditions to attract ideal positions.
When choosing headhunters or local resources, align your career goals with industry needs, weigh the pros and cons, and make the most suitable choice.
You can flexibly combine multiple job search channels based on your situation. Each channel has its advantages and limitations. You need to stay updated on market trends and enhance your competitiveness to stand out in the Thai job market.
Salary Standards

Image Source: pexels
Industry Salaries
When working in Thailand, you first need to understand salary levels across different industries. Salary differences in Thailand are significant. For example, the annual salaries of software engineers and doctors are much higher than those of teachers or hotel managers. The table below shows the average annual salaries for some popular professions:
| Profession | Average Annual Salary (THB) | Average Annual Salary (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | 1,500,000 | 42,650 |
| Doctor | 2,200,000 | 62,350 |
| Teacher | 800,000 | 22,760 |
| Hotel Manager | 1,000,000 | 28,450 |
You can see that the medical and IT industries generally offer higher salaries. Education and service industries have relatively lower salaries. When choosing an industry, assess salary levels based on your expertise and career direction.
Regional Differences
Salary standards and average salaries in Thailand vary significantly by region. Economically developed areas have noticeably higher salary levels than other regions. You can refer to the table below to understand minimum wage standards across regions:
| Region | Minimum Wage (THB/Day) | Minimum Wage (USD/Day) |
|---|---|---|
| Chachoengsao, Chonburi, Phuket, Rayong, Koh Samui | 400 | 11.55 |
| Muang District (Chiang Mai), Hat Yai District (Songkhla) | 380 | 10.97 |
| Bangkok and Surrounding Provinces | 372 | 10.74 |
| Narathiwat, Pattani, Yala | 337 | 9.73 |
You can view the distribution of minimum wages across Thailand in the chart below:
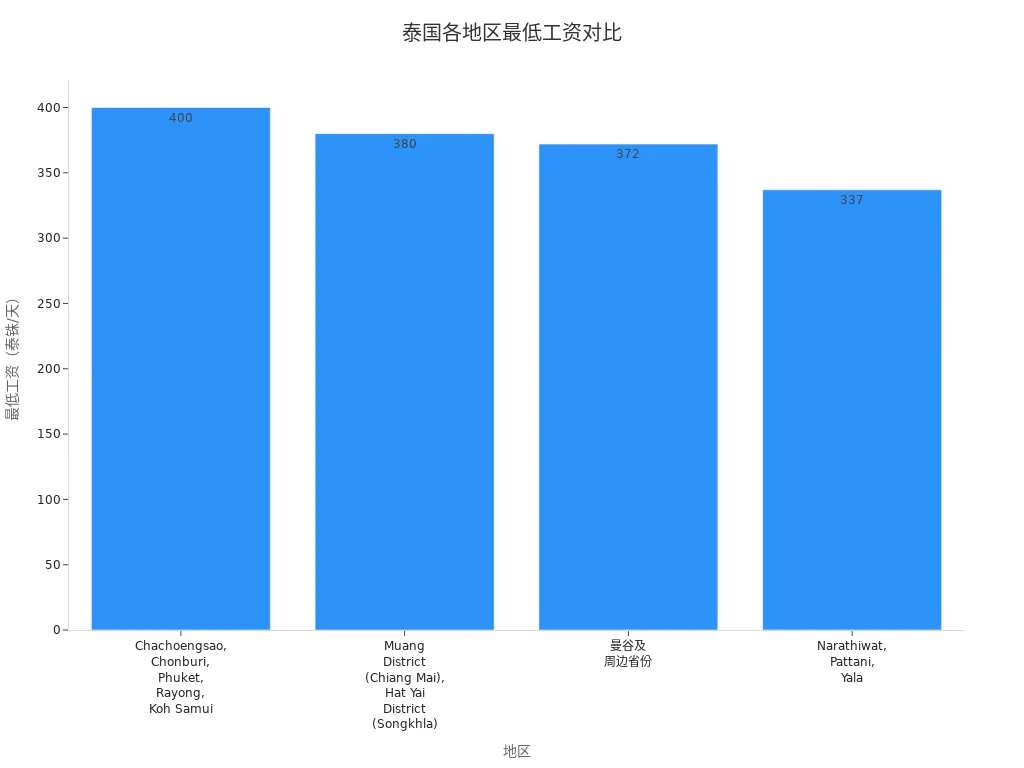
In addition to minimum wages, average salaries also vary by region. Bangkok has the highest average salary at 39,100 THB. The central region averages 30,200 THB, while the northeast averages 22,520 THB. Salary ranges also differ significantly in cities like Bangkok, Chiang Mai, and Phuket:
- Bangkok Salary: 25,000-50,000 THB
- Chiang Mai Salary: 20,000-35,000 THB
- Phuket Salary: 18,000-40,000 THB
When choosing a work location, consider the region’s economic development and living costs.
Influencing Factors
Salaries in Thailand are influenced by multiple factors. When job hunting, focus on the following key points:
| Influencing Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Industry Type | IT and medical industries offer high salaries, while education and services are lower. |
| Work City | Bangkok, Chiang Mai, and Phuket offer higher salaries than smaller cities. |
| Work Experience | More experienced workers earn higher salaries; entry-level roles have lower pay. |
| Education Level | Higher education typically leads to better starting salaries and promotion opportunities. |
| Company Size | Multinational and large companies offer better salaries and benefits. |
| Skill Certifications | Professional skills and international certifications help boost salaries. |
You can refer to the table below for salary levels in different cities and roles:
| City | Average Monthly Salary (THB) | Average Monthly Salary (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Bangkok | 100,000 | 2,846 |
| Chiang Mai | 65,000 | 1,850 |
| Phuket | 75,000 | 2,130 |
| Udon Thani | 50,000 | 1,423 |
When planning your career path, align your qualifications with market demands, improve professional skills, and enhance language proficiency to secure higher salaries and better opportunities.
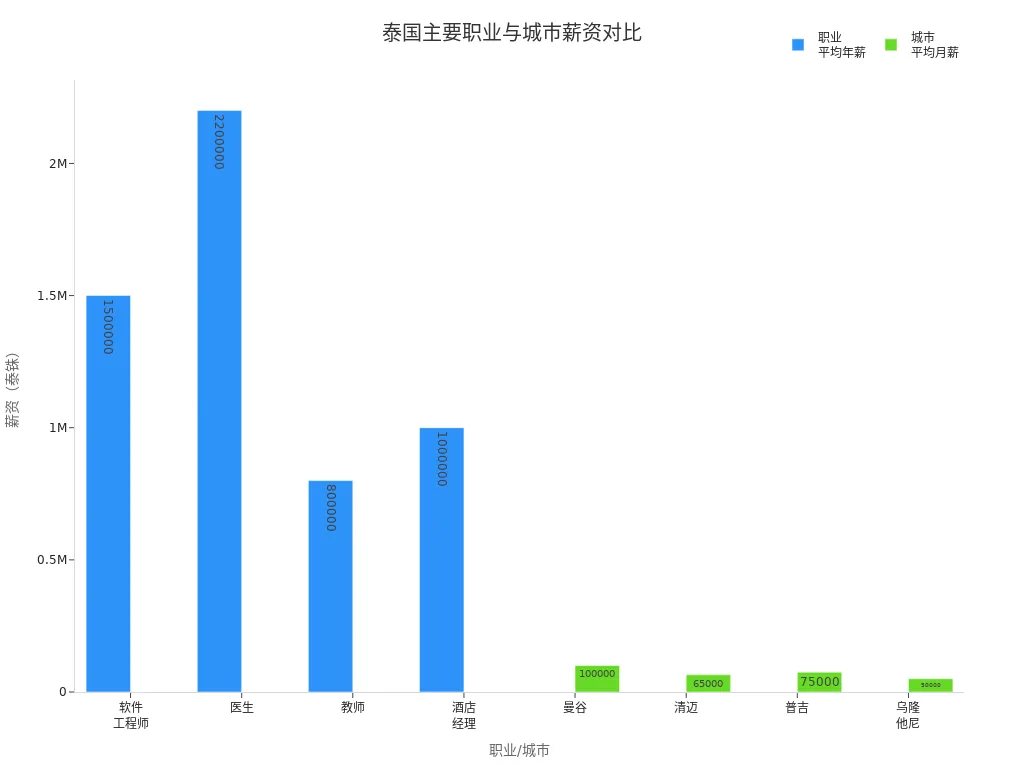
Salaries for Foreign Employees
As a foreign employee in Thailand, your salary is typically higher than that of local employees. Salary ranges vary significantly by role. The table below shows salary ranges for common foreign employee positions:
| Position Type | Foreign Employee Salary Range (THB) |
|---|---|
| Language School English Teacher | 30,000 - 50,000 |
| International School Teacher | 70,000 - 150,000 |
| Business and Finance Professionals (Marketing, Banking, etc.) | 70,000 - 200,000 |
| Technical Workers and Developers | 60,000 - 120,000 |
| Hotel Managers | 50,000 - 90,000 |
| Digital Nomads or Freelancers | Potentially over 150,000 |
When applying for foreign positions, you typically need strong professional skills and language proficiency. International school teachers, finance, and tech roles offer significantly higher salaries than regular teaching or service industry jobs. Note that some positions have strict requirements for education and experience.
Tip: When negotiating salaries, refer to industry and regional averages and leverage your qualifications to secure better compensation. Understanding Thailand’s salary structure helps you make informed career choices.
Tax Regulations
Personal Income Tax
When working in Thailand, you need to understand how personal income tax is calculated. Thailand uses a progressive tax rate, with higher incomes incurring higher tax rates. The table below shows the latest personal income tax rates for 2024:
| Taxable Income (THB) | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 – 150,000 | Exempt |
| 150,001 – 300,000 | 5% |
| 300,001 – 500,000 | 10% |
| 500,001 – 750,000 | 15% |
| 750,001 – 1,000,000 | 20% |
| 1,000,001 – 2,000,000 | 25% |
| 2,000,001 – 4,000,000 | 30% |
| Over 4,000,000 | 35% |
You can view the tax rate distribution in the chart below:
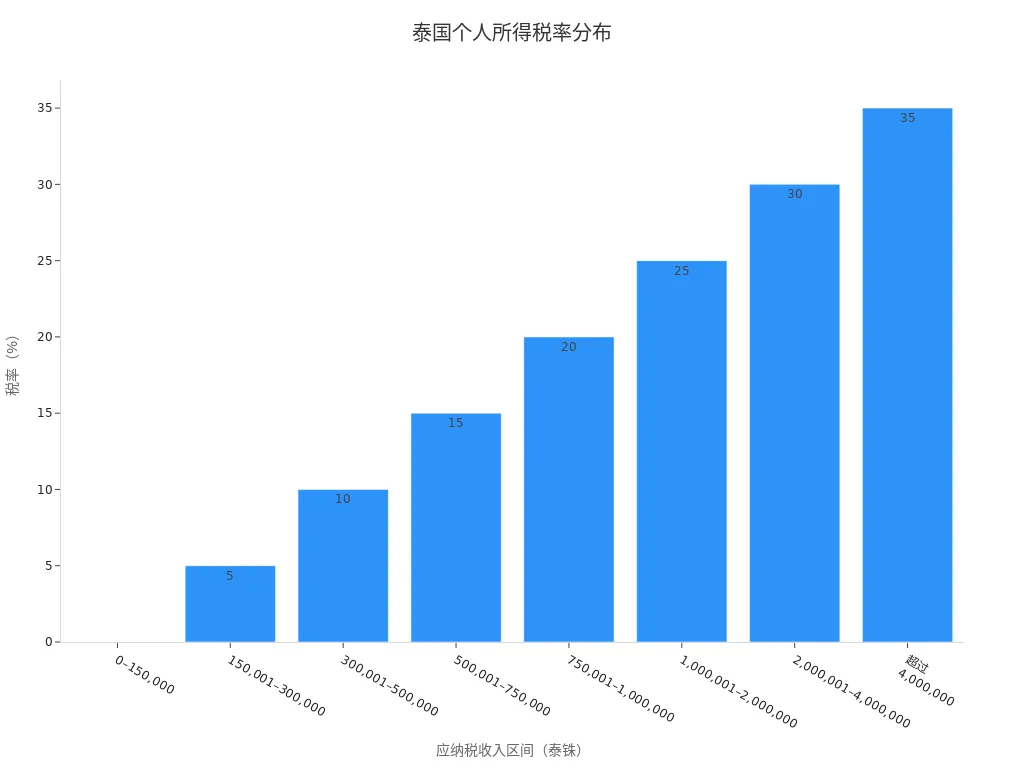
When calculating taxable income, you need to deduct statutory exemptions and related deductions. The tax office will verify your submitted information.
Social Security Fund
When employed in Thailand, both you and your employer must contribute to the social security fund. The specific regulations are as follows:
- Both employer and employee contribute 5% of monthly salary to social security.
- The contribution base ranges from a minimum of THB 1,650 to a maximum of THB 15,000.
- The maximum monthly contribution is:
- Employee: THB 750
- Employer: THB 750
- Total: THB 1,500
- If your monthly salary exceeds THB 15,000, contributions are still calculated based on THB 15,000.
Your monthly social security contributions will be deducted directly by your employer to ensure compliance.
Tax Filing Process
After working in Thailand, you need to file personal income tax annually. The filing process is as follows:
- Choose the appropriate filing form based on your income type. Use the PND 91 form for salary income only; use the PND 90 form if you have other income.
- The deadline for electronic filing is April 8, and for paper filing, it is March 31.
- If you have income from self-employment or rental properties, you must submit a mid-year filing by September 30.
You can file online through the Thai Revenue Department’s website or in person at a tax office.
Common Tax Pitfalls
When working in Thailand, common tax pitfalls include:
- VAT Registration: Companies with annual revenue exceeding THB 1,800,000 must complete VAT registration within 30 days, or face fines.
- Issuing Invoices: Invoices must meet tax office standards; fraudulent invoices can lead to fines or imprisonment.
- Withholding Tax: Different services have varying withholding tax rates, so understand these in advance to avoid underpayment.
Tip: When working in Thailand, file taxes on time and keep all invoices and income proof to avoid legal risks due to errors.
Key Considerations
Labor Laws
When working in Thailand, you need to understand local labor laws. Thai law has clear regulations on wages, working hours, breaks, and holidays. Refer to the table below for key provisions:
| Legal Provision | Description |
|---|---|
| Wages | Minimum wage is 331 THB, varying by region, approximately 9.5 USD. |
| Working Hours | Maximum of 8 hours per day, 48 hours per week. |
| Breaks and Holidays | At least 1 hour break after 5 hours of work, minimum 1 day off per week, and 13 statutory holidays annually. |
| Termination | Advance notice is required for termination, with severance pay in some cases. |
| Anti-Discrimination | Discrimination based on nationality, gender, etc., is prohibited. |
| Data Privacy | The Personal Data Protection Act safeguards your information. |
By adhering to these regulations, you can better protect your rights.
Work Visa
To work in Thailand, you must hold a valid work visa. Both you and your employer need to prepare various documents when applying for a visa. The table below lists common required documents:
| Type | Required Documents |
|---|---|
| Individual | Passport, non-immigrant visa, entry page, academic credentials, health certificate, recent photos, etc. |
| Employer | Work permit application form, company registration certificate, VAT certificate, social security contribution form, employment contract, etc. |
Preparing these documents in advance can improve application efficiency.
Annual Leave and Benefits
After working full-time in Thailand for one year, you are legally entitled to at least 6 days of paid annual leave. Most companies also offer the following benefits:
- Medical insurance covering common illnesses and hospitalization costs
- Supplementary health insurance to enhance social security coverage
- Provident fund and pension plans to help you save for the future
- A lump-sum retirement benefit upon retirement
Before joining a company, proactively inquire about its benefits policy to protect your interests.
Cultural Differences
Thai workplace culture differs significantly from that in mainland China. You need to pay attention to the following:
| Cultural Difference | Description |
|---|---|
| Respect for Authority | Emphasis on respecting superiors and elders, often using formal titles. |
| Hierarchical Structure | Decisions are often led by senior employees, with younger staff expected to show humility. |
| Indirect Communication | Preference for indirect expressions to avoid direct conflict or embarrassment. |
| Personal Relationships | Building good relationships with colleagues aids career development. |
| Work-Life Balance | Emphasis on family and personal life, with frequent leave for traditional holidays. |
By respecting these cultural norms, you can adapt more quickly to the Thai workplace.
Living Costs
When living in major Thai cities, you need to plan expenses carefully. The table below shows the average monthly living costs (in USD) for different cities:
| City | Average Monthly Living Cost (Single Person) | Average Monthly Living Cost (Family of Four) |
|---|---|---|
| Bangkok | 622.10 | 2,250.10 |
| Phuket | 520.90 | 1,877.30 |
| Chiang Mai | 498.30 | 1,791.10 |
| Thailand Average | 532.50 | 1,920.40 |
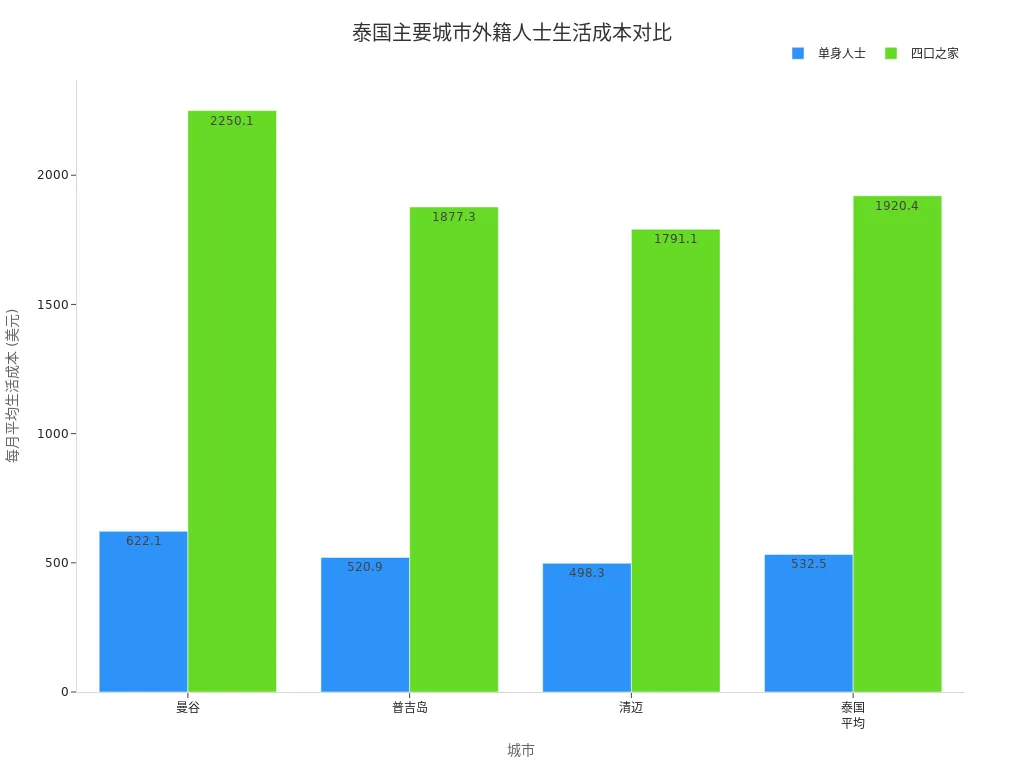
Living in Bangkok costs approximately 32% more than in Kuala Lumpur. You can choose a suitable city and lifestyle based on your needs to keep financial pressure manageable.
When working in Thailand, focus on these four key points:
- Choose appropriate job search channels, align with your background and industry trends, and enhance skills and networks.
- Evaluate salary standards, understand regional and industry differences, and set clear career goals.
- File taxes compliantly, understand labor laws, and ensure you obtain a legal work permit and social security.
- Pay attention to cultural differences and living costs to plan your career path effectively.
Thailand’s labor and tax policies change frequently. Stay updated through industry reports and professional websites. Continuous learning and skill enhancement will help you remain competitive in the Thai job market.
FAQ
What are the basic requirements for working in Thailand?
You need a valid work visa. Your employer must apply for a work permit on your behalf. You also need to meet job requirements, such as academic qualifications and language skills.
Tip: Prepare academic credentials and health certificates in advance to expedite the application process.
What is Thailand’s minimum wage standard?
Thailand’s minimum wage varies by region. Bangkok and surrounding areas have a minimum wage of approximately 10.74 USD/day. Some southern regions have a minimum of 9.73 USD/day. Check the specific standard for your work city.
How do foreign employees file personal income tax?
You need to file annually by April through the Thai Revenue Department’s website or in person. Use the PND 91 form for salary income. Prepare all income proof during filing.
What should I pay attention to regarding Thai workplace culture?
Respect superiors and elders. Use indirect communication to avoid conflict. Building good colleague relationships helps you adapt to the work environment.
Are living costs in Thailand high?
The average monthly living cost for a single person in Bangkok is about 622.10 USD. Costs in Chiang Mai and Phuket are slightly lower. Choose a suitable city and plan expenses based on your needs.
You have completed the full analysis of working in Thailand, thoroughly understanding everything from job search channels and salary standards to complex tax and compliance requirements. Given that expatriate salaries in Thailand are often higher than local wages (e.g., international school teachers earning 70,000 - 150,000 THB), you certainly don’t want to stumble when it comes to cross-border money management. Whether transferring part of your monthly income home or engaging in overseas investment, you will face pain points like high bank fees, non-transparent exchange rate markups, and long waiting periods associated with traditional banking.
You need an efficient, compliant, and cost-transparent FinTech platform to manage your Thai income and global assets.
BiyaPay is your ideal choice for connecting your Thai income with the global market. We offer real-time exchange rate inquiry and conversion services for fiat currencies, with remittance fees as low as 0.5% and zero commission on contract limit orders, helping you maximize your retained earnings. BiyaPay supports the inter-conversion of various fiat and digital currencies and offers same-day fund arrival, significantly improving capital turnover speed. Moreover, you can simultaneously engage in global asset allocation, including US and Hong Kong stocks, without needing a complex overseas account. Register quickly with BiyaPay now, and leverage ultimate capital efficiency to support your success in the Thai workplace.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















