- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
The Cost of Studying in France and Financial Management: Tuition Fees, Scholarships, and Remittance Services

Image Source: pexels
The cost of studying in France mainly includes tuition, accommodation, food, transportation, and health insurance. You need to understand these expenses in advance and plan your budget wisely. The table below shows the annual tuition and living expenses for different types of students:
| Tuition Type | Annual Tuition (€) | Living Expenses (€) |
|---|---|---|
| EU/EEA Students | 170 (Undergraduate) | 9,900 |
| 243 (Master’s) | ||
| 380 (PhD) | ||
| Non-EU/EEA Students | 2,770 (Undergraduate) | |
| 3,770 (Master’s) | ||
| 380 (PhD) |
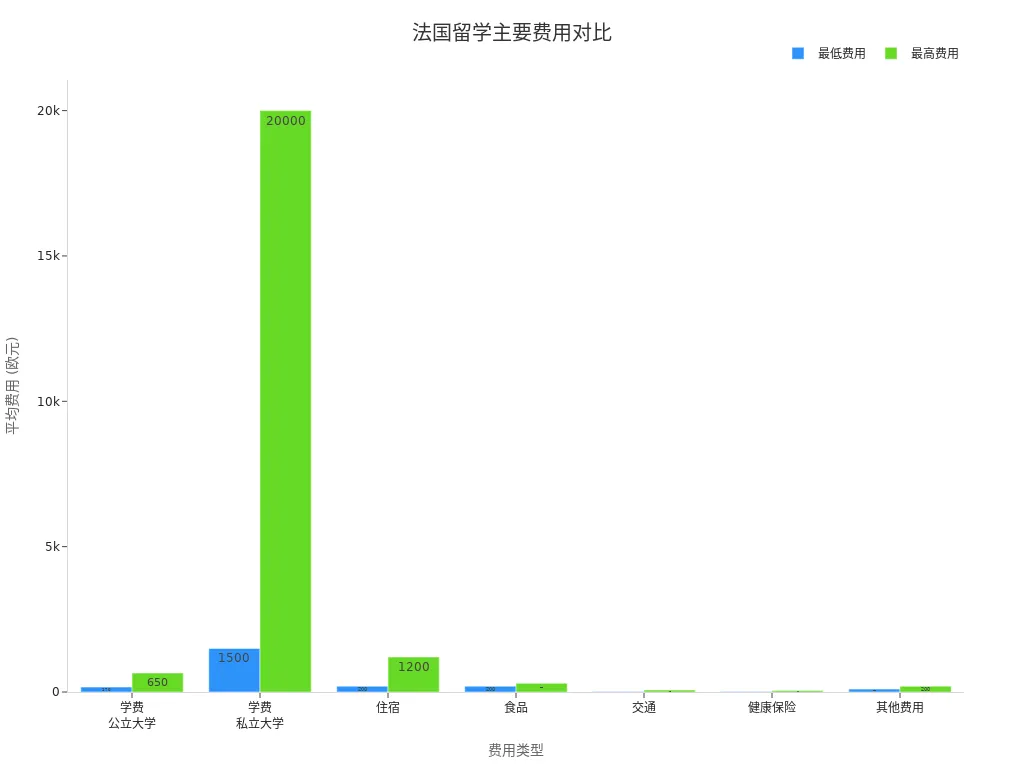
You can manage and transfer funds through bank transfers or third-party platforms to ensure financial security during your studies.
Key Points
- Understand tuition and living expenses in France to plan your budget effectively. EU/EEA students enjoy lower tuition, with monthly living expenses ranging from €800 to €1,200.
- Open a French bank account to manage funds conveniently and avoid high international transaction fees. Create a detailed budget, prioritizing essential expenses.
- Apply for scholarships to ease financial burdens. Explore opportunities from government, universities, and private organizations, and prepare application materials in advance.
- Choose the right remittance method by comparing fees and transfer speeds of bank transfers, international money orders, and third-party platforms to ensure fund safety.
- Regularly track expenses, cut unnecessary spending, and manage living costs to ensure a smooth study and living experience in France.
Overview of the Cost of Studying in France
Tuition and Living Expenses
When studying in France, your primary expenses include tuition, accommodation, food, transportation, and health insurance. The cost of studying in France varies significantly depending on the type of institution, city, and personal lifestyle. You need to understand these expenses in advance to plan your budget effectively.
In France, living expenses for international students vary depending on the city, lifestyle, and accommodation type. Typically, international students’ monthly living expenses range from €800 to €1,200 (approximately $864–$1,296), covering basic expenses such as accommodation, food, transportation, and health insurance.
The table below shows the typical monthly living expense breakdown:
| Expense Category | Estimated Monthly Cost (EUR) | Estimated Monthly Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Accommodation | €300–€600 | $324–$648 |
| Food and Dining | €200–€300 | $216–$324 |
| Transportation | €30–€70 | $32–$76 |
| Health Insurance | €25–€40 | $27–$43 |
| Utilities and Internet | €50–€100 | $54–$108 |
| Entertainment and Miscellaneous | €100–€200 | $108–$216 |
| Total | €800–€1,200 | $864–$1,296 |
Accommodation costs in Paris are typically higher, ranging from €1,200 to €1,800 ($1,296–$1,944). In smaller cities like Nice or Bordeaux, accommodation costs are lower, around €650 to €800 ($702–$864). Different accommodation types and locations directly impact your overall cost of studying in France.
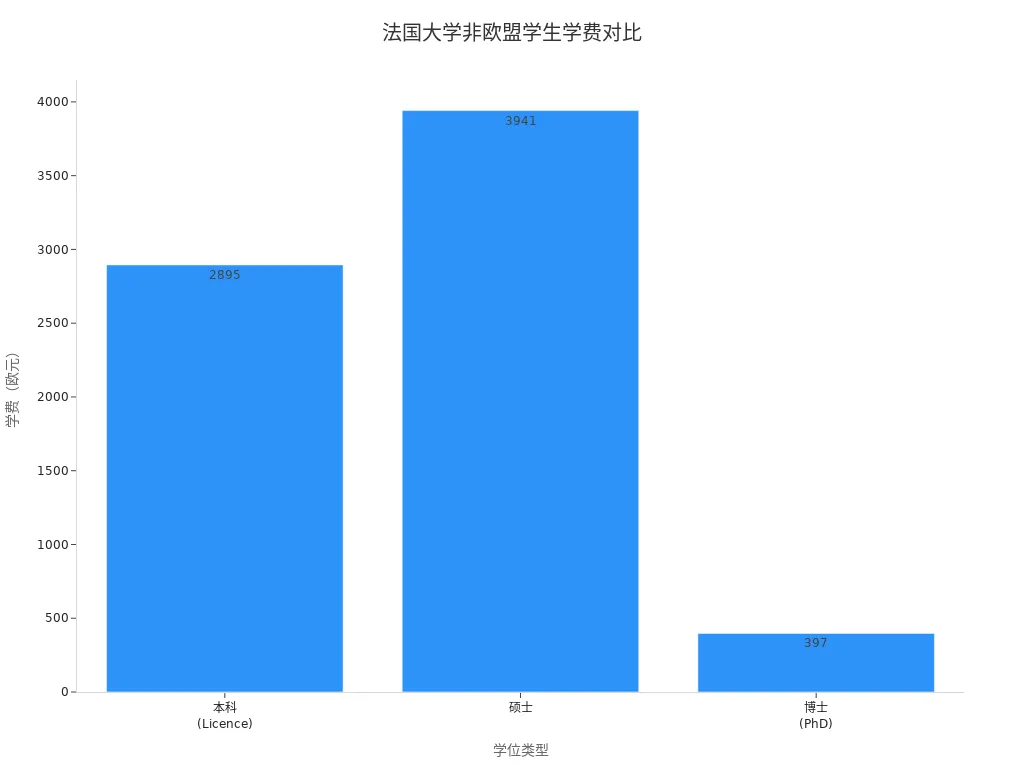
In terms of tuition, French public universities have relatively low fees due to government subsidies. Tuition fees for non-EU students at public universities are as follows:
| Degree Type | Tuition (EUR) | Tuition (USD, approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| Undergraduate (Licence) | €2,895 | $3,127 |
| Master’s | €3,941 | $4,256 |
| PhD | €397 | $429 |
Private universities generally charge higher tuition, with some business schools and engineering institutes costing €10,000–€30,000 ($10,800–$32,400) annually. When choosing a school, you need to consider your financial situation and scholarship opportunities to assess the overall cost of studying in France.
The bar chart below visually illustrates the tuition fee differences for non-EU students across different degree types:
Financial Management Methods
During your studies in France, managing funds effectively is crucial. Common financial management methods include:
- Opening a French bank account to facilitate daily expenses and tuition payments, avoiding high currency exchange fees.
- Creating a detailed budget, listing all monthly expenses, prioritizing essential costs, and setting savings goals.
- Utilizing student discounts for transportation, entertainment, and more by carrying your student ID.
- Working part-time (if permitted by your visa) to supplement living expenses and reduce financial pressure.
- Participating in the sharing economy, such as sharing accommodation or transportation costs with classmates to lower individual expenses.
- Purchasing second-hand items from websites or flea markets for furniture, electronics, etc., to save money.
- Tracking expenses using mobile apps or spreadsheets to identify areas for cost-cutting.
- Planning for emergencies by setting aside a budget for unexpected situations to enhance financial security.
- Choosing the right bank by comparing services, fees, and student benefits to select the most suitable account type.
- Online banks (e.g., N26, Revolut) are popular among international students for their convenience and low fees.
You can also look for affordable accommodation in advance, consider sharing rentals with classmates to reduce rent, shop at supermarkets and markets, cook your own meals to save on dining costs, use public transportation monthly passes to avoid high single-ticket costs, participate in free cultural events and festivals for low-cost entertainment, and use student discounts and coupons to reduce shopping expenses.
Through effective financial management, you can control the cost of studying in France, reduce financial stress, and focus on your studies and life experiences.
Tuition

Image Source: pexels
Public vs. Private Institutions
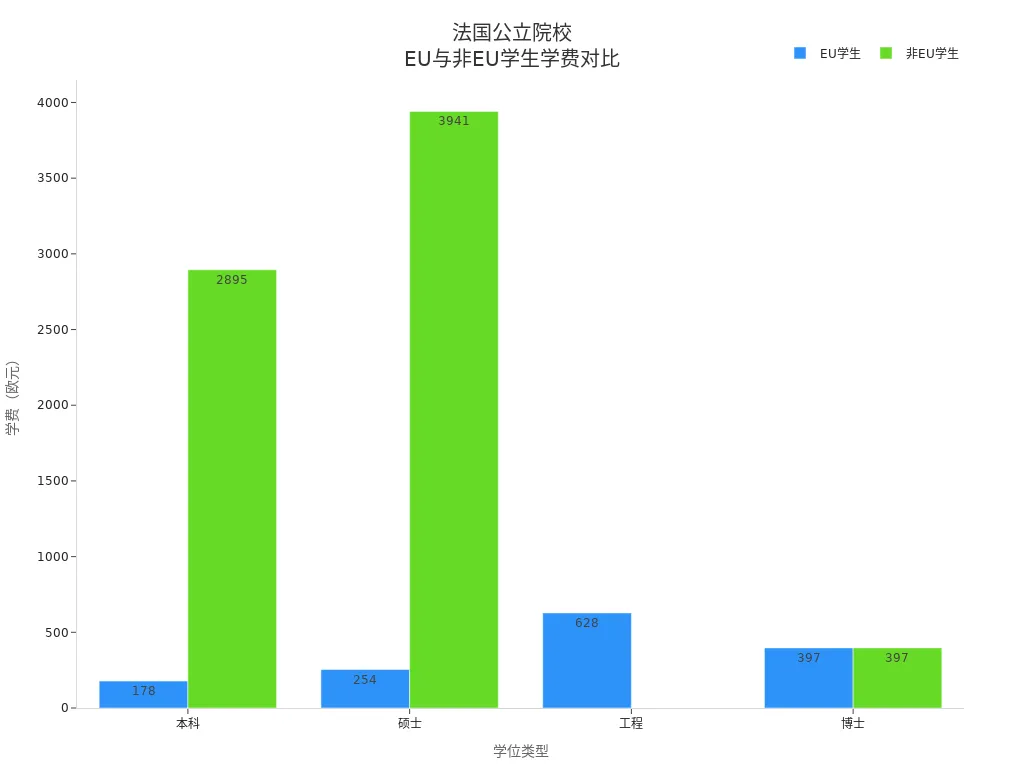
When choosing a university in France, you first need to understand the tuition differences between public and private institutions. French public universities are heavily subsidized by the government, resulting in relatively low tuition fees. Private universities, especially business schools and engineering institutes, charge significantly higher fees.
The table below shows the annual tuition ranges for different institution types and degrees (converted at 1 EUR ≈ 1.08 USD):
| Institution Type | Degree Type | EU/EEA Student Tuition (USD/Year) | Non-EU/EEA Student Tuition (USD/Year) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Public University | Undergraduate | $184 - $702 | $2,992 - $4,072 |
| Master’s | $262 - $791 | $2,992 - $4,072 | |
| Private University | Undergraduate | $3,240 - $12,960 | $5,400 - $16,200 |
| Master’s | $3,240 - $21,600 | $5,400 - $32,400 |
You can see that non-EU students pay significantly higher tuition at public universities compared to EU students. Private universities charge higher fees for all students, with some popular programs being even more expensive.
When choosing a school, you need to consider your financial situation and scholarship opportunities to assess the overall cost of studying in France.
The chart below compares tuition fees for EU and non-EU students at French public universities:
Program Differences
Tuition fees also vary significantly depending on the program you choose in France. Programs in engineering and business typically have higher tuition than humanities.
The table below lists annual tuition fees for common programs (converted to USD):
| Program | EU Students (USD/Year) | Non-EU Students (USD/Year) |
|---|---|---|
| Undergraduate | $184 | $2,992 |
| Master’s | $262 | $4,072 |
| Engineering | $649 | Up to $32,400 |
| PhD | $410 | $410 |
When studying engineering at French public universities, tuition fees are significantly higher than for general undergraduate and master’s programs. Some top engineering institutes and business schools may charge up to $30,000 annually.
- For example, at the University of Orléans, undergraduate tuition is approximately $184, master’s $262, and engineering $649.
- At Grenoble Alpes University, undergraduate tuition is $189, master’s $270, and engineering $667.
When choosing a program, it’s recommended to check the target institution’s official website for specific tuition fees to better plan your cost of studying in France.
Payment Process
When registering at a French university, you typically need to pay the full annual tuition at the start of the academic year in September. Some institutions allow installment payments, with specific policies detailed on their websites.
Common payment methods include:
| Payment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Online Payment | You can pay tuition directly via credit card on the school’s website or registration system. Some schools allow payments in three installments (for tuition exceeding $2,700). |
| Bank Transfer | You can pay tuition via bank transfer, including your name and student ID, with processing times typically 3-5 days. |
| Check | Some schools accept checks made payable to the designated accounting officer. |
| Direct Debit | For tuition exceeding $1,080, you can set up automatic installment payments. |
| Scholarship Deduction | If you receive a Crous scholarship, you may be eligible to offset tuition directly. |
Before paying tuition, it’s advisable to contact your bank to ensure your credit card or account can handle international payments.
Keep payment receipts for registration or visa verification purposes.
During your studies in France, planning tuition payment timing and methods can help avoid delays that may affect registration or visa progress. Prepare tuition funds in advance and choose secure, convenient payment channels.
Scholarships
Scholarship Types
When studying in France, you can apply for various types of scholarships. France offers government-funded, university-specific, and private organization scholarships for international students. These scholarships help reduce tuition and living expenses, attracting outstanding students from around the world.
Common scholarship types include:
- Government-funded scholarships: Such as social criteria grants and housing assistance.
- University-specific scholarships: Awarded by universities based on academic merit or financial need.
- Private organization scholarships: Provided by foundations or companies, often targeting specific programs or countries.
You can also explore the following notable scholarship programs:
- Eiffel Excellence Scholarship: Provides monthly stipends for international master’s and PhD students.
- Charpak Scholarship: Primarily for Indian students, offering tuition waivers and living allowances.
- Regional Scholarships: Some French regions provide funding for international students studying at local universities.
Application Process
When applying for French scholarships, you need to meet the eligibility requirements of different programs. Most scholarships require admission to a French institution, and some demand excellent academic performance or specific backgrounds.
The table below lists the eligibility, deadlines, and amounts (in USD) for major scholarships:
| Scholarship Name | Eligibility | Deadline | Amount/Benefits (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eiffel Excellence Scholarship | Enrolled in master’s or PhD program | January | Master’s $1,276/month, PhD $1,944/month |
| ENS International Selection | Pursuing arts, humanities, or sciences | December | $1,080/month, three years |
| Ampère Excellence Scholarships | Holds a bachelor’s degree | January | $1,080/month, 12 months |
| Paris-Saclay International Master’s | International students under 30 | May | $10,800/year |
| Émile Boutmy Scholarship | Pursuing bachelor’s or master’s | Bachelor’s: March, Master’s: December | Bachelor’s $5,098–$10,260/year, Master’s $14,040/year |
| HEC Paris MBA Scholarship | Pursuing HEC Paris MBA | Automatically considered upon admission | 50% of tuition |
| Grenoble INP Foundation | Holds a bachelor’s degree | February | $5,400/semester, two years |
| Paris Cité – SMARTS-UP | Holds a bachelor’s degree | January | $10,800/year |
| Aix-Marseille TIGER Master’s | Holds a bachelor’s degree | Automatically considered upon admission | $10,800/year |
| EDHEC Co-financed Scholarship | Pursuing master’s in management | May | 50% of tuition |
You need to monitor scholarship application deadlines and prepare materials accordingly.
Disbursement and Management
When applying for scholarships in France, you typically submit applications online, ensuring you meet eligibility criteria and upload required documents. Scholarship authorities will review your application, and upon approval, you will receive confirmation of your scholarship status.
For government scholarships (e.g., CROUS), you need to complete a Student Social File (DSE) between January and May. Three months later, you will receive a conditional scholarship notification, and funds will be disbursed to your French bank account upon final confirmation.
Keep all application and disbursement documents to ensure funds arrive on time, supporting your study abroad experience in France.
Remittance Services

Image Source: pexels
Bank Transfers
You can transfer tuition and living expenses from China/Chinese Mainland to France via bank transfers. This method is suitable for large amounts, offering high security and traceability. You can send tuition directly to the school’s account and living expenses to your personal account. The table below shows typical international transfer fees and processing times for common banks (in USD, 1 EUR ≈ 1.08 USD):
| Bank Name | Fee Range (USD) | Processing Time |
|---|---|---|
| Crédit Agricole | $59–$72 | 1–3 days |
| BNP Paribas | $26–$113 | 1–3 days |
| Société Générale | $31–$97 | 1–3 days |
| Caisse d’Épargne | From $57 | 1–3 days |
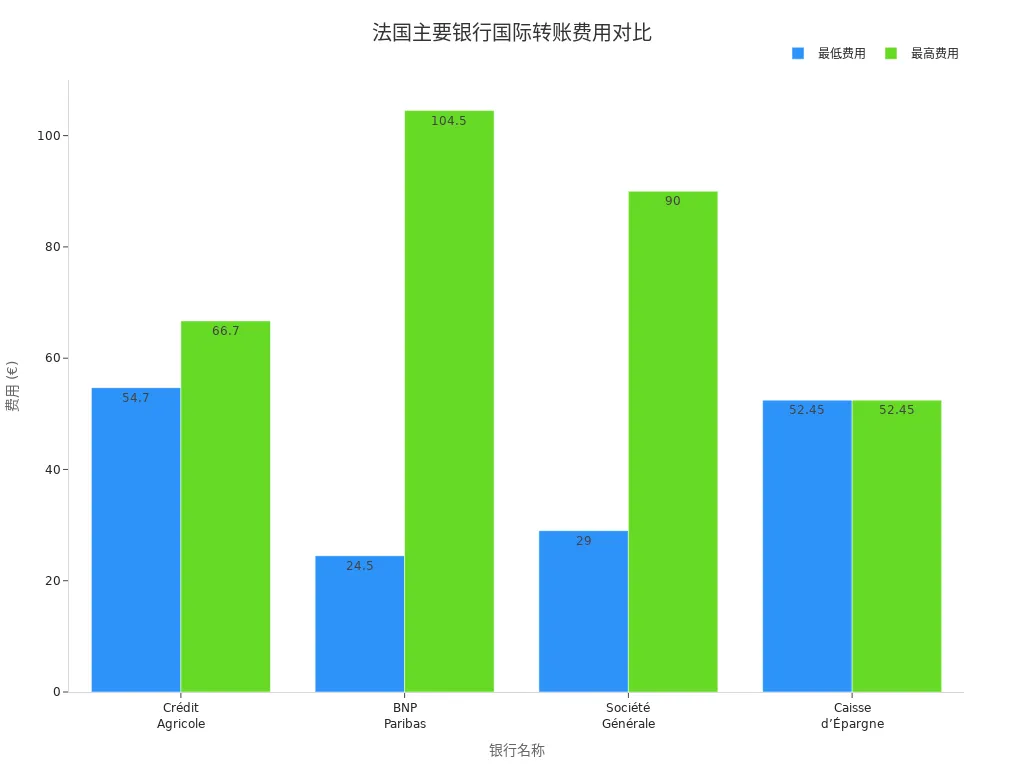
Note that some banks may charge additional handling fees, and processing times may extend to 10 days.
International Money Orders
You can also opt for international money orders. You issue a money order in your name at a bank in China/Chinese Mainland and deposit it into your account upon arrival in France. International money order fees typically start at $10, with some banks or postal services charging more (e.g., USPS charges $49.95). Ensure the French bank accepts money orders, prepare recipient information, complete forms, and mail them. When cashing the money order, the bank will settle at the current exchange rate, and the actual amount received may be slightly lower than the original.
Third-Party Platforms
Third-party remittance platforms offer faster, lower-cost options. Popular platforms like Equals Money, Panda Remit, and Instarem support student remittances. You can benefit from transparent low fees and quick transfers. For example, Panda Remit uses 256-bit TLS encryption, with fees typically one-tenth of traditional banks. These platforms also allow you to lock in exchange rates for better budgeting.
| Platform Name | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Equals Money | Lockable exchange rates for budgeting and cost management, efficient and secure transfers. |
| Panda Remit | High security, low fees, fast transfers. |
| Instarem | Student-friendly, lower fees than traditional banks, quick transfers. |
Cash Carrying
You can carry a small amount of cash (recommended not to exceed $2,160, approx. €2,000) for immediate needs upon arrival in France. Per EU regulations, carrying $10,800 (approx. €10,000) or more requires customs declaration. Local cash transactions in France are limited to $1,080 (approx. €1,000), with transactions above this amount requiring written documentation.
- When entering or leaving the EU, cash of $10,800 or more must be declared.
- Exceeding the limit may require additional documentation within 30 days.
Pros and Cons Comparison
When choosing a remittance method, consider your needs and fund security. The table below compares common remittance methods:
| Remittance Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Bank Transfer | Convenient, traceable, suitable for large amounts | High fees, longer processing times, possible hidden fees |
| International Money Order | Low cost, secure, traceable | Long processing times, slow transfers |
| Third-Party Platform | Transparent fees, fast, convenient | Possible exchange rate differences, some services have restrictions |
| Cash Carrying | Immediate access to funds, suitable for emergencies | Low security, limited amounts |
Choose the most suitable remittance method based on fund purpose, transfer speed, and fee budget to ensure financial safety and convenience during your studies in France.
Financial Management Tips
Budgeting and Spending
When studying in France, effective budgeting helps control the cost of studying. It’s recommended to create a monthly budget, prioritizing essential expenses. Use a spreadsheet to track all income and expenses to monitor your balance. The table below shows average expenses for common activities to help you allocate funds wisely:
| Activity | Average Cost (USD) |
|---|---|
| Housing | $594-$756/month |
| Dining | $13-$16/meal |
| Utilities and Internet | $216-$324/month |
| Transportation | $79-$95/month |
| Entertainment | $108-$216/month |
You can follow these steps to manage daily expenses:
- Set a monthly budget, prioritizing rent and tuition.
- List all income sources, such as scholarships, part-time work, and family support.
- Categorize expenses and allocate monthly amounts.
- Record expenses after each transaction to avoid overspending.
- Reserve funds for emergencies each month.
Regularly track expenses, reduce unnecessary spending, and limit dining out to better control the cost of studying in France.
Bank Accounts
During your time in France, it’s advisable to open a local bank account early to avoid international transaction fees and facilitate scholarship and wage payments. Required documents include:
- Valid passport or ID
- Student visa or residence permit
- University admission letter
- Proof of address (e.g., lease agreement or utility bill)
Some banks may require a minimum initial deposit, typically $16-$54. You can choose traditional banks for in-person services or online banks for lower fees and convenience. If you lack a fixed address, request a proof of residence from your university’s international office.
After opening a local account, manage tuition, living expenses, and scholarships centrally for easier spending and tracking.
Part-Time Work and Safety
With a student visa in France, you can legally work part-time, up to 964 hours annually, to supplement living expenses. Common jobs include tutoring, restaurant service, and campus assistance. The table below summarizes relevant policies:
| Allowed Work Hours | Job Types | Other Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| 964 hours/year | Any legal job | Valid visa |
No additional work permit is required. Prioritize jobs related to your studies and manage time to maintain academic performance. Part-time income can be deposited into your French bank account for added security. Protect personal information to avoid account fraud.
Combining scholarships, part-time work, and family remittances allows you to fund your studies through multiple channels, reducing financial stress and ensuring academic success.
When studying in France, effective financial planning is critical. Consider the following tips:
- Research scholarships and financial aid, prepare a detailed budget, and avoid underestimating living costs.
- Prioritize university dorms or shared rentals, cook your own meals, and use student discounts and transportation passes to save money.
- Choose secure, efficient remittance methods to ensure timely fund transfers.
- Use cost-of-living calculators to make informed decisions based on your circumstances.
Comprehensive preparation is key to successfully managing the financial challenges of studying in France.
FAQ
What methods can you use to pay French university tuition?
You can use credit card online payments, bank transfers, international money orders, or checks. Most schools offer multiple payment options. Check the school’s website for specific requirements.
How long does it take for scholarships to be disbursed?
Scholarships are typically disbursed to your French bank account within 1-3 months after the semester starts. Monitor notifications from the school or scholarship agency.
Can you work part-time while studying in France?
You can legally work part-time, up to 964 hours annually, with a valid student visa. Part-time income can help cover living expenses.
How do you choose a secure and efficient remittance method?
Compare fees and transfer speeds of bank transfers, third-party platforms, and international money orders. Third-party platforms often offer lower fees and faster transfers for daily expenses.
What documents do you need to open a French bank account?
You need a passport, student visa, admission letter, and proof of address. Some banks require a minimum initial deposit. Consult your university’s international office for guidance.
Studying in France involves significant costs like tuition (non-EU undergrad €2,770+), living expenses (€800-€1,200 monthly), and cross-border remittance fees. Traditional bank transfers incur high fees ($25-$113), rate markups (3-6%), and delays (1-10 days), potentially disrupting tuition or living expense payments. As a cost-conscious student, you need a low-fee, fast, and secure platform to streamline fund management.
BiyaPay offers the perfect solution, with real-time exchange rate queries to track USD-to-EUR rates and convert fiat to crypto, avoiding volatility losses. Remittance fees start at just 0.5%, with zero-cost contract orders and global same-day delivery. Plus, you can invest in US and Hong Kong stocks on BiyaPay without an overseas account, enhancing your study funds.
Sign up for BiyaPay today to unlock seamless cross-border finance! From tuition to daily expenses, cut costs and speed up transfers for a worry-free study experience. Don’t let high fees and delays derail your plans—join BiyaPay now for a smarter France study journey!
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















