- EasyCard
- Trade
- Help
- Announcement
- Academy
- SWIFT Code
- Iban Number
- Referral
- Customer Service
- Blog
- Creator
Sending Money by Mail: A Safe and Efficient Way of Fund Transfer

Image Source: pexels
When making international transfers, you may be concerned about the safety and efficiency of your funds. Sending money by mail offers a reliable option for those without bank accounts. Many users face issues in digital payments, such as difficulty tracking funds, non-refunded transactions, and fraud risks. By choosing the right mailing method and taking security measures, you can better ensure the safety of your funds.
Key Takeaways
- Sending money by mail provides a secure and reliable way to transfer funds for those without bank accounts, suitable for international transfers.
- When choosing a mailing method, prioritize cashier’s checks and money orders, which are safer and trackable.
- When mailing funds, avoid sending cash directly and use trackable mailing services to reduce risks.
- Recipients must present valid identification at designated locations to collect funds, ensuring information accuracy to avoid errors.
- Stay vigilant, regularly check account and mail status, and promptly address suspicious activities.
Process of Sending Money by Mail

Image Source: pexels
Sending money by mail offers various methods, each with different use cases and considerations. You can choose the most suitable process based on your needs and fund security considerations. The following sections detail each step of the process.
Choosing a Method
When sending money by mail, common methods include personal checks, cashier’s checks, money orders, and professional remittance services. Each method varies in security, cost, and processing speed. You can refer to the table below to understand the pros and cons of each method:
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Personal Check | Widely accepted, convenient, no fees | Risk of fraud or theft, processing delays, no instant confirmation |
| Cashier’s Check | Guaranteed funds, trackable, secure, fast clearing | Possible fees, not issued by all banks, theft risk |
| Money Order | Guaranteed funds, suitable for international payments, recipient doesn’t need a bank account | Transaction limits, risk of theft during mailing, cashing delays |
When choosing, prioritize trackable and insurable methods. Cashier’s checks and money orders are generally safer, ideal for large or cross-border mailings. Professional remittance services also offer tracking and insurance, suitable for high-security scenarios.
Preparing Funds
When preparing funds, you need to follow official packaging and documentation requirements. Proper preparation reduces the risk of fund loss and information leaks. Below are common preparation steps:
| Step/Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Address | Provide accurate recipient address to ensure correct delivery |
| Mail Size and Weight | Choose appropriate envelopes, control weight (e.g., 1 oz, 2 oz) to avoid excess charges |
| Annual Volume | Estimate annual mailing volume for management and reporting |
| Form Completion | Complete required forms (e.g., PS Form 3615) and submit to postal and relevant authorities |
| USPS Account Setup | Set up a USPS account to obtain a unique ZIP+4 code for tracking and management |
| Packaging Guidelines | Use standard envelopes, mail through official channels like USPS |
| Personal Information Requirements | Include identification forms (e.g., Form 3210) in the package, use double packaging, and attach shipping labels inside and outside |
When preparing funds, avoid mailing cash directly. Using cashier’s checks or money orders can effectively reduce theft risks. You should also keep mailing receipts and related forms for future inquiries and tracking.
Mailing Process
When mailing, you need to choose reliable mailing channels. The United States Postal Service (USPS) and international courier companies offer tracking services. You can complete the mailing process with these steps:
- Visit a post office or courier company counter, submit the prepared envelope and related forms.
- Choose mailing services with tracking and insurance, and obtain a tracking number.
- Keep the receipt and tracking number for future reference.
- For large sums (over USD 10,000), you must complete and submit FinCEN Form 105 in advance to ensure compliance.
Tip: When receiving suspicious texts or emails, do not click any links. Visit the official postal or courier website directly and enter the tracking number to check progress. This helps prevent fraud and information leaks.
Receiving Process
When receiving funds, you typically need to present valid identification at a designated bank or post office to collect the funds. Processing times vary by method:
| Payment Method | Average Processing Time |
|---|---|
| Check | Usually clears within one to two business days |
| Certified Check | Usually available the next business day |
| Remittance | Usually available the same day if initiated before the cutoff time |
| Money Order | Funds usually available immediately upon cashing |
During the receiving process, you may encounter these common issues:
- Exchange rate fluctuations or additional fees causing the received amount to differ from expectations.
- Errors in information entry during the transfer process leading to amount discrepancies.
- Discrepancies between receipt amounts and actual received amounts.
If these issues arise, you can contact the remittance service provider to request a refund or adjustment to ensure the correct amount is received. You should keep all receipts and proof for future verification and dispute resolution.
Security of Sending Money by Mail

Image Source: pexels
Types of Risks
When sending money by mail, you may encounter various risks. The most common risks include mail loss, theft, information leaks, and fraud. Mailing cash directly poses the highest risk, as it is nearly impossible to recover if lost. You may also face issues like counterfeit checks or stolen money orders.
Common fraud tactics include email compromise scams, such as Business Email Compromise (BEC) and Email Account Compromise (EAC). These scams often trick you into sending funds to incorrect accounts by forging recipient information or altering account details. You need to be cautious of sudden changes in recipient account information, especially if it differs from previous records.
Security Measures
You can take multiple measures to enhance the security of sending money by mail.
- Avoid mailing cash directly, and prioritize trackable and cancellable methods like cashier’s checks or money orders.
- Choose mailing services with tracking and insurance, allowing compensation if mail is lost.
- Mail near the post office’s blue collection boxes during official collection times to reduce theft risks.
- Handle mailing and receiving directly at post offices or licensed Hong Kong bank branches to ensure the safety of funds and personal information.
- For international remittances, provide identification and comply with regulations like Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) to prevent money laundering and fraud.
- Set up two-factor authentication to prevent account theft. Disable automatic email forwarding to external addresses and use spam filters to reduce fraudulent email impacts.
Tip: When using mobile banking or online services, ensure you access secure, legitimate websites and avoid operating through unknown links.
Prevention Tips
You can further reduce risks with these methods:
- Keep all mailing receipts and tracking numbers for future reference.
- Double-check recipient information to avoid fund loss due to errors.
- Regularly monitor account and mail status, contacting the post office or bank promptly if anomalies are detected.
- Avoid using free web-based email accounts, and prioritize high-security email services.
- Set up two-factor or multi-factor authentication for important mail to enhance account security.
- When receiving emails about fund changes, verify the sender’s identity via phone or other channels to prevent scams.
- For cross-border mailing, understand regulations in mainland China and the recipient’s country to ensure compliance.
By implementing these measures, you can significantly enhance the security of sending money by mail. As long as you stay vigilant and choose legitimate channels and secure methods, you can effectively mitigate most risks.
Efficiency and Costs
Timeliness
When choosing to send money by mail, timeliness is a key consideration. Mailing is generally slower than electronic transfers, especially for cross-border transactions. You need to wait for mail transportation, clearing, and receiving processes, which may take days to a week. In contrast, bank transfers or third-party payment platforms typically deliver funds the same day or the next.
Factors affecting the efficiency of sending money by mail include:
- Transfer method: Different service providers have varying processing speeds. Some offer expedited options at higher costs.
- Recipient country: Delivery times vary due to local regulations and banking practices.
- Postal reliability: The stability of the destination’s postal system directly affects delivery speed.
- Holidays and weather: Special periods or adverse weather may cause delays.
When you need fast delivery, prioritize electronic transfers. If security and compliance are your focus, sending money by mail is more suitable.
Costs
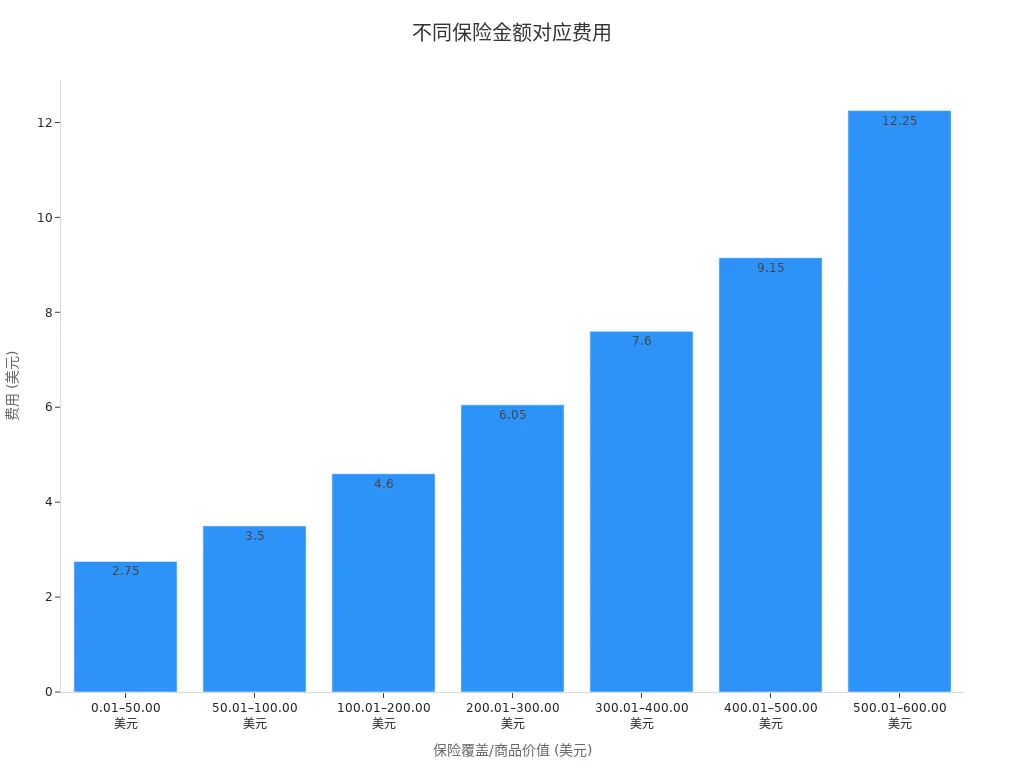
When sending money by mail, costs include postage, insurance, and certification service fees. You can choose different insurance levels based on the amount and security needs. The table below shows fees for different insurance amounts (in USD):
| Insurance Coverage/Item Value (USD) | Fee (USD) |
|---|---|
| 0.01 – 50.00 | 2.75 |
| 50.01 – 100.00 | 3.50 |
| 100.01 – 200.00 | 4.60 |
| 200.01 – 300.00 | 6.05 |
| 300.01 – 400.00 | 7.60 |
| 400.01 – 500.00 | 9.15 |
| 500.01 – 600.00 | 12.25 |
| 600.01 – 5,000.00 | 12.25 + 1.90 per additional 100 USD (or part thereof) above 600 |
You also need to pay postage and certification fees, such as:
- Forever Stamp at $0.78 each.
- Certified Mail® service at $5.30 per item.
- Physical green card return receipt at $4.40.
- Electronic return receipt at $2.82.
When sending money by mail, consider both timeliness and costs. For large sums, purchasing insurance and certification services is recommended to enhance security. You can also flexibly choose service combinations based on actual needs to manage costs effectively.
Method Comparison
Bank Transfers
When making international remittances, bank transfers are a common choice. Licensed Hong Kong banks typically support local bank transfers and international wire transfers. You can initiate transfers through bank counters, online banking, or mobile banking. Bank transfers offer secure and standardized processes, suitable for large and complex transactions. You can transfer funds directly to the recipient’s account, avoiding the risks of carrying cash.
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Local Bank Transfer | Cost-effective, convenient, fast processing, local currency transactions | May take days to arrive, some fees, slightly less reliable than wire transfers |
| International Wire Transfer | Suitable for large, complex cross-border transactions, highly reliable | Higher fees, longer processing times |
When choosing bank transfers, ensure the recipient has a bank account. If the recipient lacks an account, bank transfers cannot be completed.
Third-Party Payments
You can also use third-party payment platforms for international remittances. Common platforms include PayPal, Alipay, and WeChat Pay. These platforms allow quick completion of small transfers with convenient account management. Third-party payment platforms typically employ multiple security measures, including data encryption, real-time risk monitoring, and two-factor authentication.
The table below shows the security and accessibility features of major third-party payment platforms:
| Payment Platform | Security Features | Accessibility Features |
|---|---|---|
| PayPal | PCI DSS compliant, SMS verification, real-time risk monitoring | Fast transactions, convenient account management |
| Alipay | PCI DSS compliant, electronic signatures, digital authentication, risk monitoring | Complex account setup, requires Chinese bank account |
| WeChat Pay | PCI DSS compliant, real-time security monitoring, data encryption | Fast transactions, convenient account management |
When using third-party payment platforms, note that some platforms have restrictions on account types and locations. For example, Alipay requires a Chinese bank account, which may not be directly accessible to some users.
Use Cases for Sending Money by Mail
When you lack a bank account or cannot use third-party payment platforms, sending money by mail offers a unique solution. You can securely deliver funds to recipients using money orders or cashier’s checks. Sending money by mail is suitable for these scenarios:
- The recipient has no bank account and cannot receive electronic transfers.
- You need to send money to remote or financially underdeveloped areas.
- You want to ensure fund safety through trackable and insurable methods.
- You need to meet compliance requirements, avoiding identity verification issues with electronic payments.
Tip: When choosing to send money by mail, prioritize fund safety and compliance. For large or critical funds, opt for mailing services with insurance and tracking.
You can flexibly choose bank transfers, third-party payments, or sending money by mail based on your needs. Each method has unique advantages. By considering the recipient’s situation and fund security needs, you can find the most suitable transfer method.
Practical Tips
Reducing Risks
When sending money by mail, you can take practical steps to reduce risks. Choose to mail from inside a post office rather than using outdoor mailboxes to minimize theft risks. Monitor your mailbox to detect anomalies promptly. Request signature confirmation to ensure important mail reaches the correct recipient. When packaging funds, use durable cartons and cushioning materials, such as bubble wrap or padding, to protect contents. Seal all openings with strong tape and accurately label recipient and sender information. Purchase shipping insurance to protect funds from loss or damage during transit. Most insurance policies do not cover damage due to improper packaging, so ensure the packaging process is standardized and addresses are accurate.
Tip: Using online bill payments can effectively reduce check fraud risks. Double-check all information before mailing to avoid fund loss due to errors.
Amount Selection
When choosing the amount and frequency for sending money by mail, refer to industry safety thresholds. Properly planning transfer frequency and amounts helps reduce compliance risks. The table below shows common transfer frequency recommendations:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal Business Safe Harbor Threshold | 100 transfers |
| Annual Transfer Frequency | Approximately 2 transfers per week |
| Proposed New Threshold | 500 transfers |
You can plan mailing amounts based on actual needs. For large transfers, prioritize insurance and certification services to ensure fund safety. Avoid frequent small mailings to reduce management costs and operational risks. For cross-border mailing, understand regulations in mainland China and the recipient’s country to ensure compliance.
When choosing a fund transfer method, consider your needs and specific scenarios. The table below helps you quickly compare different methods:
| Aspect | Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) | Wire Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Speed | 1-2 business days | Minutes to instant |
| Security | Reversible, regulated | Irreversible |
| Use Case | Regular payments, small amounts | Urgent, large amounts |
When sending money by mail, pay attention to these safety details:
- Send funds only to trusted recipients
- Verify recipient identity
- Monitor account activity to prevent suspicious operations
Choosing the right method and focusing on safety details can effectively ensure your funds’ security.
FAQ
Can I Send Cash Directly by Mail?
You cannot send cash directly by mail. Choose cashier’s checks, money orders, or certified checks to reduce the risk of loss and theft, ensuring fund safety.
How Long Does It Take for Mailed Money to Arrive?
You typically need to wait 3 to 7 business days. The exact time depends on the mailing method, destination country, and local postal service efficiency.
Does Sending Money by Mail Require Declaration or Compliance?
For amounts exceeding USD 10,000, you must complete relevant declaration forms (e.g., FinCEN Form 105). Comply with regulations in mainland China and the recipient’s country to ensure compliance.
Can Funds Be Recovered If Mail Is Lost?
If you choose services with insurance and tracking, you can apply for compensation if mail is lost. Keep all receipts and tracking numbers for follow-up processing.
Can I Receive Funds Without a Bank Account?
You can receive funds via money orders or postal remittances without a bank account. Simply present valid identification at the designated institution to collect funds.
While mailing money offers a basic solution for the unbanked, its slow speed (3–7 days), physical risks (loss, theft), and cumbersome compliance make it inefficient and risky in today’s digital world. When you need to send funds quickly and securely to family in mainland China or Hong Kong, traditional mail falls short.
BiyaPay redefines cross-border remittance: no more checks, no more waiting. Send money from Canada, the US, Europe, or elsewhere directly to bank accounts in mainland China or Hong Kong—with same-day sending and receipt. Fees as low as 0.5%, and access to near mid-market exchange rates via the real-time converter, so you get more value on every EUR, CAD, or USD sent.
Beyond sending, BiyaPay breaks barriers—recipients don’t need overseas accounts. Funds can be used instantly to invest in US and HK stocks with zero fees on contract trades. Whether supporting family, funding education, or managing overseas income, BiyaPay offers a safer, faster, and smarter alternative to mailing money. Sign up today and experience next-generation, paperless global finance.
*This article is provided for general information purposes and does not constitute legal, tax or other professional advice from BiyaPay or its subsidiaries and its affiliates, and it is not intended as a substitute for obtaining advice from a financial advisor or any other professional.
We make no representations, warranties or warranties, express or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness or timeliness of the contents of this publication.




Contact Us
Company and Team
BiyaPay Products
Customer Services
is a broker-dealer registered with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) (No.: 802-127417), member of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) (CRD: 325027), member of the Securities Investor Protection Corporation (SIPC), and regulated by FINRA and SEC.
registered with the US Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), as a Money Services Business (MSB), registration number: 31000218637349, and regulated by FinCEN.
registered as Financial Service Provider (FSP number: FSP1007221) in New Zealand, and is a member of the Financial Dispute Resolution Scheme, a New Zealand independent dispute resolution service provider.




















