- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Complete Guide to Currency Exchange in Korea: Ensuring Fund Security and Smooth Remittance

Image Source: unsplash
When performing currency exchange and remittance in South Korea, you should pay special attention to fund security and transfer efficiency. You can choose regulated banks or professional remittance companies, understand exchange rate fluctuations in advance, prepare recipient information, verify fees and expected arrival times, and protect personal privacy. The global remittance market continues to grow, showing strong resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic. The demand for remittances in high-income countries is also increasing due to immigrant communities. You need to combine this information and flexibly apply the currency exchange guide to ensure every step is secure and smooth.
Key Takeaways
- Choose regulated banks or compliant remittance companies to ensure fund security and compliance.
- Prepare personal identification and recipient information in advance to improve processing efficiency and avoid delays.
- Monitor exchange rate changes and use digital tools to lock in the best rates, reducing exchange costs.
- Keep records of every transaction and regularly check the receipt status to promptly identify and address issues.
- Choose the right timing for remittances, avoiding holidays or market volatility periods to ensure smooth fund transfers.
Currency Exchange Guide and Channels

Image Source: unsplash
Bank Channels
When exchanging currency in South Korea, bank channels are one of the most common options. Banks are typically subject to strict regulation by South Korean financial authorities, providing safe and reliable services. You can exchange currency directly at ATMs or bank branches in South Korea, with clear processes and high fund security.
- Advantages:
- Banks offer competitive exchange rates, suitable for large transactions.
- Bank branches and ATMs are widespread across South Korea, making currency exchange convenient.
- Fund transfers are transparent and highly compliant, ideal for users prioritizing security.
- Disadvantages:
- Banks may charge foreign exchange fees, which can be high in some cases.
- Some banks’ exchange rates may not be as competitive as local exchange booths or certain online services.
- Processing is limited by bank operating hours, reducing flexibility.
When choosing bank channels, you can prioritize branches of Hong Kong-licensed banks in South Korea. These banks typically have international compliance credentials, offering more comprehensive currency exchange services. Before exchanging, you should compare exchange rates and service fees across banks to secure the best deal.
Tip: Before exchanging, you can check real-time exchange rates and fees via bank websites or by phone to avoid extra costs due to information asymmetry.
Remittance Companies and Third-Party Platforms
If you need cross-border remittances or online exchanges, you can opt for professional remittance companies or third-party platforms. These institutions typically use smart compliance solutions, strictly adhering to South Korea’s anti-money laundering (AML), know-your-customer (KYC), and data privacy regulations.
- Advantages of remittance companies:
- Fast processing and short arrival times, ideal for urgent fund transfers.
- Sophisticated compliance strategies reduce transaction risks, ensuring fund security.
- Available both online and offline, offering high flexibility.
- Disadvantages of remittance companies:
- Some companies charge high fees, requiring you to review fee structures in advance.
- Exchange rates may fluctuate, necessitating real-time market monitoring.
Third-party platforms are also very active in the South Korean market, with common platforms like XM, Vantage, and IC Markets offering diverse currency pair options and transparent fee structures. You can choose a suitable platform based on your needs, combining the currency exchange guide to enhance fund transfer efficiency.
- Features of common third-party platform services:
- Offer a wide range of currency pair options to meet exchange needs across countries.
- Transparent fee structures, with some platforms offering no commissions or low spreads.
- Suitable for frequent traders or users with specific financial needs.
When using remittance companies or third-party platforms, always verify their compliance credentials to ensure fund security.
Online and Offline Methods
When exchanging currency in South Korea, you can choose between online and offline methods.
- Online methods:
- You can handle exchanges and remittances online via bank websites, mobile apps, or third-party platforms.
- Online operations are convenient, supporting real-time exchange rate checks and fee inquiries, ideal for quick processing.
- Online channels typically include multi-factor authentication and data encryption to protect your personal information.
- Offline methods:
- You can visit bank branches, remittance company offices, or exchange booths to process transactions.
- Offline processing is suitable for users needing face-to-face consultations or handling large sums.
- Offline channels provide physical receipts, facilitating subsequent fund tracking and verification.
When choosing online or offline methods, consider your needs and fund security, applying the currency exchange guide flexibly to ensure compliance and efficiency.
Note: When handling currency exchanges and remittances, always keep transaction receipts and regularly check receipt status to mitigate potential risks.
Operating Procedures
Document Preparation
Before exchanging currency or remitting funds in South Korea, preparing the necessary documents in advance can significantly improve efficiency and reduce delays.
Below are common preparation steps:
- Prepare personal identification documents, such as a passport or Alien Registration Card (ARC).
- Register an account and provide personal information, including your phone number and ID number.
- Collect recipient information, including their name, bank account, bank code (e.g., SWIFT/BIC), and receiving bank address.
- If you are a corporate user, prepare business registration certificates, seal registration certificates, business licenses, and CEO identification, along with supporting documents for the remittance purpose (e.g., contracts, invoices).
- Specify the remittance type (bank transfer, debit, or credit card transfer) and verify if the recipient’s account supports the chosen method.
Tip: When preparing documents, confirm the required document list with the bank or remittance company in advance to avoid delays due to incomplete materials.
Offline Process
When choosing offline channels for currency exchange or remittances, the process is typically standardized. Using Hong Kong-licensed bank branches in South Korea as an example, the offline process is as follows:
- Confirm that the selected bank offers currency exchange services and check service hours.
- Reserve the required currency to ensure the bank has sufficient USD stock.
- Bring cash or required documents to the bank branch. If you are not a bank customer, bring identification documents.
- Fill out the application form and submit all required documents, including recipient information and proof of remittance purpose.
- Bank staff will review the documents, create a telegraphic transfer (T/T) request, and confirm details with you.
- After approval, you can collect the exchanged funds immediately or wait for the bank’s notification to pick up the funds at the branch.
Note: When processing offline transactions, keep physical transaction receipts for future tracking and verification.
Online Process
If you choose online channels for currency exchange or remittances, you can complete the process via bank websites, mobile apps, or third-party platforms. The standard process is as follows:
- Register or log into your online account and navigate to the currency exchange or remittance page.
- Click “Send Now” or a similar button to start the transfer process.
- Select South Korea as the destination and enter the USD amount you wish to exchange or remit.
- Choose the recipient method (e.g., bank account, credit card, debit card) and review the estimated arrival time.
- Enter recipient details, including name, bank account, and bank code.
- Complete the payment using PayPal, a bank account, credit card, or debit card.
- The system will generate an electronic receipt, allowing you to track transaction progress at any time.
Tip: When using online channels, enable multi-factor authentication to enhance account security.
Security Tips
When handling currency exchanges and remittances, fund security and information protection are critical. Follow these safety recommendations:
- Verify the legitimacy of recipient information to prevent fraud.
- Monitor exchange rate fluctuations to secure the best transaction timing.
- Inquire about additional fees from service providers to avoid hidden costs.
- Choose regulated banks or remittance companies, prioritizing compliance credentials.
- Regularly check receipt status and keep all transaction records.
- Avoid conducting sensitive financial transactions on public networks to prevent data leaks.
Note: Throughout the currency exchange guide process, prioritize safety and compliance, selecting channels and methods based on your needs.
Fees and Exchange Rates
Transaction Fees
When exchanging currency or remitting funds in South Korea, transaction fees are a primary cost. Fee differences vary significantly across channels. Refer to the table below for an overview of common methods’ fee structures and processing times:
| Method | Processing Time | Overseas Transfer Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Airwallex | Same-day arrival | No account opening fees, monthly fees, or hidden costs |
| Bank Wire Transfer | 1-5 business days | Base fees around USD6.5-USD26, plus possible additional charges |
| Currency Exchange Providers | 1-5 business days | Multiple fees may apply |
When choosing third-party platforms, fees vary by payment method. For example, Xoom charges USD4.99 for PayPal balance payments and USD15.00 for credit card payments. Bank of America charges USD45 for USD transfers, while foreign currency transfers are free but include exchange rate markups. Western Union fees range from USD2.90 to USD75, depending on the amount and payment method. You should select the most suitable channel based on your needs, combining the currency exchange guide for optimal results.
Exchange Rate Differences
Exchange rates directly affect the amount you receive. Rates vary significantly across channels. Refer to the table below for a comparison of fee characteristics:
| Channel | Fee Characteristics | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Airport | Rates slightly higher than city centers, convenient for initial use | Suitable for cash exchanges upon arrival |
| Banks | Competitive rates, service fees around 1%-3% | Passport required |
| ATMs | Competitive rates, check fees in advance | Available at subway stations and convenience stores |
| Currency Exchange Booths | Competitive rates, long operating hours | Compare multiple options |
| Hotels | Less favorable rates than banks or booths but convenient | Available in major tourist areas |
You can also refer to the chart below for a visual comparison of exchange fees across major South Korean banks and third-party platforms:
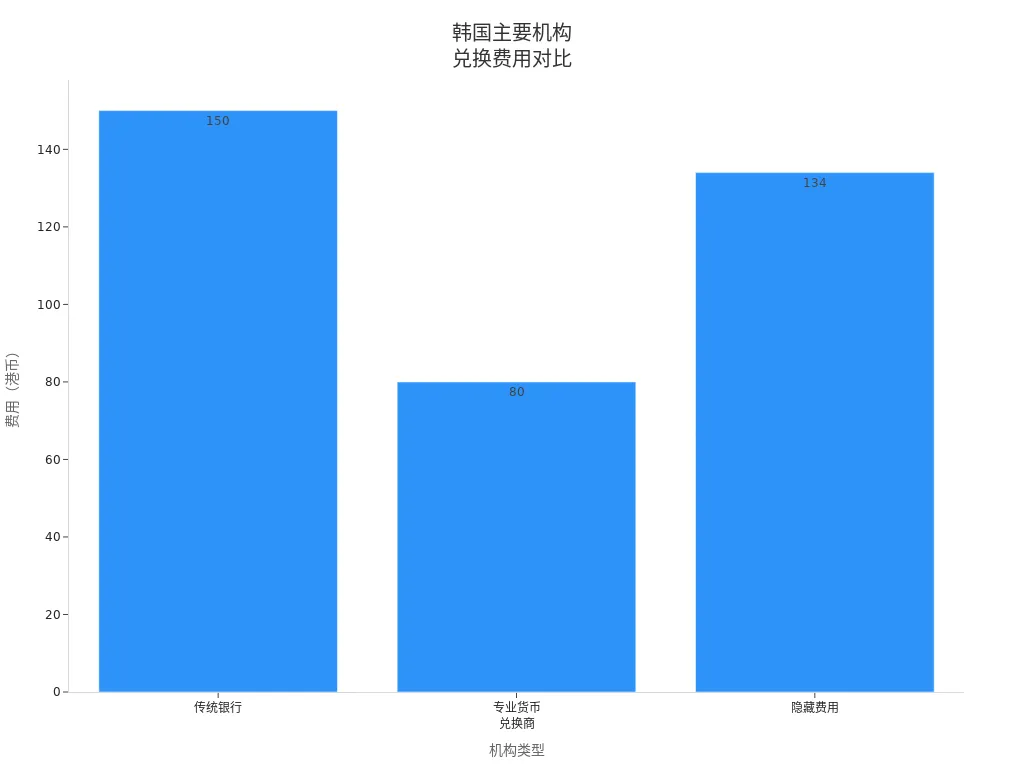
When performing transactions, check real-time exchange rates in advance to avoid losses due to rate fluctuations.
Hidden Costs
When handling currency exchanges or remittances, beyond visible fees and rates, be cautious of hidden costs. Common hidden fees include:
- Some services hide commissions in exchange rates, appearing fee-free but costing more overall.
- Banks and international remittance services offer different rates, potentially reducing the received amount.
- Some platforms claim no fees but charge hidden commissions through rate adjustments.
- Carefully review rate commissions and transfer fees to ensure no extra costs.
- Choose platforms using mid-market rates to effectively reduce hidden costs.
When applying the currency exchange guide, pay attention to all fee details to avoid increased losses due to overlooked hidden costs.
Security Measures

Image Source: pexels
Regulated Channels
When handling currency exchanges and remittances in South Korea, choosing regulated channels is critical. Regulated banks and compliant remittance companies ensure fund security. South Korea imposes strict regulations on foreign exchange transactions, and foreign financial institutions must comply with the Foreign Exchange Transactions Act, meeting business type, financial soundness, and registration requirements. The table below summarizes key regulatory requirements:
| Key Requirement | Description |
|---|---|
| Business Type and Financial Soundness | Foreign institutions must meet business type and financial soundness standards under the Foreign Exchange Transactions Act. |
| Foreign Exchange Business Scope | Includes forex spot transactions and forex swaps. |
| Registration Requirements and Procedures | Must meet registration requirements and sign credit extension agreements with multiple institutions. |
| Obligations of Overseas Forex Agents | Verify customer identity and transaction compliance, reporting details to the Bank of Korea. |
| Sound Management and Oversight | Set limits on forward forex positions, with oversight by the Bank of Korea. |
When selecting service providers, prioritize banks or remittance companies with international credentials and strong reputations. Keep transaction records for future tracking and verification.
Information Protection
When processing currency exchanges and remittances, protecting personal information is crucial. Ensure you enter identity and bank account details only on regulated platforms. Banks and compliant platforms typically use multi-factor authentication and data encryption to reduce the risk of data leaks. Avoid conducting sensitive financial transactions on public networks and never share personal information with strangers. Regularly update account passwords to enhance security.
Reminder: After each transaction, check the receipt status and securely store electronic or physical receipts.
Risk Mitigation
When exchanging currency or remitting funds in South Korea, be aware of various risks. Common risks include currency inconvertibility, fund transfer restrictions, asset expropriation, and contract breaches. The table below lists major risk types and descriptions:
| Risk Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Currency Inconvertibility | External factors prevent currency conversion. |
| Fund Transfer Restrictions | Foreign governments restrict or prohibit fund transfers. |
| Asset Expropriation | Government nationalization, confiscation, or license revocation. |
| Political Violence | Risks from war, terrorism, sabotage, or civil unrest. |
| Contract Breach | Failure to fulfill contract terms. |
| Financial Obligation Non-Performance | Failure to meet financial obligations. |
| War Risks | Inability to conduct business due to war. |
| Natural Disasters | Business disruptions from natural disasters or international sanctions. |
| Force Majeure | Inability to conduct business due to force majeure events. |
You can mitigate these risks by choosing regulated institutions, verifying service reputations, keeping transaction records, and monitoring market dynamics. If you encounter issues, promptly contact the bank or platform’s customer service to protect your funds.
Compliance Requirements
Foreign Exchange Regulations
When handling currency exchanges and remittances in South Korea, you must understand local foreign exchange regulations. South Korea has strict rules for foreign exchange transactions, and all banks, including foreign ones, can conduct forex business. You need to notify the foreign exchange bank in advance and prepare relevant documents. The Foreign Exchange Transactions Act requires additional monitoring for certain transactions, particularly those involving national security or public order.
The South Korean government allows foreign investors to repatriate profits after investment approval. Banks handle the approval process to ensure fund compliance. In special circumstances, the government may restrict capital outflows to maintain economic stability.
Refer to the following points for a quick overview of South Korea’s foreign exchange regulations:
- All banks can handle forex transactions, requiring advance notification and document submission.
- Certain transactions require additional scrutiny, especially in sensitive sectors.
- Foreign investment profits can be repatriated, with banks handling approvals.
- The government may restrict fund outflows during special periods.
Reminder: For large remittances, consult your bank in advance to understand the latest policies and approval processes to avoid delays due to policy changes.
Tax Reporting
When conducting currency exchanges and cross-border remittances in South Korea, tax reporting is equally important. South Korean tax authorities require individuals and businesses to accurately report foreign exchange income and fund movements. You must keep all transaction records, including bank receipts and remittance records.
If you are a mainland Chinese resident, familiarize yourself with the tax treaty between mainland China and South Korea to ensure compliant fund movements. When remitting funds, consider the following:
| Reporting Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Remittance Amount | Amounts exceeding a certain threshold must be reported to tax authorities. |
| Fund Source | Prove the legal source of funds to avoid tax risks. |
| Transaction Records | Keep bank receipts and related documents for verification. |
| Tax Treaty | Review the tax treaty between mainland China and South Korea. |
Proactively reporting and keeping records can effectively reduce tax risks. If you have questions, consult a professional tax advisor or bank staff to ensure compliance and safety.
FAQs
How long does it take for funds to arrive?
When handling currency exchanges or cross-border remittances in South Korea, arrival time is a key concern. Transfer times vary by amount. Refer to the table below for common arrival times:
| Transfer Amount | Estimated Arrival Time |
|---|---|
| Less than 950,000 KRW | Usually same business day |
| Over 950,000 KRW | Up to 2 business days |
If you use bank channels, USD funds typically arrive within 1 to 2 business days. Third-party platforms or remittance companies may offer same-day arrivals. Before processing, consult the service provider to confirm expected arrival times to avoid delays affecting fund use.
Reminder: Remittances during holidays or weekends may face delays. Plan your transfers accordingly.
Handling Failed Transactions
When processing remittances or exchanges, you may occasionally encounter failed transactions. Take the following steps to resolve issues quickly:
- First, verify that your documents are complete, including recipient name, bank account, and bank code.
- Next, confirm your account balance is sufficient and the payment method supports international transfers.
- If the system indicates a failure, contact the bank or platform’s customer service, explaining the situation for professional assistance.
- Keep all transaction records for future verification or disputes.
If funds are frozen or returned, promptly contact the service provider to identify the cause and provide additional documents if needed. Most cases are resolved within 1 to 3 business days.
Tip: When entering recipient information, double-check to avoid errors causing transaction failures.
Fund Tracking
After a cross-border remittance, you may need to track fund movements to ensure safe arrival. You can track funds through the following methods:
- Log into your bank or third-party platform account to check transaction progress and status.
- Use the transaction number or remittance receipt to inquire about fund movements with customer service.
- Monitor receipt notifications to verify if the recipient’s account has received USD funds.
- Keep electronic or physical transaction records for verification or disputes.
If you encounter delays or issues, proactively contact the service provider for detailed fund movement information. Most regulated banks and platforms offer real-time tracking to help you stay informed.
Note: During fund tracking, protect personal information and avoid sharing account details with strangers.
Practical Tips
Prepare Documents in Advance
When handling currency exchanges or remittances in South Korea, preparing documents in advance ensures a smoother process. Organize your passport, Alien Registration Card, recipient bank account details, and bank codes. For corporate users, prepare business registration certificates and supporting documents. Store all documents systematically for easy access. Confirm the required document list with the bank or remittance company in advance to avoid delays due to incomplete materials. During operations, back up important documents with photos to prevent loss.
Monitor Exchange Rates
When applying the currency exchange guide, monitoring exchange rate fluctuations is crucial. You can access real-time forex quotes through digital trading platforms to flexibly choose exchange timing. Using automated tools reduces operational risks and human errors. You can also lock in optimal rates with digital tools to complete transactions at the best moment. Generating transaction histories regularly helps analyze issues and develop effective exchange strategies. Before operations, compare rates across multiple channels to select the most favorable option.
Tip: During significant rate fluctuations, exchange USD in batches to reduce risks.
- Use digital trading platforms for real-time forex quotes.
- Adopt automated tools to reduce operational risks.
- Lock in optimal rates with digital tools.
- Generate transaction histories to analyze issues.
Choose the Right Timing
When handling currency exchanges or remittances in South Korea, choosing the right timing can save significant costs. Monitor U.S. market economic data and major policy releases, as these affect USD exchange rates. During holidays or market volatility periods, exchange or remit funds in advance to avoid cost increases due to sudden rate changes. Set rate alerts to act when rates reach your ideal range. By combining the currency exchange guide’s recommendations, flexibly choose exchange timing to enhance fund arrival efficiency and security.
When handling currency exchanges and remittances in South Korea, security and efficiency are equally important. Prioritize regulated banks or compliant remittance companies to protect personal information and avoid data leaks. Compare fees and exchange rates across channels to plan fund transfers wisely. By flexibly applying the guide’s recommendations based on your needs, you can ensure secure and efficient fund arrivals.
Reminder: After each transaction, keep receipts and regularly check receipt status to promptly identify and resolve issues.
FAQs
How long does it take for funds to arrive?
You can typically receive USD funds within 1 to 2 business days. Third-party platforms may offer same-day arrivals. Consult the service provider in advance to confirm specific times.
Reminder: Holiday or weekend remittances may face delays. Plan transfers accordingly.
What to do if a remittance fails?
Check recipient information and account balance. If correct, contact the bank or platform’s customer service. Keep transaction records for disputes or verification.
How to track fund movements?
Log into your bank or third-party platform account to check transaction progress. Use the transaction number to inquire with customer service. Keep electronic or physical receipts to ensure fund security.
Will incomplete documents affect remittances?
Incomplete documents may cause banks or platforms to reject remittances. Prepare identification and recipient details in advance to avoid delays. Back up important documents with photos.
How to check fees and exchange rates?
Check USD exchange rates and fees in real-time via bank websites or third-party platforms. Compare channels to choose the best option. Watch for hidden costs to maximize received amounts.
You’ve fully mastered the complete guide to currency exchange and money transfers in South Korea, including choosing regulated banks or compliant remittance providers, adhering to the annual $50,000 transfer limit, and how to compare fee structures and exchange rate differences. When making cross-border fund transfers, you naturally want a modern financial solution that balances security, compliance, and low cost.
However, traditional bank wire transfers come with high fees (approximately USD 6.5–USD 26) and long processing times (1–5 business days), while some third-party platforms may apply hidden markups on exchange rates. For users with global asset allocation needs or those who require seamless switching between fiat currencies and digital assets, you need a more comprehensive and advanced financial platform.
BiyaPay is your ideal choice for efficiently transferring funds to South Korea. We offer real-time exchange rate checks and fiat currency conversion services, with remittance fees as low as 0.5% and zero fees on contract order placements—effectively reducing your overall costs. BiyaPay supports most countries and regions worldwide, enabling same-day sending and same-day arrival, significantly improving your capital efficiency. More importantly, you can manage global investments such as US and Hong Kong stocks all within one platform—no complex overseas accounts required—and enjoy seamless conversion between fiat currencies and digital assets like USDT. Register with BiyaPay today and ensure your funds reach South Korea securely, compliantly, and swiftly, with full transparency and exceptional efficiency.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















